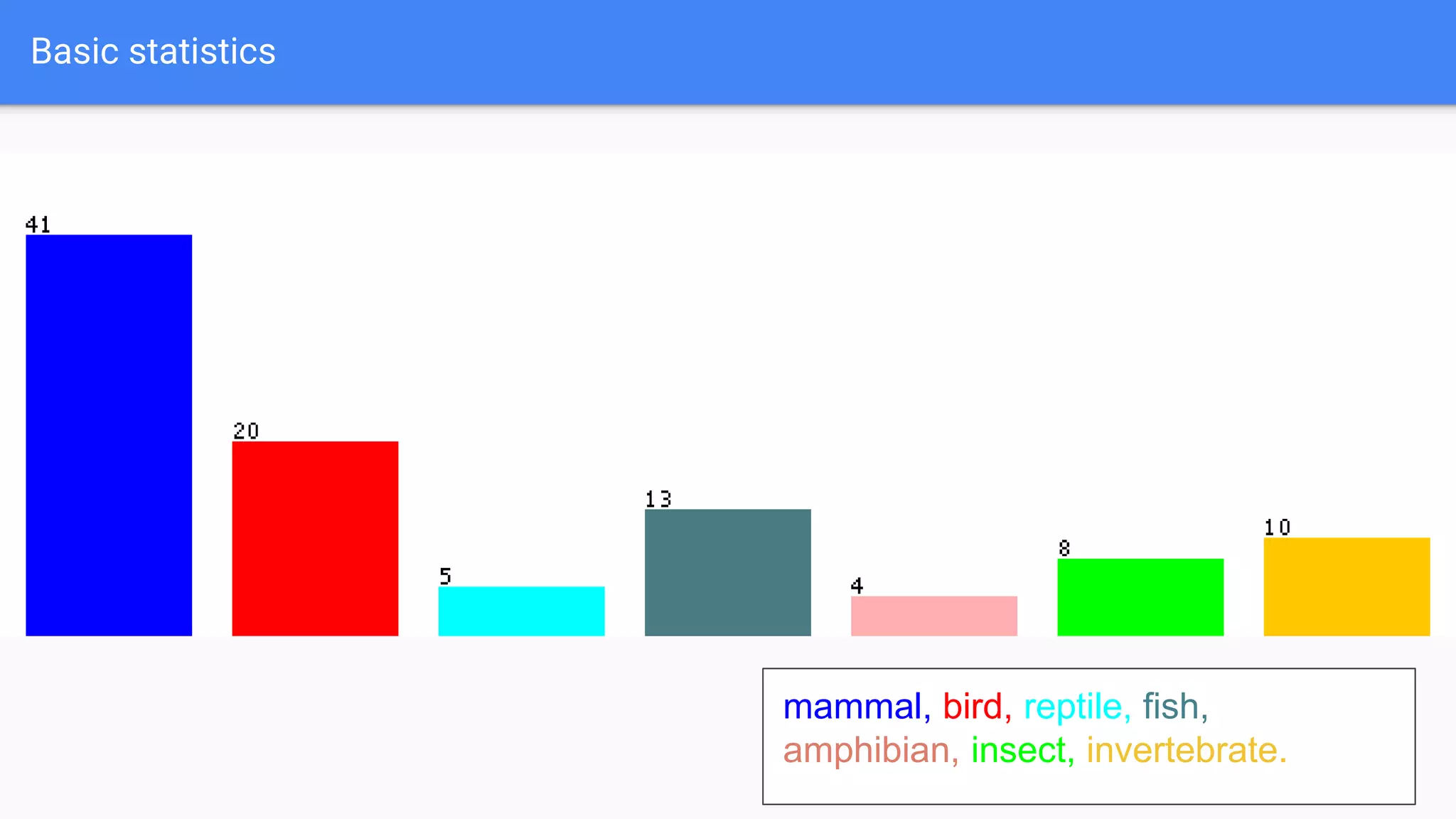
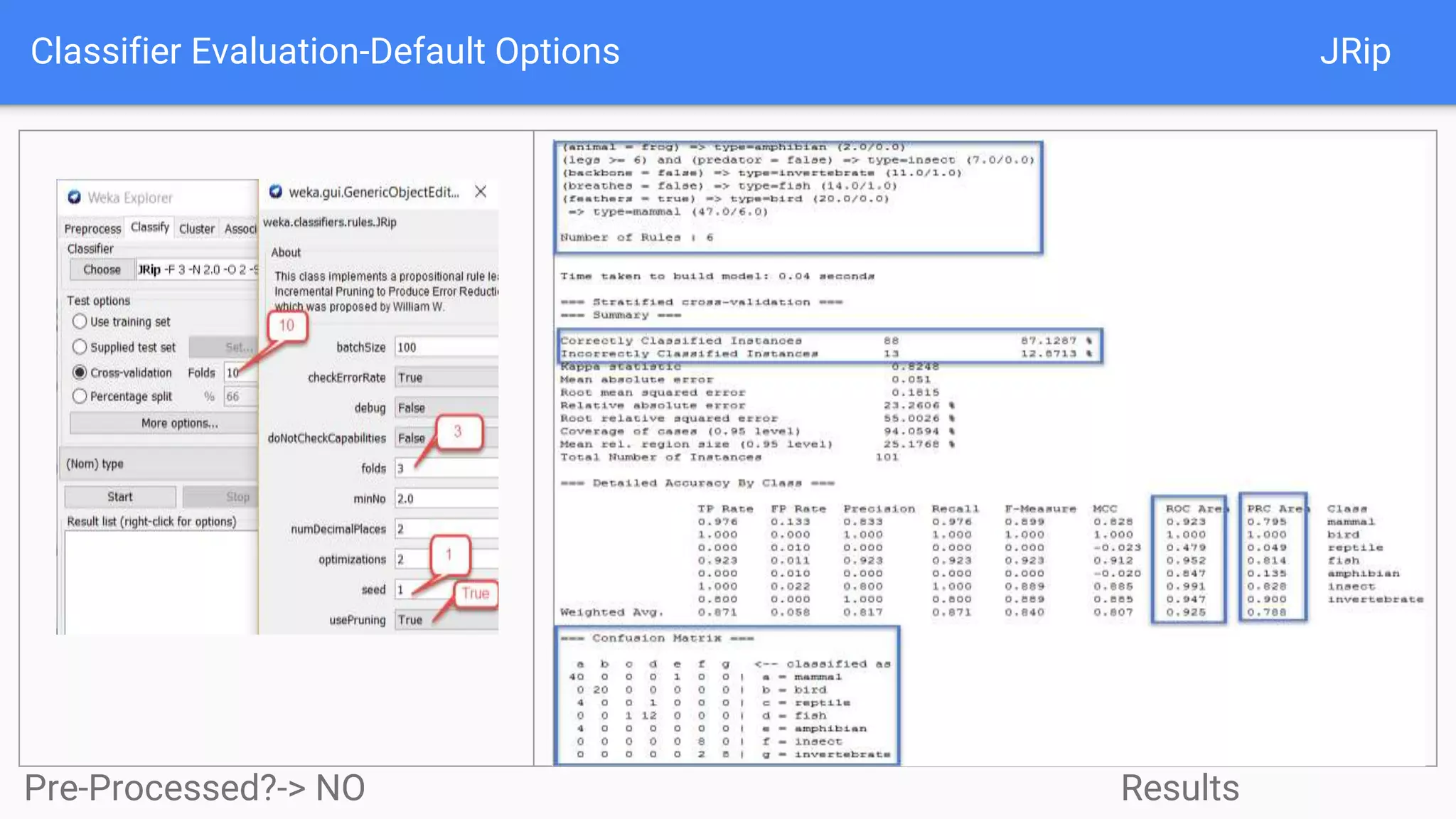
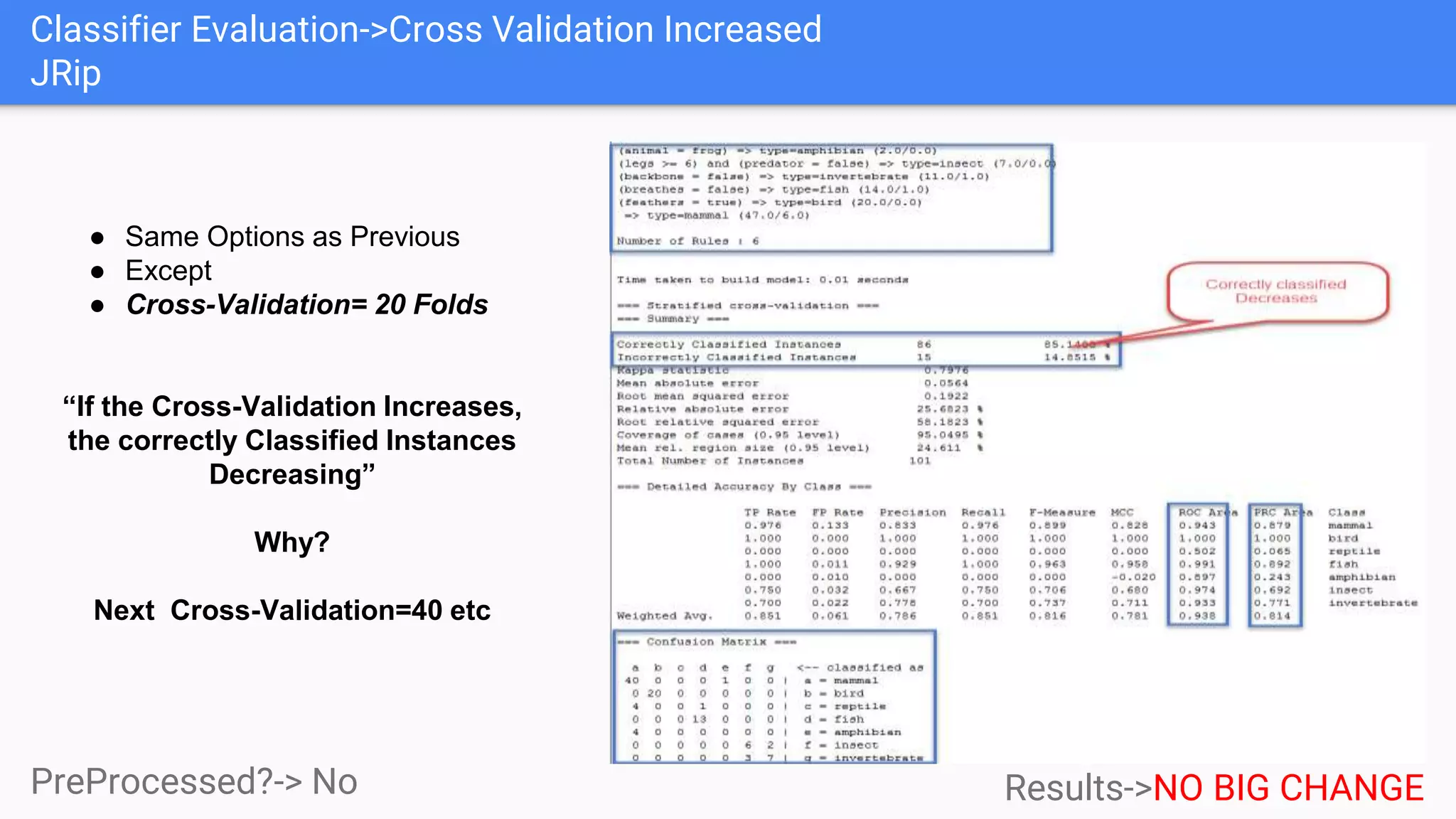
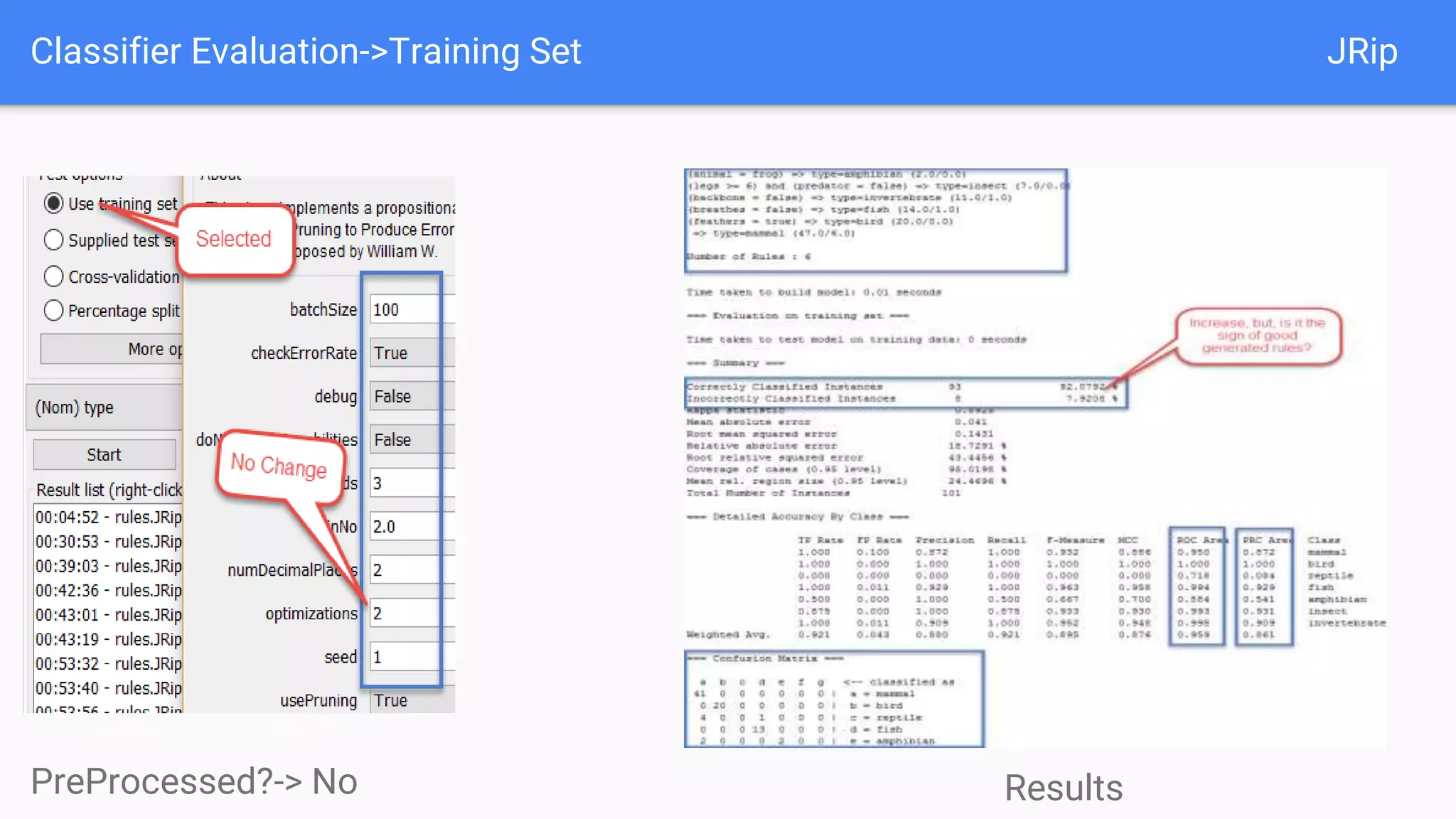
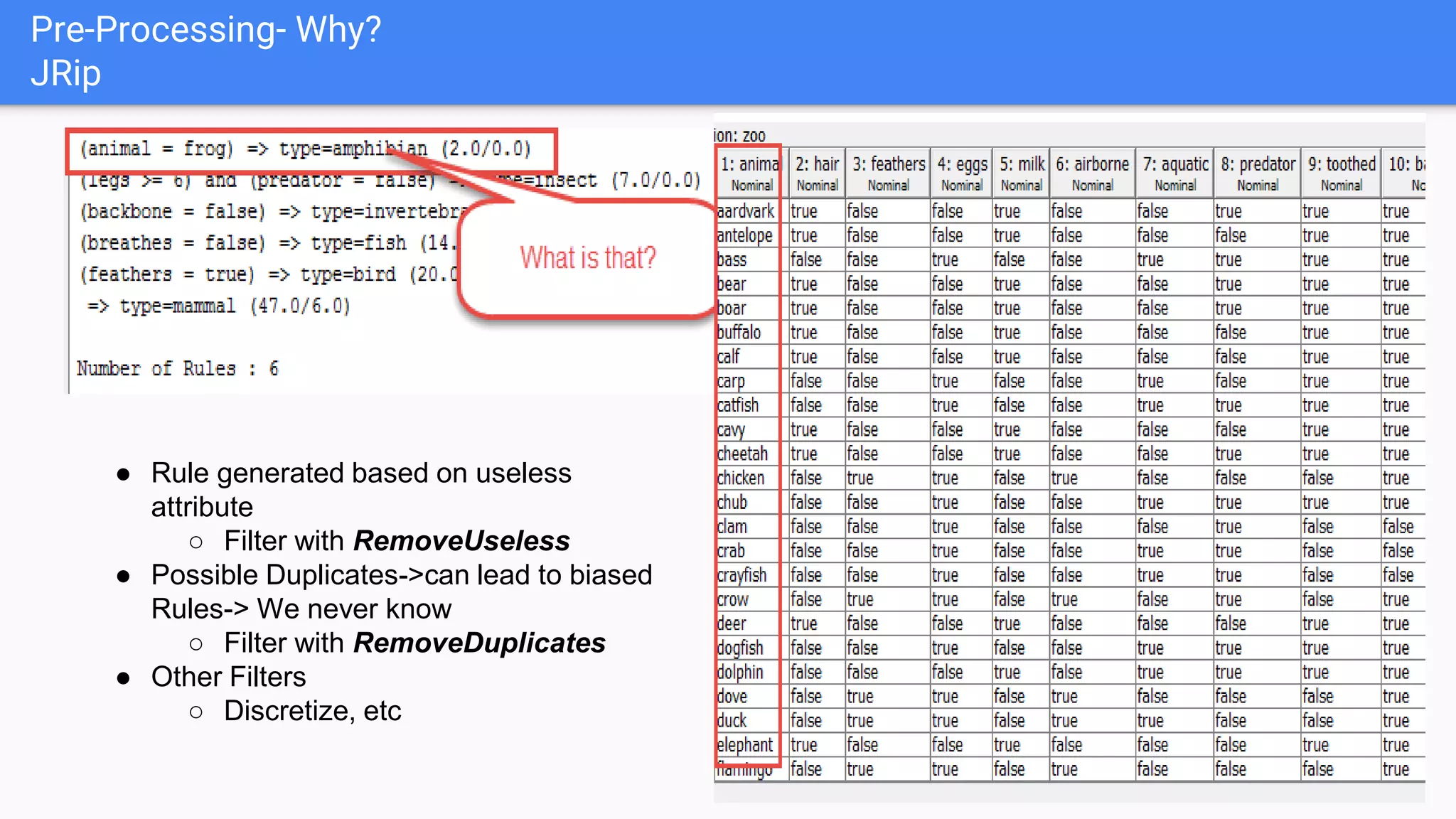
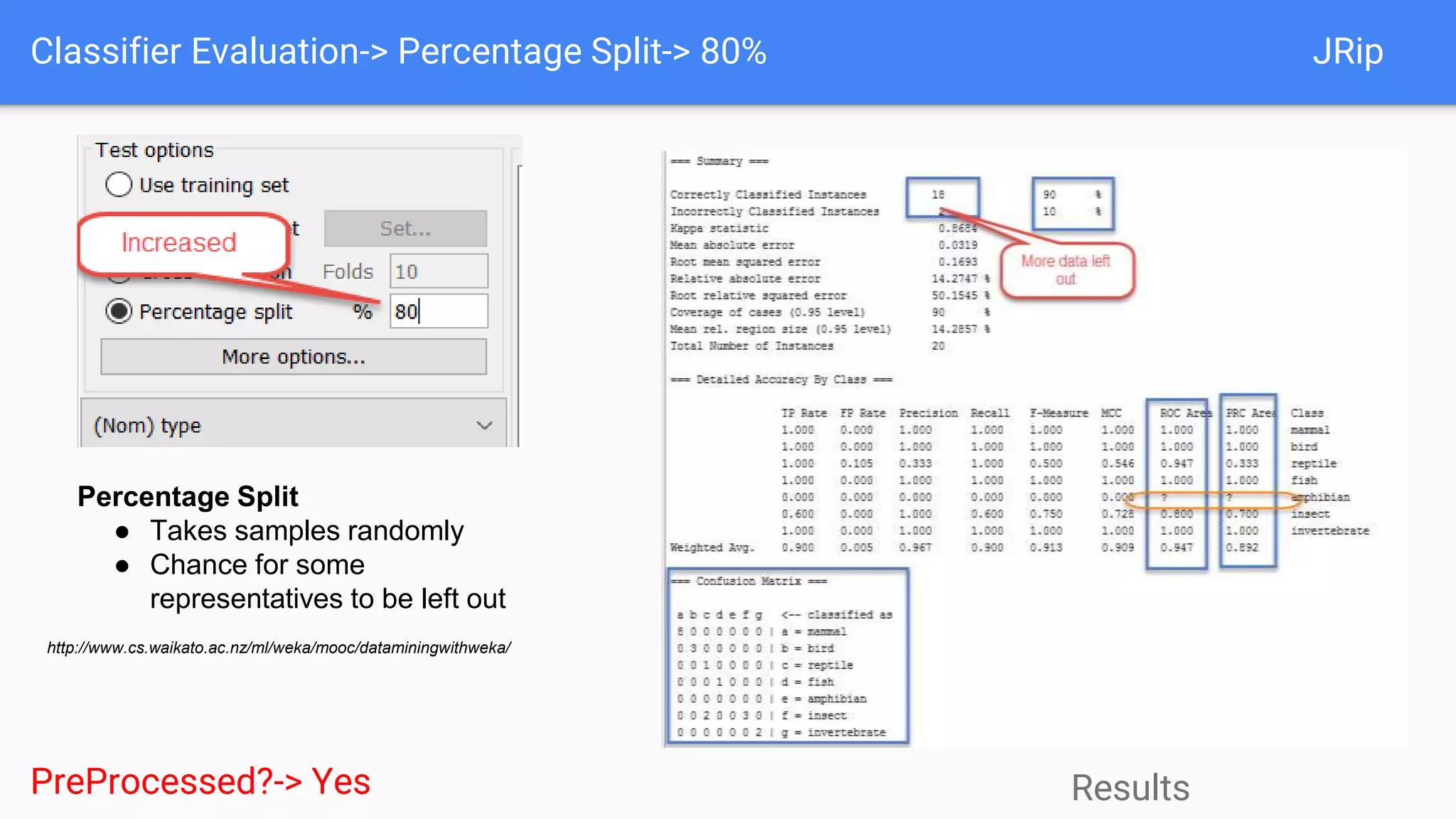
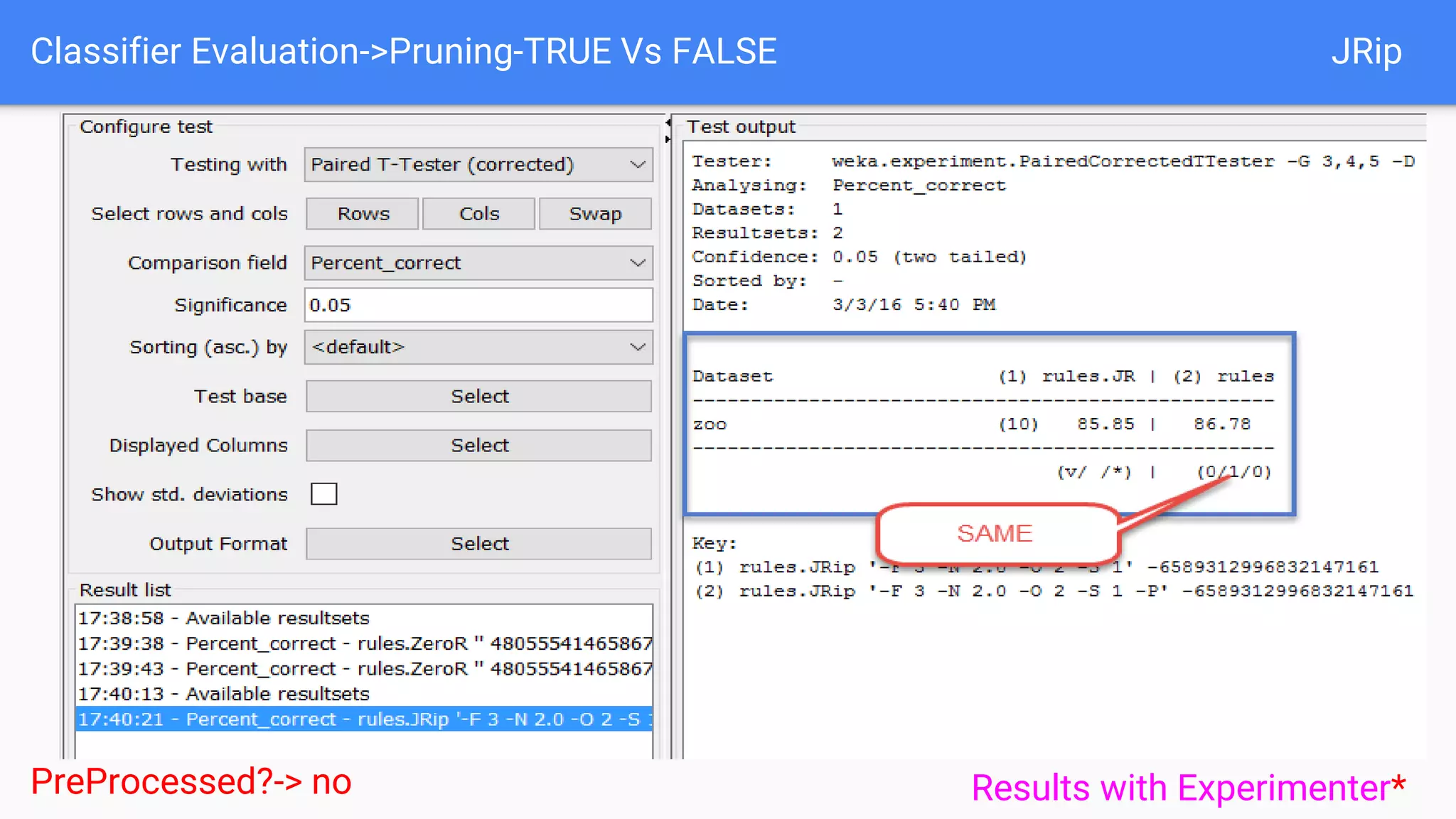
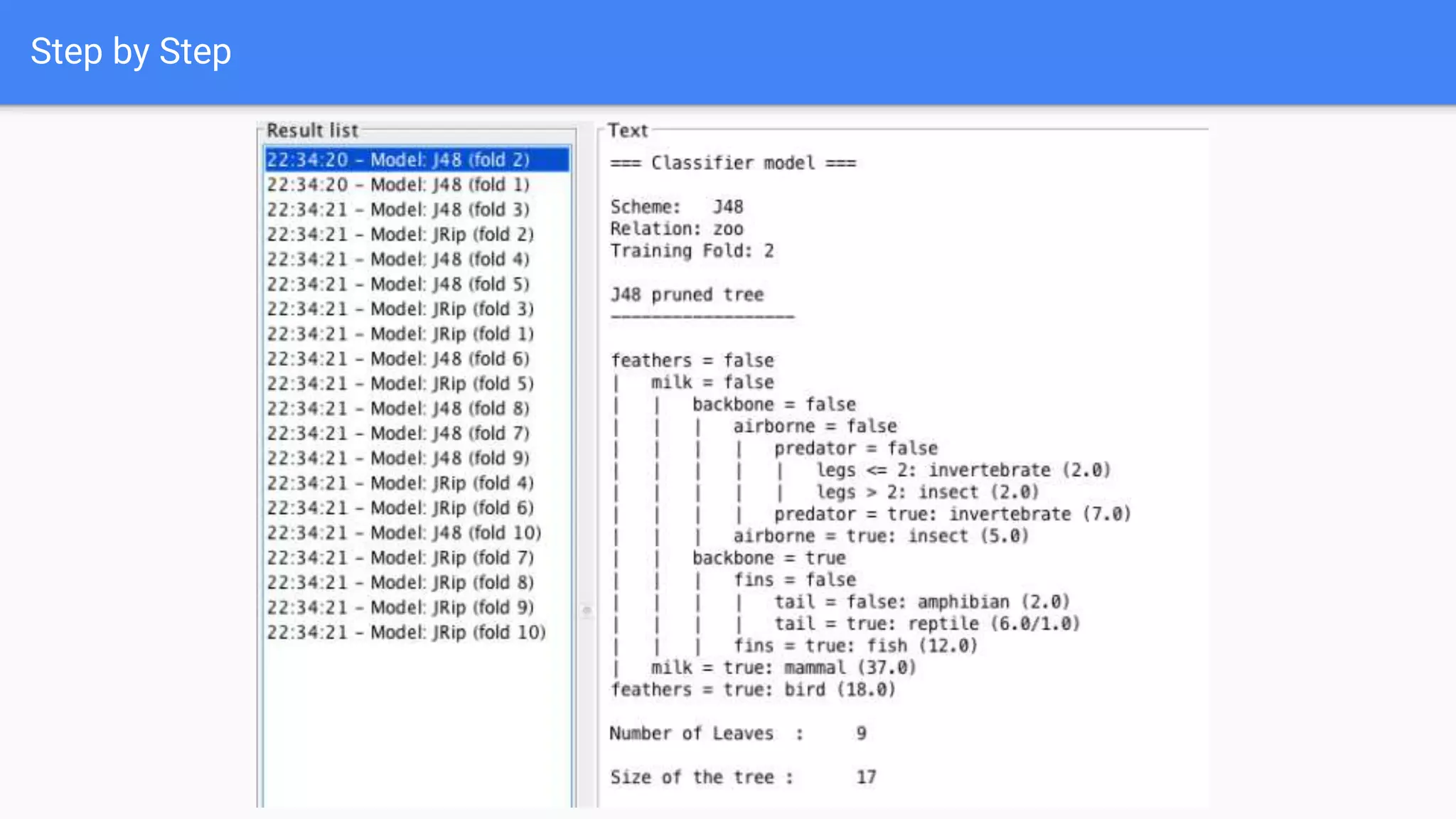
This document discusses using two classifiers, JRip and J48, on a zoo dataset containing animal attributes. It explores various preprocessing and evaluation techniques in Weka, including removing duplicates and useless attributes, cross validation, percentage splits, and comparing the classifiers using Experimenter. J48 slightly outperforms JRip on this dataset when run with default options and 10-fold cross validation. The document concludes that while J48 may generate more complex trees, it beats JRip for this small dataset without preprocessing. Experimenter and Knowledge Flow are useful Weka tools for comparing classifiers and understanding intermediate steps.