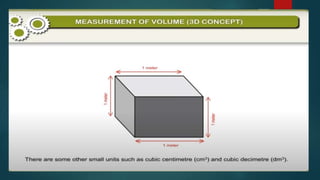
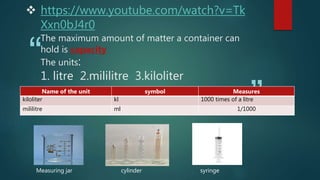
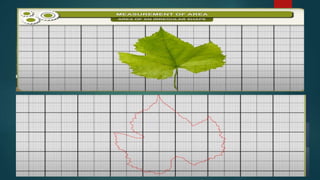
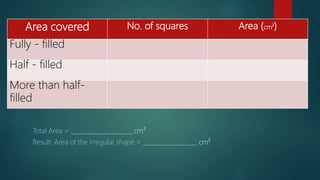
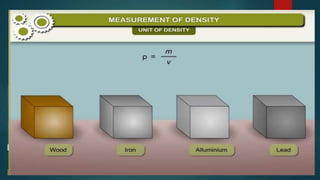
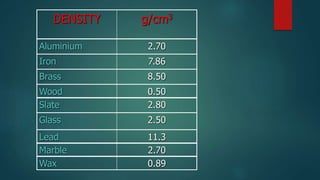
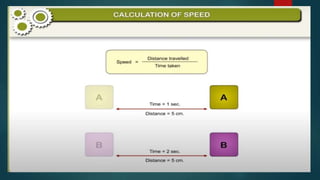
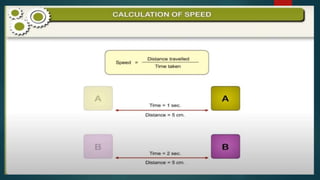
The document discusses measurement concepts in physics, covering volume, capacity, area, density, and speed. It includes methods for measuring irregular shapes, numerical problems with solutions, and key takeaways for each physical quantity. Additionally, there are evaluation questions including true/false and fill-in-the-blank formats to reinforce understanding of the concepts.