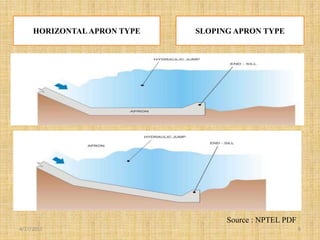
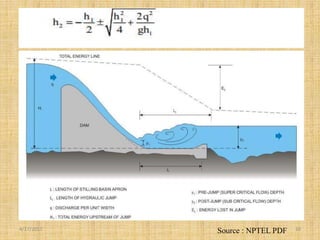
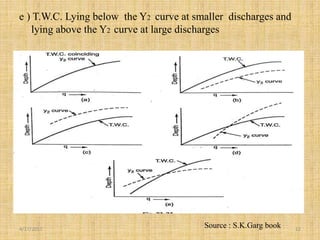
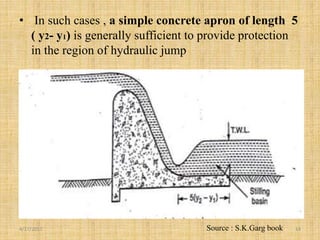
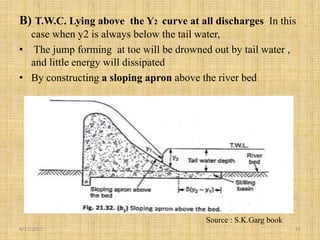
This document discusses energy dissipators, which are structures that reduce the kinetic energy of water flowing over spillways to prevent erosion. It describes two main types of energy dissipators - stilling basins and bucket dissipators. Stilling basins use either horizontal or sloping concrete aprons and hydraulic jumps to dissipate energy. Bucket dissipators include solid roller, slotted roller, and ski jump designs. The document explains how dissipator selection depends on the relationship between tailwater curve and flow depth. Appropriate dissipators maintain stable hydraulic jumps or direct flow into the air to safely dissipate kinetic energy for different tailwater conditions.