More Related Content
PPTX
PPT
PDF
PPTX
DOCX
PPTX
PPTX
PPT
59137949-Cluster-Computing (1).ppt ..... Similar to Distributed Computing and Cloud Computing 2
PPT
PDF
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
PDF
Unit 1.pdfmVDLMlbjsdvljjjjjjjljbeelfbkadbf;bk;s PPT
High Performance computing for Resercher PPT
Clusters (Distributed computing) PPTX
PPT
System models for distributed and cloud computing PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
Lecture_1.pptx Introduction Introduction PDF
R21 Sasi Engineering College cloud-computing-notes.pdf PPT
Lecture 3 - Types of Distributed Systems.ppt PPTX
Computer_Cluster in Parallel and Distributed computer.pptx PPT
PDF
Computer_Clustering_Technologies PDF
PDF
Recently uploaded
PPTX
ManageIQ - Sprint 278 Review - Slide Deck PDF
REST in Peace (Laravel Senegal Meetup 2025) PDF
DSD-INT 2025 Flexible quadtree submodelling with MODFLOW 6 - Case Hegewarren ... PDF
Python Core Interview Cheat Sheet for a Senior Interview PDF
From Sound Workflow Nets to LTLf Declarative Specifications PPTX
The Triple Bottom Line of Software: Uses, Misuses, and Strategic Risks PDF
DSD-INT 2025 Groundwater table lowering due to surface water lowering - Reusen PPTX
Inside An AI Powered ERP System for Process Manufacturers PDF
Cloud Engineering Services | Infysion Technologies PPTX
UAE-Based Insurer Transforms Operations with InsureEdge PPTX
How Swiggy Assure Scaled B2B Procurement for the HORECA Supply Chain PPTX
EMR Software for Pulmonology Clinics Why EasyClinic Supports Accuracy, Contin... PPTX
Testing Strategies for Agile Teams in 2026 PPTX
A practical and beginner-friendly guide to understanding data structures in J... PPTX
How to Extract Google Maps Business Leads Efficiently PDF
Driving Finance Growth with Business Central ERP PPTX
Dreamforce ‘25 Tour: Boost Productivity with AI-Assisted API Development PDF
DSD-INT 2025 Multi-scale modeling to simulate Land Subsidence in the Central ... PDF
Latest Courier Management Software 2026 | Complete Courier & Logistics Solution PDF
Inside An AI Powered ERP System for Process Manufacturers Distributed Computing and Cloud Computing 2
- 1.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 1
1
Distributed and Cloud Computing
Distributed and Cloud Computing
K. Hwang, G. Fox and J. Dongarra
K. Hwang, G. Fox and J. Dongarra
Chapter 2: Computer Clusters for
Chapter 2: Computer Clusters for
Scalable parallel Computing
Scalable parallel Computing
(suggested for 3 lectures in 150 minutes)
(suggested for 3 lectures in 150 minutes)
Prepared by Kai Hwang
Prepared by Kai Hwang
University of Southern California
University of Southern California
March 30, 2012
March 30, 2012
- 2.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 2
2
Figure 2.3 The Top-500 supercomputer performance from
1993 to 2010 (Courtesy of http://www.top500.org [25)
- 3.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 3
3
Figure 2.2 Architectural share of the Top-500
systems
(Courtesy of http://www.top500.org [25])
- 4.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 4
4
What is a computing cluster?
A computing cluster consists of a collection of
interconnected stand-alone/complete computers,
which can cooperatively working together as a single,
integrated computing resource. Cluster explores
parallelism at job level and distributed computing
with higher availability.
A typical cluster:
Merging multiple system images to a SSI
(single-system image ) at certain functional levels.
Low latency communication protocols applied
Loosely coupled than an SMP with a SSI
- 5.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 5
5
Multicomputer Clusters:
Cluster:
Cluster: A network of computers supported
A network of computers supported
by middleware and interacting by message passing
by middleware and interacting by message passing
PC Cluster (Most
PC Cluster (Most Linux clusters
Linux clusters)
)
Workstation Cluster
Workstation Cluster (NOW, COW)
(NOW, COW)
Server cluster or Server Farm
Server cluster or Server Farm
Cluster of
Cluster of SMPs
SMPs or
or ccNUMA
ccNUMA systems
systems
Cluster-structured massively parallel processors
Cluster-structured massively parallel processors
(MPP) – about 85% of the top-500 systems
(MPP) – about 85% of the top-500 systems
- 6.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 6
6
Multi-Computer Cluster Components
Multi-Computer Cluster Components
- 7.
- 8.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 8
8
Operational Benefits of Clustering
System availability (HA) : Cluster offers inherent high system
availability due to the redundancy of hardware, operating
systems, and applications.
Hardware Fault Tolerance: Cluster has some degree of
redundancy in most system components including both
hardware and software modules.
OS and application reliability : Run multiple copies of the OS
and applications, and through this redundancy
Scalability : Adding servers to a cluster or adding more
clusters to a network as the application need arises.
High Performance : Running cluster enabled programs to
yield higher throughput.
- 9.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 9
9
Cluster Opportunities :
MPP/DSM:
Compute across multiple systems: parallelism.
Network RAM:
Idle memory in other nodes. Page across other nodes’ idle
memory
Software RAID:
file system supporting parallel I/O and reliability, mass-
storage.
Multi-path Communication:
Communicate across multiple networks: Ethernet, ATM,
Myrinet
- 10.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 10
10
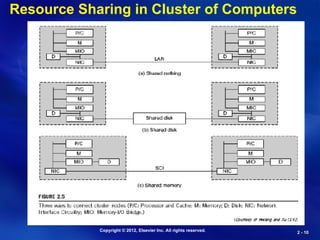
Resource Sharing in Cluster of Computers
- 11.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 11
11
Size Scalability (physical & application)
Enhanced Availability (failure management)
Single System Image (Middleware, OS extensions)
Fast Communication (networks & protocols)
Load Balancing (CPU, Net, Memory, Disk)
Security and Encryption (clusters and Grids)
Distributed Environment (User friendly)
Manageability (Jobs and resources )
Programmability (simple API required)
Applicability (cluster- and grid-awareness)
Issues in Cluster Design
- 12.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 12
12
Operational Benefits of Clustering
System availability (HA) : Cluster offers inherent high system
availability due to the redundancy of hardware, operating
systems, and applications.
Hardware Fault Tolerance: Cluster has some degree of
redundancy in most system components including both
hardware and software modules.
OS and application reliability : Run multiple copies of the OS
and applications, and through this redundancy
Scalability : Adding servers to a cluster or adding more
clusters to a network as the application need arises.
High Performance : Running cluster enabled programs to
yield higher throughput.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 16
16
Compute Node Architectures :
Compute Node Architectures :
- 17.
- 18.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 18
18
Cluster Interconnects :
Cluster Interconnects :
- 19.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 19
19
IBM BlueGene/L Supercomputer: The World
Fastest Message-Passing MPP built in 2005
Built jointly by IBM and LLNL teams and
funded by US DoE ASCI Research Program
- 20.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 20
20
Overview of Blue Gene L
Blue Gene L is a supercomputer jointly developed
by IBM and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
It occupies 17 of the top 100 slots in the rankings at
top500.org, including 5 of the top 10
360 TeraFLOPS theoretical peak speed
Largest configuration:
At Lawrence Livermore Nat’l Lab.
Runs simulations on US nuclear weapon stockpile
64 physical racks
65,536 compute nodes
Torus interconnection network of 64 x 32 x 32
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 25
25
Cluster Middleware
Resides Between OS and Applications and
offers in infrastructure for supporting:
Single System Image (SSI)
System Availability (SA)
SSI makes collection appear as single
machine (globalised view of system
resources). Telnet cluster.myinstitute.edu
Checkpointing and process migration..
- 26.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 26
26
What is Single System Image (SSI) ?
A single system image is the illusion, created by
software or hardware, that presents a collection of
resources as an integrated powerful resource.
SSI makes the cluster appear like a single machine
to the user, applications, and network.
A cluster with multiple system images is nothing
but a collection of independent computers
(Distributed systems in general)
- 27.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 27
27
Desired SSI Services
Single Entry Point
telnet cluster.usc.edu
telnet node1.cluster.usc.edu
Single File Hierarchy: xFS, AFS, Solaris MC Proxy
Single Control Point: Management from single GUI
Single virtual networking over multiple physical networks
Single memory space - Network RAM / DSM
Single Job Management: GlUnix, Codine, LSF, etc.
Single User Interface: Like CDE in Solaris/NT
- 28.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 28
28
Single Entry Point to access a
Cluster from any physical point
- 29.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 29
29
Four SSI Features
Four SSI Features in
in
Networking, I/O Space, Memory
Networking, I/O Space, Memory
Sharing, and Cluster Control
Sharing, and Cluster Control
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 32
32
Availability Support Functions
Single I/O Space (SIO):
Any node can access any peripheral or disk devices without the
knowledge of their physical location.
Single Process Space (SPS)
Any process has cluster wide process id and they
communicate through signal, pipes, etc, as if they are on a
single node.
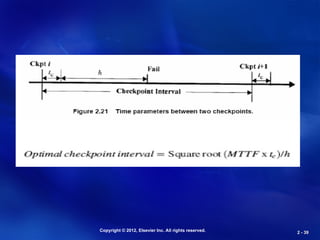
Checkpointing and Process Migration.
Saves the process state and intermediate results from memory
in rollback recovery from fails.
- 33.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 33
33
Distribute RAID - The RAID-x Architecture
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 38
38
Single Points of Failure in SMP and Clusters
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 47
47
Figure 2.4 Country share of the Top-500
supercomputers over time [25]
- 48.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 48
48
Figure 2.5 Application-area share of Top-500 systems over time.
(Courtesy of http://www.top500.org [25])
- 49.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 49
49
Top- 500 Release in June 2010
Top- 500 Release in June 2010
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 56
56
The Cray XT-5 Jagaur
The Cray XT-5 Jagaur
Supercomputer
Supercomputer
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 59
59
IBM
IBM
Roadrunner
Roadrunner
System
System
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 62
62
(Courtesy of Bill Dally, 2011)
- 63.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 63
63
(Courtesy of Bill Dally, 2011)
- 64.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 64
64
(Courtesy of Bill Dally, 2011)
- 65.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 65
65
A proposed Nivdia GPU chip processor architecture with 128 cores (160 GFlpos each) plus
A proposed Nivdia GPU chip processor architecture with 128 cores (160 GFlpos each) plus
8 latency processors (LP) connected to 1024 SRAMs (L2 caches) by a NoC, where MS are
8 latency processors (LP) connected to 1024 SRAMs (L2 caches) by a NoC, where MS are
the memory controllers connecting to off-chip DRAMS and NI is the network interface to
the memory controllers connecting to off-chip DRAMS and NI is the network interface to
next level of network (Courtesy of Bill Dally, reprint with permission [10] ).
next level of network (Courtesy of Bill Dally, reprint with permission [10] ).
(Courtesy of Bill Dally, 2011)
- 66.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 66
66
The architecture of a GPU cluster built with a hierarchical network of
The architecture of a GPU cluster built with a hierarchical network of
processor chips (GPUs) that can deliver 2.6 PFlops per cabinet. It takes at
processor chips (GPUs) that can deliver 2.6 PFlops per cabinet. It takes at
least N = 400 cabinets to achieve the desired PFlops or EFlops performance.
least N = 400 cabinets to achieve the desired PFlops or EFlops performance.
(Courtesy of Bill Dally, reprint with permission [10] ).
(Courtesy of Bill Dally, reprint with permission [10] ).
- 67.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 67
67
(Courtesy of Bill Dally, 2011)
- 68.
Copyright © 2012,Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 68
68
Paper/Books on Clusters and MPPs:
Paper/Books on Clusters and MPPs:
1.
1. G. Bell, J. Gray. And A. Szalay, “Petascale Computational
G. Bell, J. Gray. And A. Szalay, “Petascale Computational
Systems : Balanced Cyberstructure in a Data-Centric
Systems : Balanced Cyberstructure in a Data-Centric
World”,
World”, IEEE Computer Magazine,
IEEE Computer Magazine, 2006.
2006.
2. K. Hwang, G. Fox. And J. Dongarra, Distributed and Cloud
Computing Systems, Chapter 2, Kauffmann, 2011
3.
3. G. F. Phister,
G. F. Phister, In Search of Clusters,
In Search of Clusters, (second Edition)
(second Edition)
Prentice-Hall, N.J. 2001.
Prentice-Hall, N.J. 2001.
Updated Studies:
Updated Studies: Conduct an updated Study of the Top 5
Conduct an updated Study of the Top 5
Systems in the latest Top- 500 List . Produce an updated Table 2.3
Systems in the latest Top- 500 List . Produce an updated Table 2.3
and describe the No.1 system in details like the treatment of
and describe the No.1 system in details like the treatment of
Tianhe-1A, Jagaur, and Roadrunner in 2011. 2010. and 2009,
Tianhe-1A, Jagaur, and Roadrunner in 2011. 2010. and 2009,
respectively, in Chapter 2.
respectively, in Chapter 2.


![Copyright © 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 3
3
Figure 2.2 Architectural share of the Top-500
systems
(Courtesy of http://www.top500.org [25])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter02-260110194150-6ff51226/85/Distributed-Computing-and-Cloud-Computing-2-3-320.jpg)









































![Copyright © 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 47
47
Figure 2.4 Country share of the Top-500
supercomputers over time [25]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter02-260110194150-6ff51226/85/Distributed-Computing-and-Cloud-Computing-2-47-320.jpg)
![Copyright © 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 48
48
Figure 2.5 Application-area share of Top-500 systems over time.
(Courtesy of http://www.top500.org [25])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter02-260110194150-6ff51226/85/Distributed-Computing-and-Cloud-Computing-2-48-320.jpg)
















![Copyright © 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 65
65
A proposed Nivdia GPU chip processor architecture with 128 cores (160 GFlpos each) plus
A proposed Nivdia GPU chip processor architecture with 128 cores (160 GFlpos each) plus
8 latency processors (LP) connected to 1024 SRAMs (L2 caches) by a NoC, where MS are
8 latency processors (LP) connected to 1024 SRAMs (L2 caches) by a NoC, where MS are
the memory controllers connecting to off-chip DRAMS and NI is the network interface to
the memory controllers connecting to off-chip DRAMS and NI is the network interface to
next level of network (Courtesy of Bill Dally, reprint with permission [10] ).
next level of network (Courtesy of Bill Dally, reprint with permission [10] ).
(Courtesy of Bill Dally, 2011)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter02-260110194150-6ff51226/85/Distributed-Computing-and-Cloud-Computing-2-65-320.jpg)
![Copyright © 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
2 -
2 - 66
66
The architecture of a GPU cluster built with a hierarchical network of
The architecture of a GPU cluster built with a hierarchical network of
processor chips (GPUs) that can deliver 2.6 PFlops per cabinet. It takes at
processor chips (GPUs) that can deliver 2.6 PFlops per cabinet. It takes at
least N = 400 cabinets to achieve the desired PFlops or EFlops performance.
least N = 400 cabinets to achieve the desired PFlops or EFlops performance.
(Courtesy of Bill Dally, reprint with permission [10] ).
(Courtesy of Bill Dally, reprint with permission [10] ).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter02-260110194150-6ff51226/85/Distributed-Computing-and-Cloud-Computing-2-66-320.jpg)

