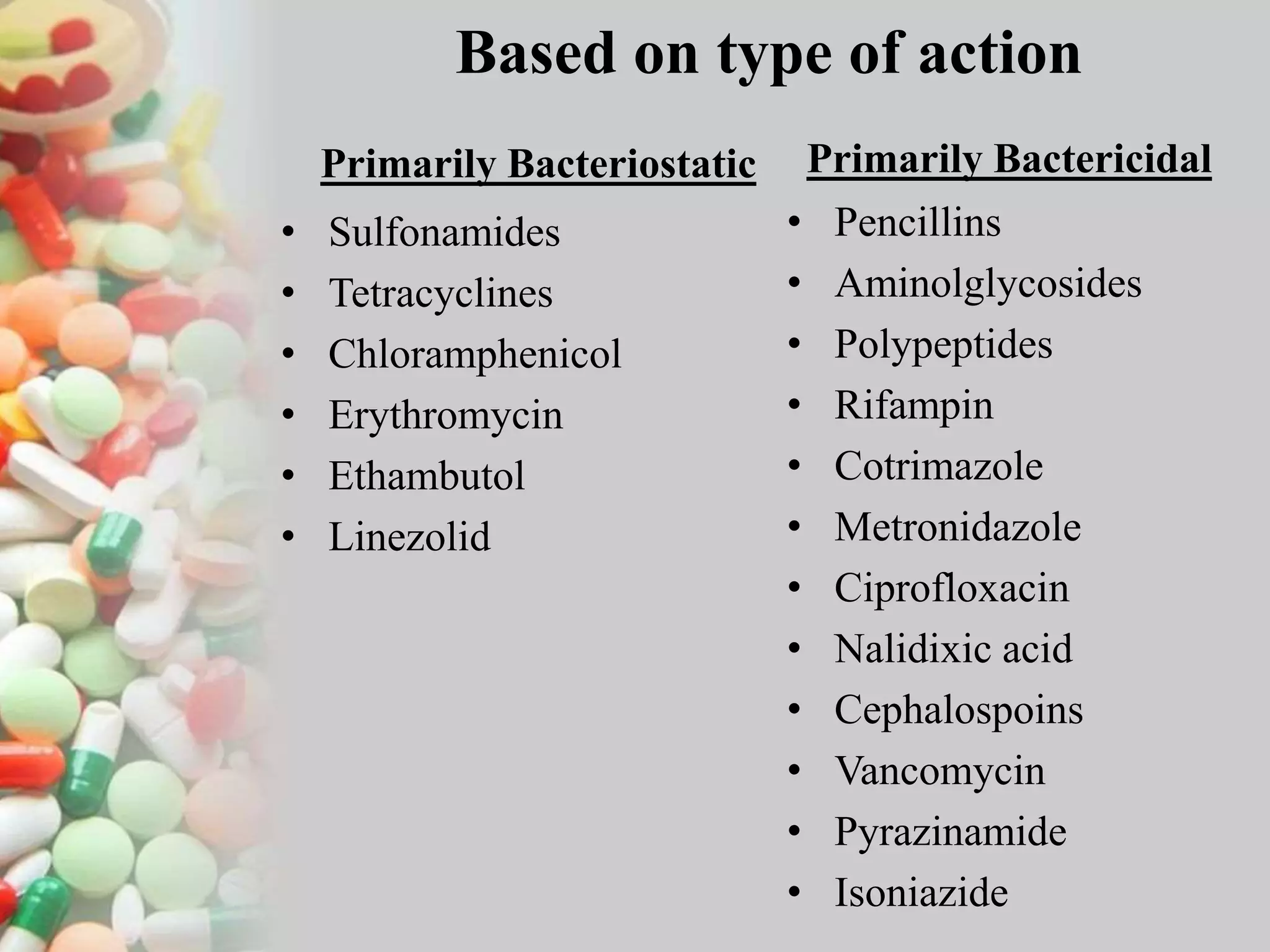
This document classifies antibiotics based on their chemical structure, mechanism of action, spectrum of activity, and origin. It divides antibiotics into categories such as beta-lactams, tetracyclines, aminoglycosides, and others. Within each category it provides examples of common antibiotics and briefly explains their mechanism of action and whether they are primarily bacteriostatic or bactericidal. The document also differentiates antibiotics based on whether they are narrow or broad spectrum and whether they target bacteria, fungi, protozoa, or viruses. It concludes by noting antibiotics can be obtained from fungi, bacteria, or actinomycetes.