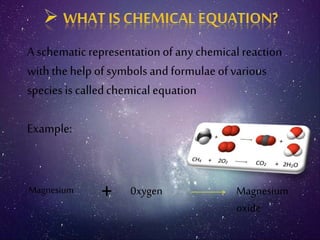
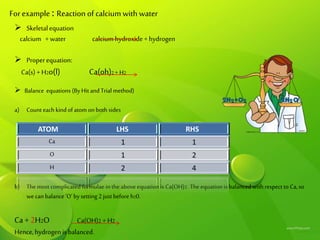
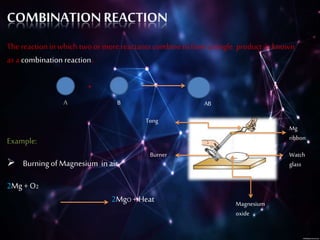
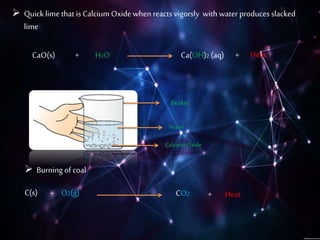
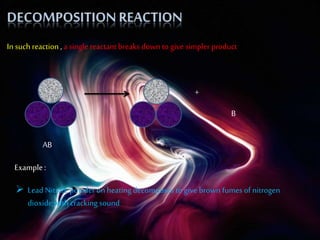
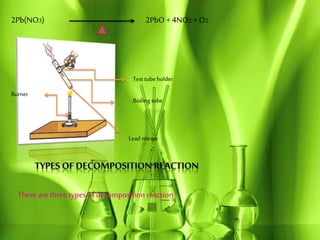
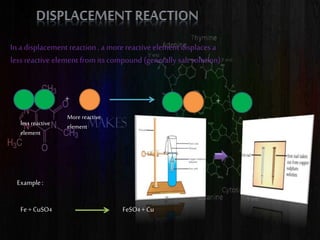
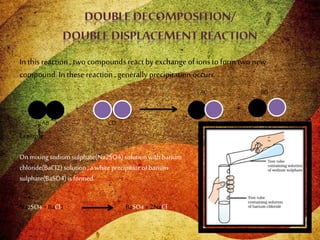
This document discusses different types of chemical reactions including combination reactions, decomposition reactions, displacement reactions, and oxidation-reduction reactions. It provides examples of each type of reaction to illustrate the key concepts. The document also discusses corrosion, rancidity, polymerization reactions, and precipitation reactions.