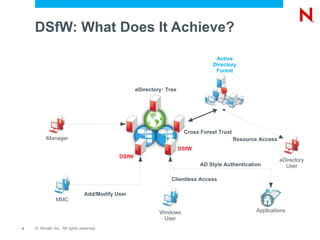
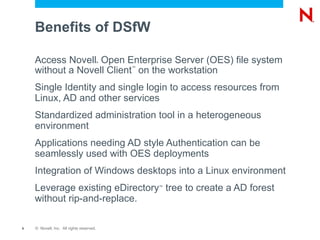
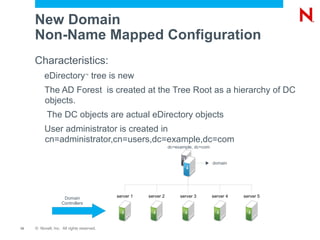
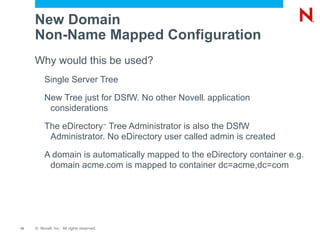
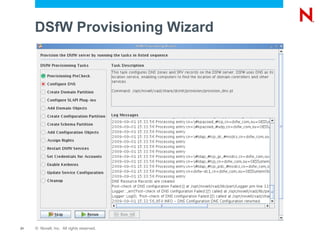
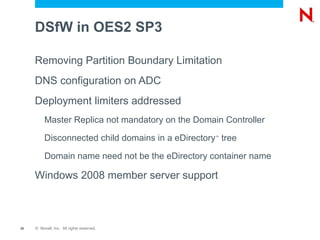
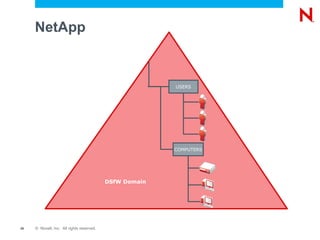
This document provides an overview and agenda for Domain Services for Windows (DSfW). DSfW allows users from an eDirectory tree to access resources on an Active Directory forest using a cross-forest trust. The document discusses what DSfW is, prerequisites for implementation, deployment scenarios including a new domain configuration and adding DSfW to an existing eDirectory tree, and a demonstration of deployment. It also covers DSfW in later versions of Open Enterprise Server and support for third-party applications like Citrix.
![Domain Services for Windows: Best Practices for Windows Interoperability Biswajeet Mahapatra Product Manager [email_address] David Shepherd Senior Technical Specialist [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cl310-101204115345-phpapp01/85/Cl310-1-320.jpg)