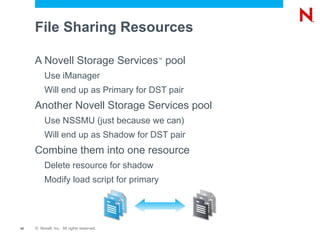
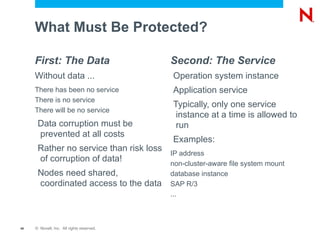
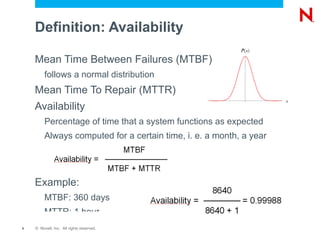
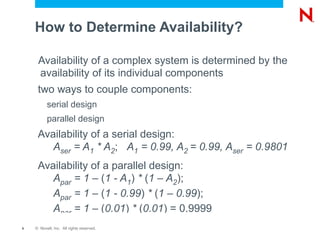
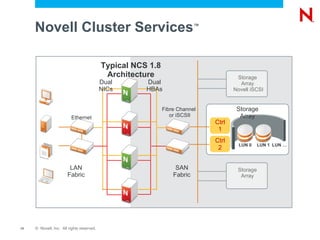
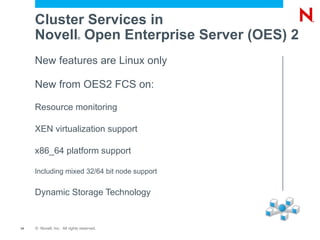
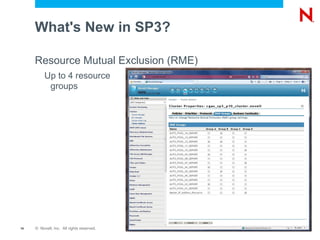
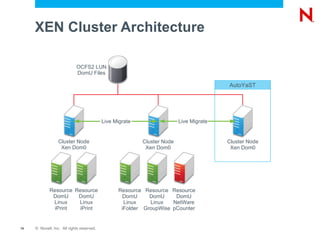
The document discusses high availability and fault tolerance using Novell Cluster Services. It defines key concepts like availability, mean time between failures, and mean time to repair. It then covers best practices for deploying Novell Cluster Services, including hardware and software setup, connectivity rules, naming and addressing, and testing the cluster. It also discusses which types of resources can be clustered, like file sharing, iPrint, iFolder, and DHCP.
![High-Availability with Novell Cluster Services ™ for Novell ® Open Enterprise Server on Linux Tim Heywood , CTO, NDS8 [email_address] Martin Weiss , Senior Technical Specialist [email_address] Dr. Frieder Schmidt , Senior Technical Specialist [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cl306-101204115323-phpapp01/75/Cl306-1-2048.jpg)












![High-Availability by Clustering Redundant setup “clustered” to act as one avoid Single Point of Failure (SPOF) Primary focus is availability , but can allow for increased performance HA via fail-over: In case [an application on] a server failure is detected, another server takes over Results achieved depend on failure detection time and startup delays The [virtual] hand moves faster than the eye The fault is masked before the user really notices](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cl306-101204115323-phpapp01/85/Cl306-20-320.jpg)