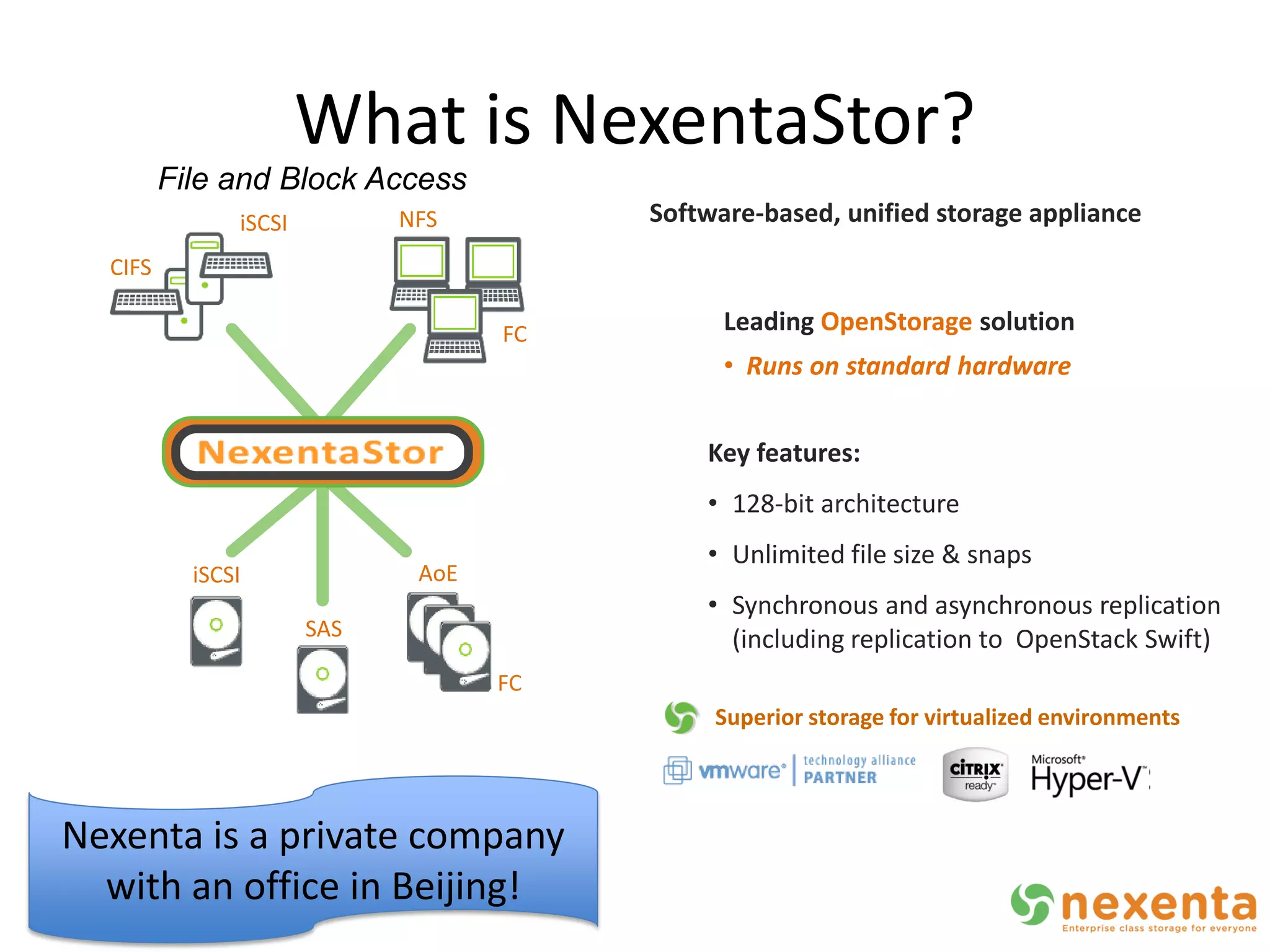
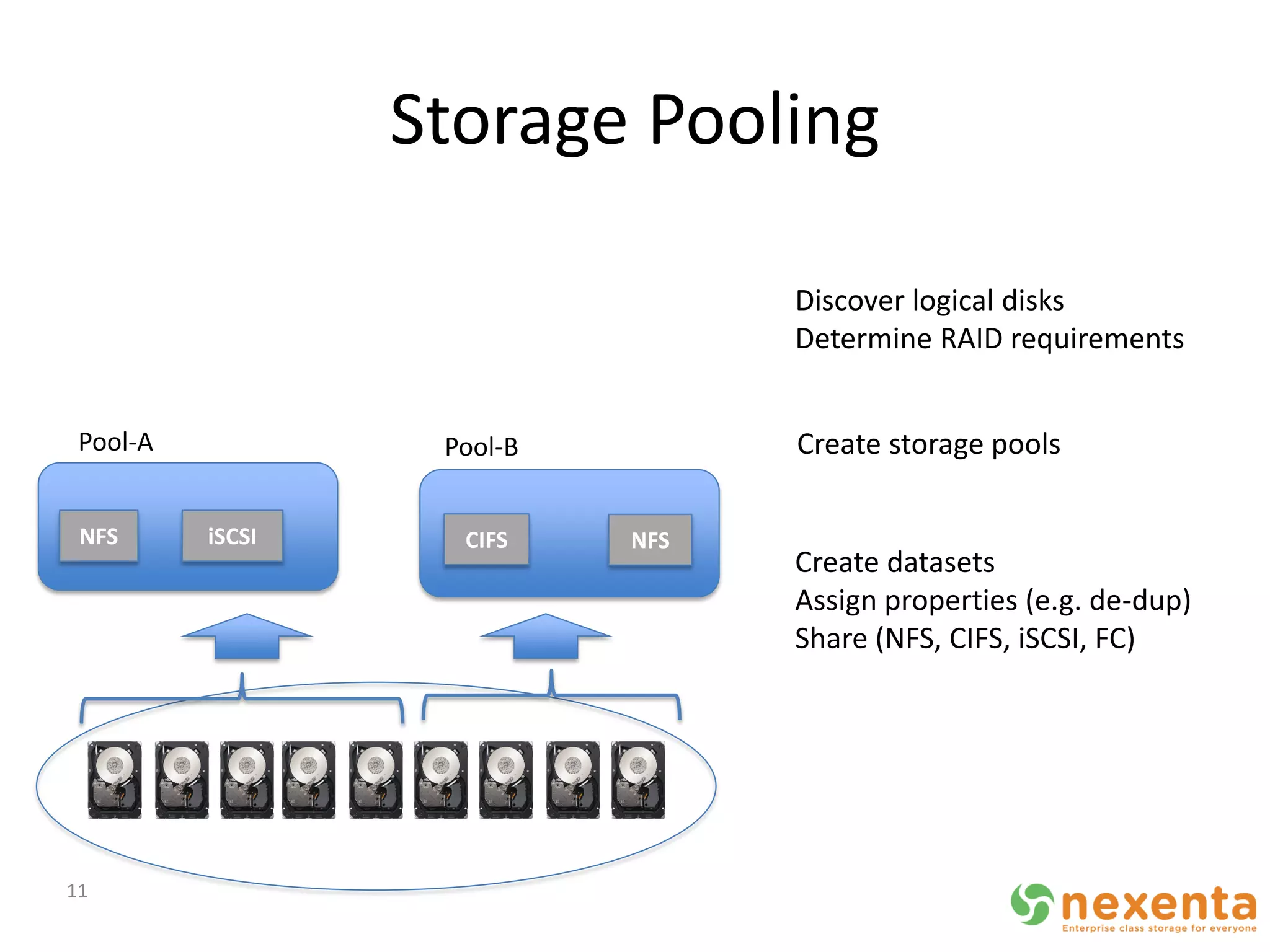
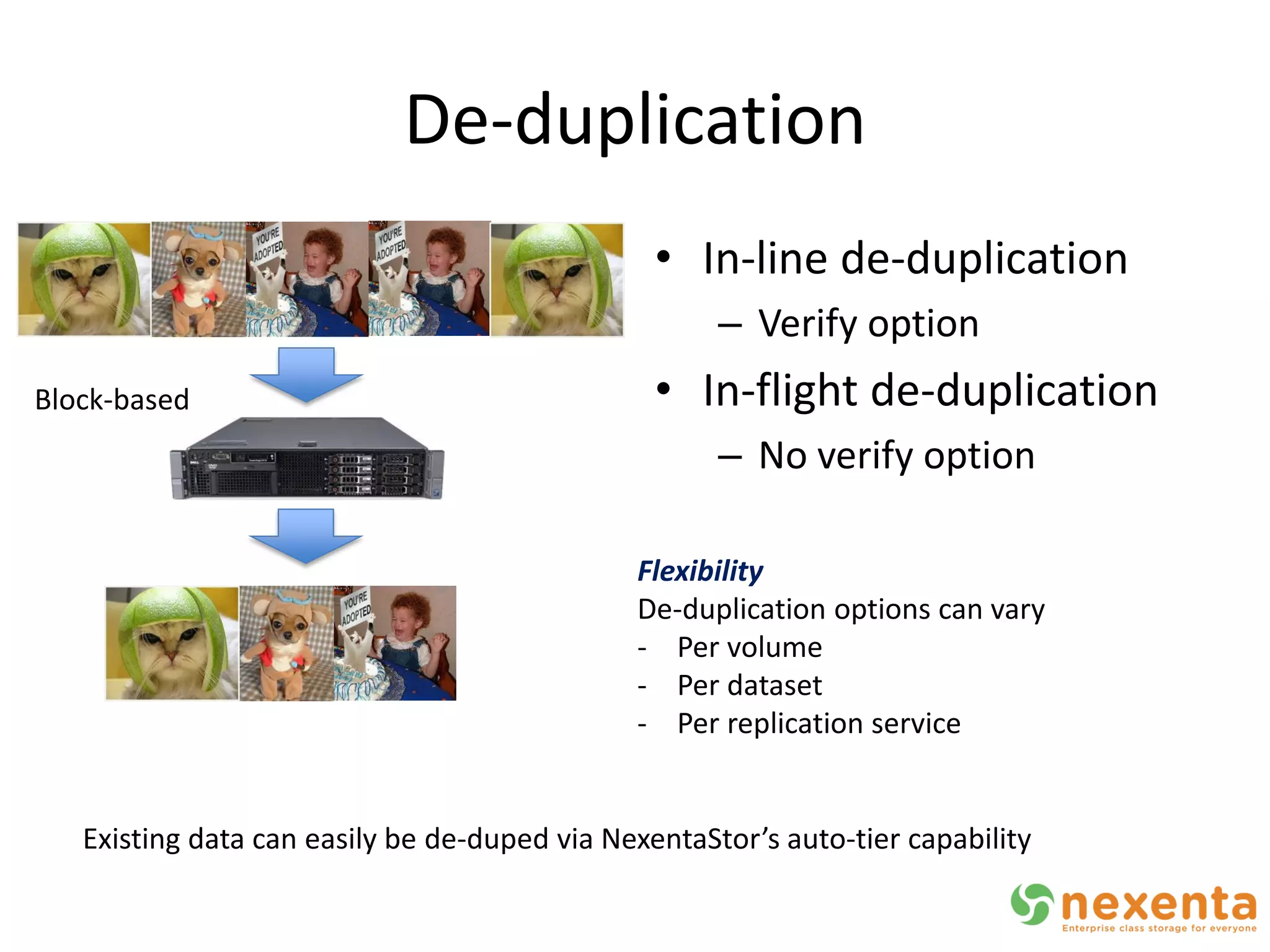
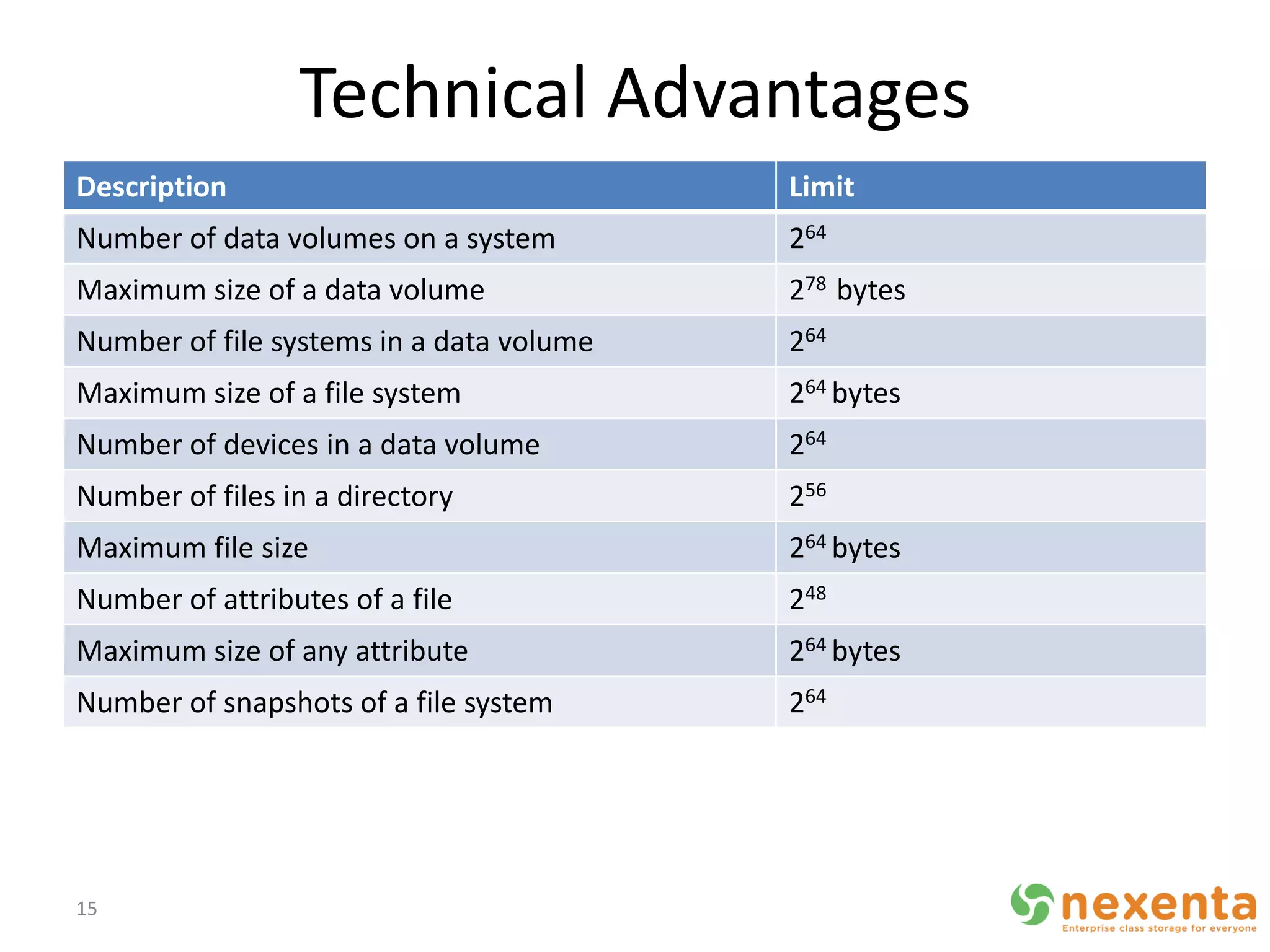
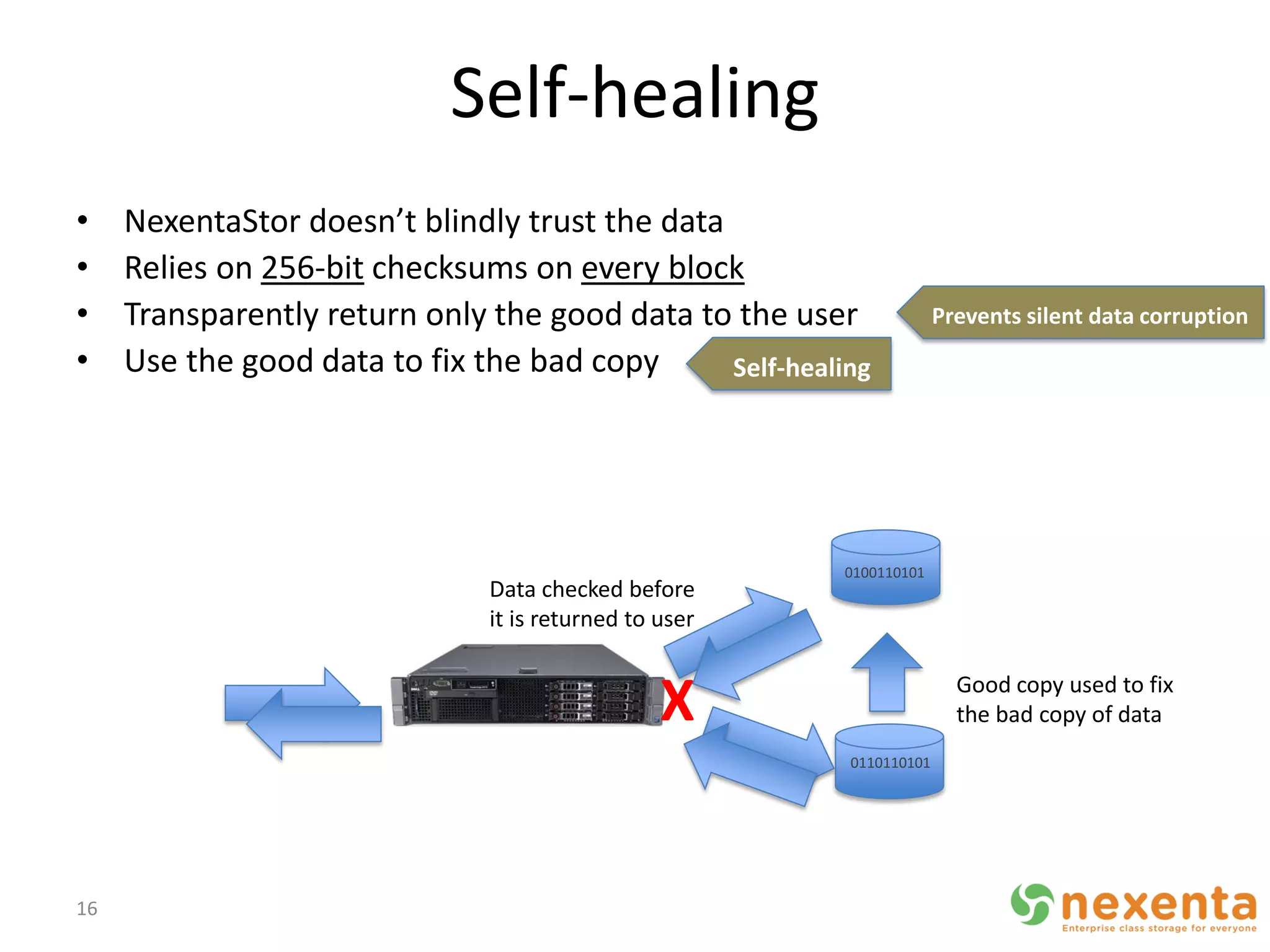
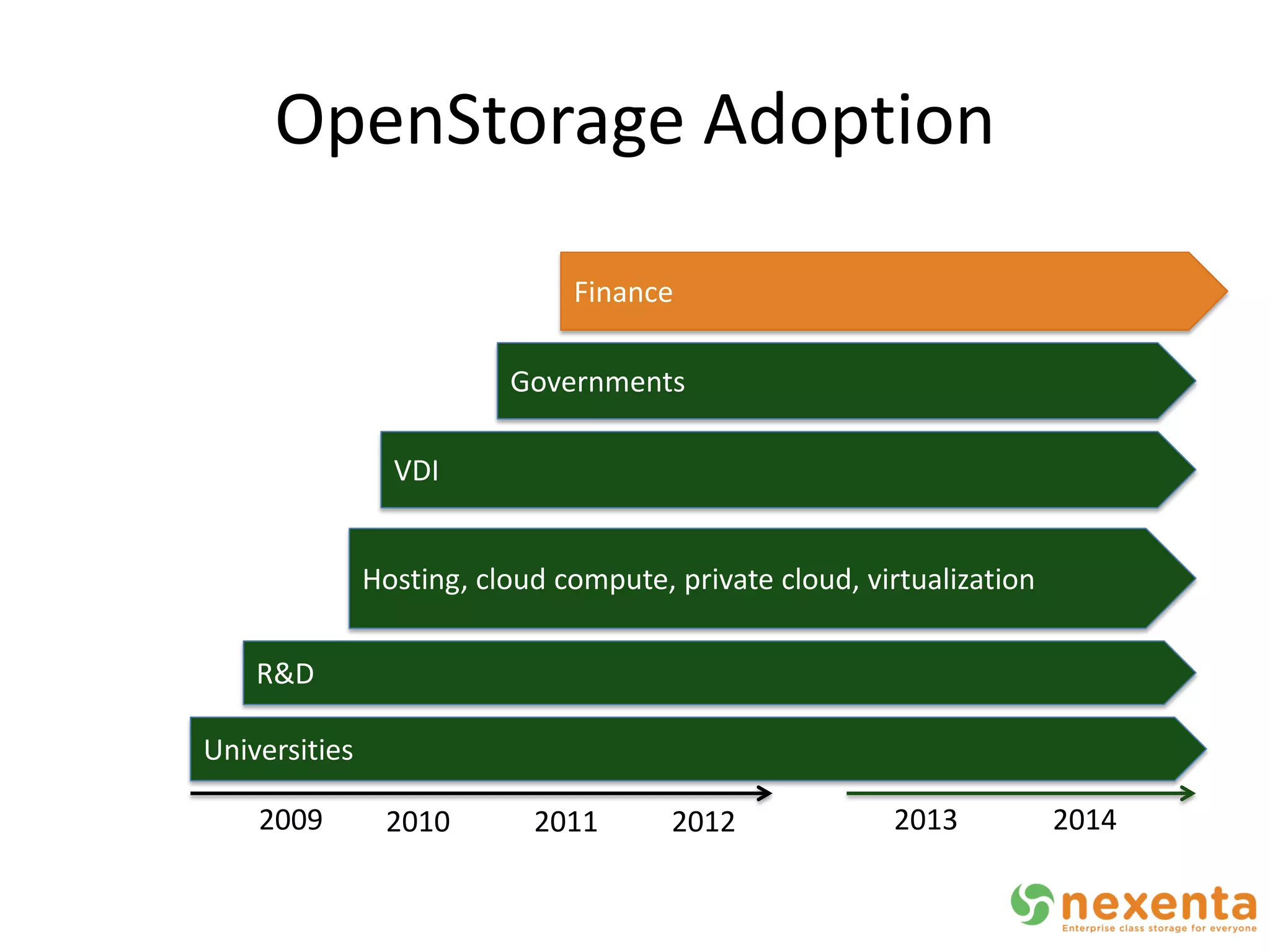
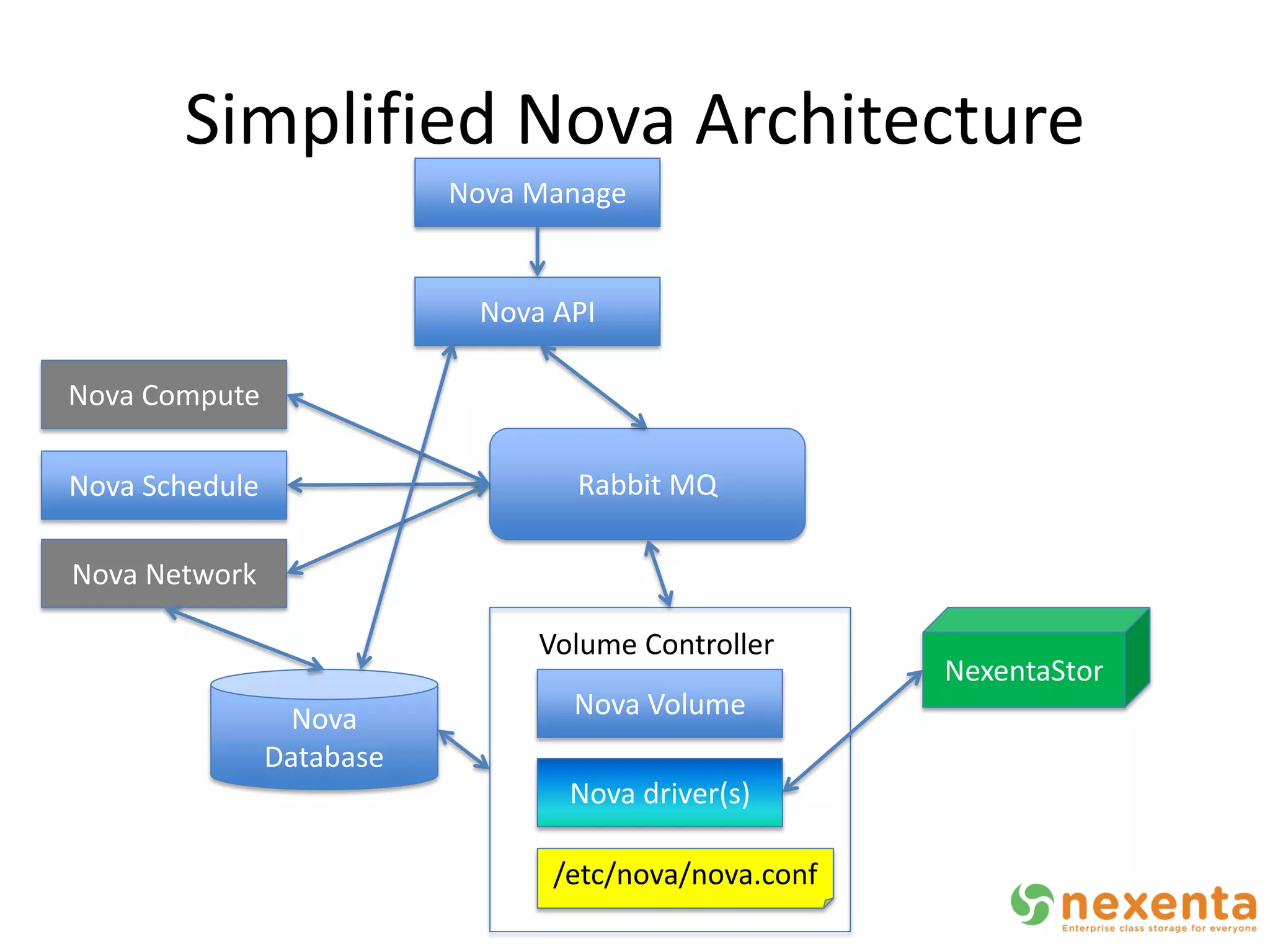
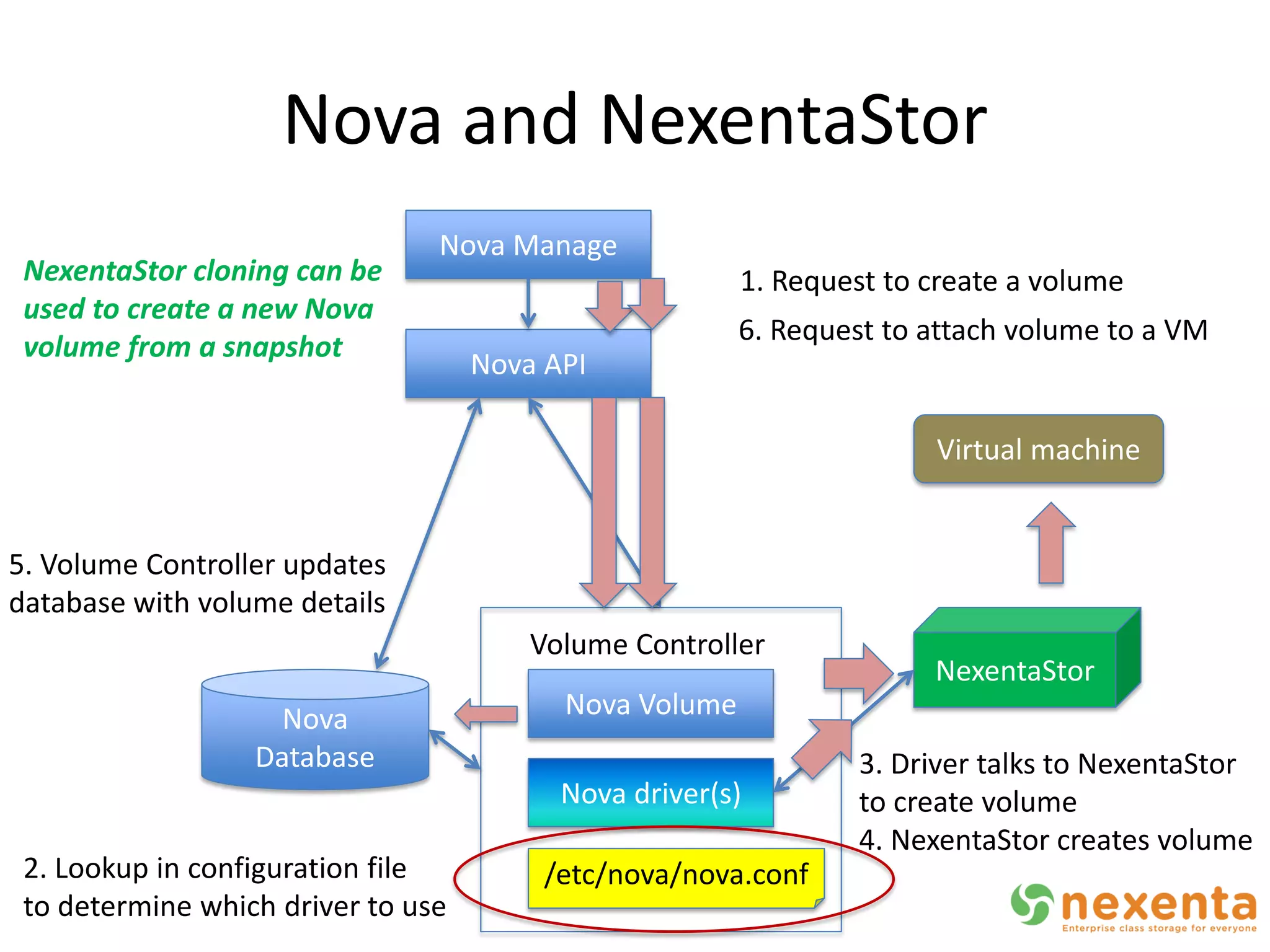
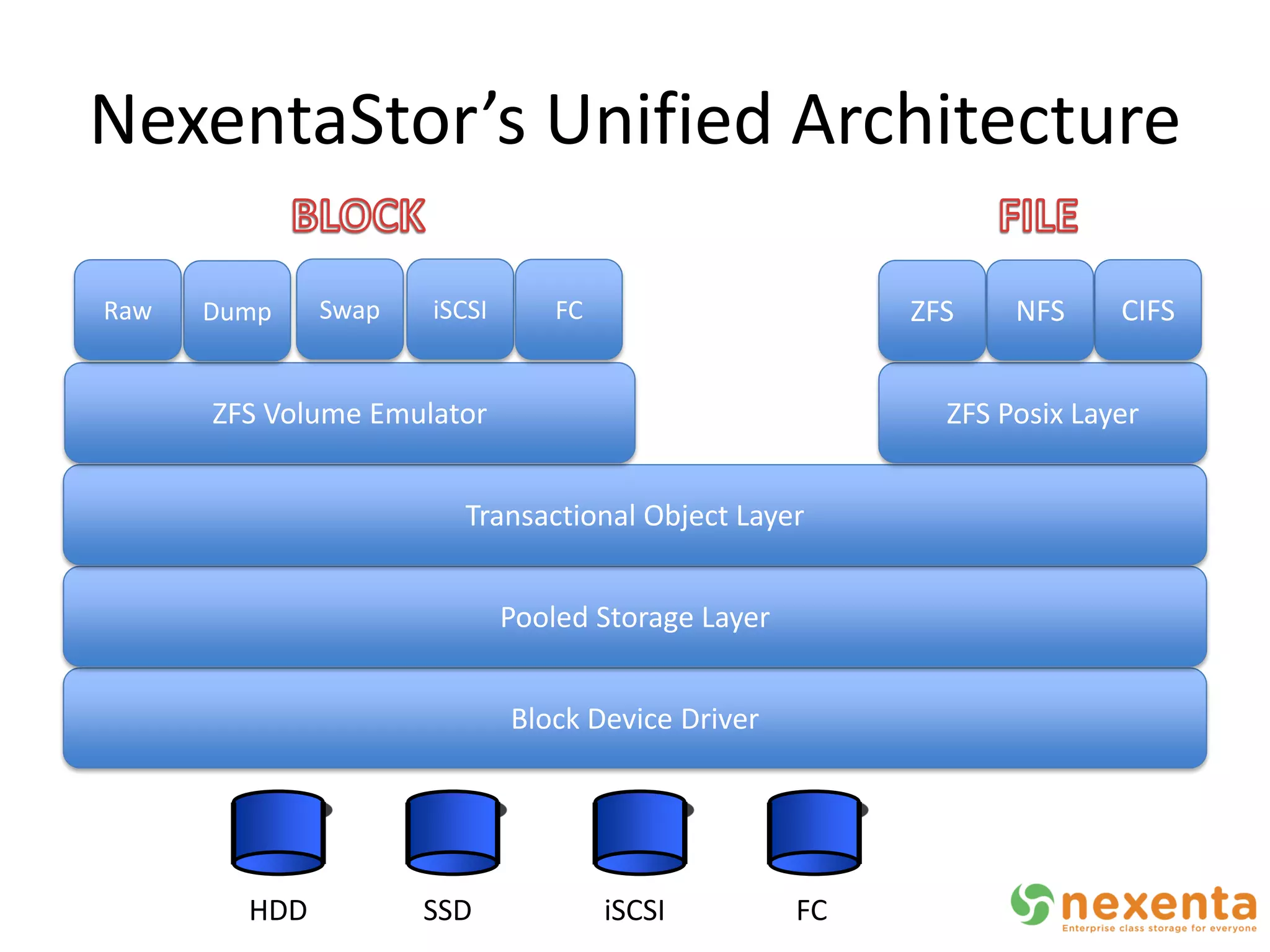
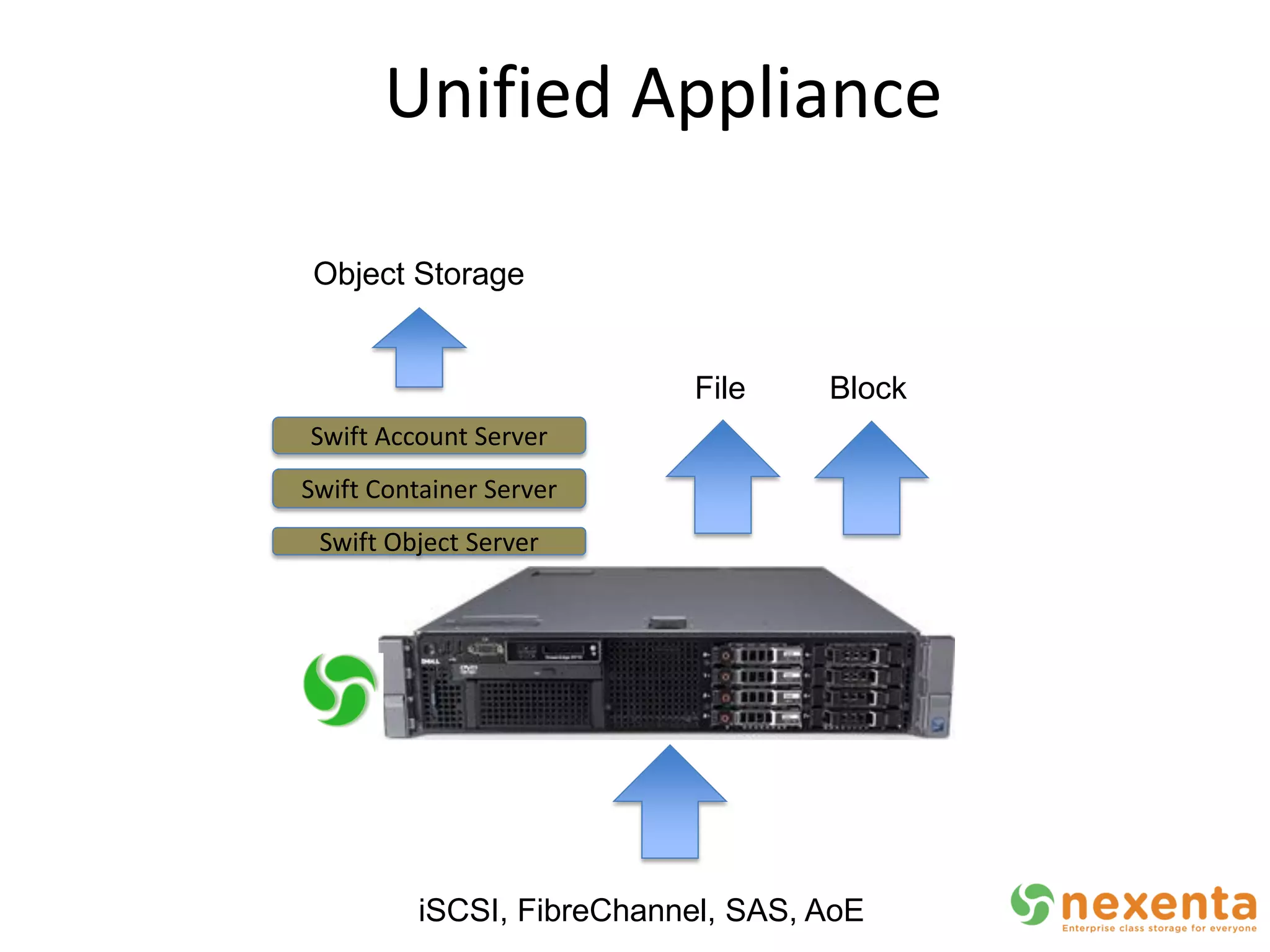
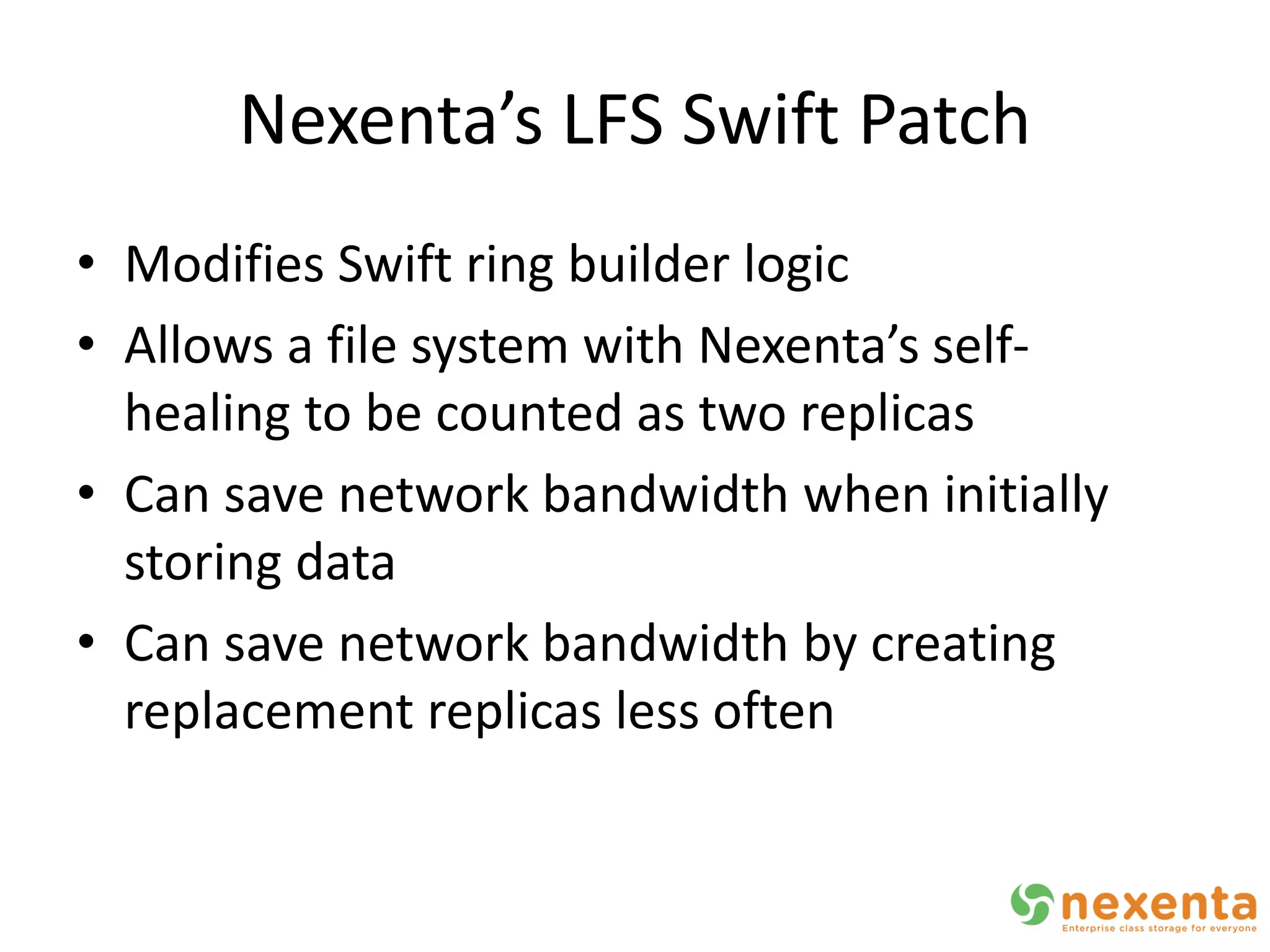
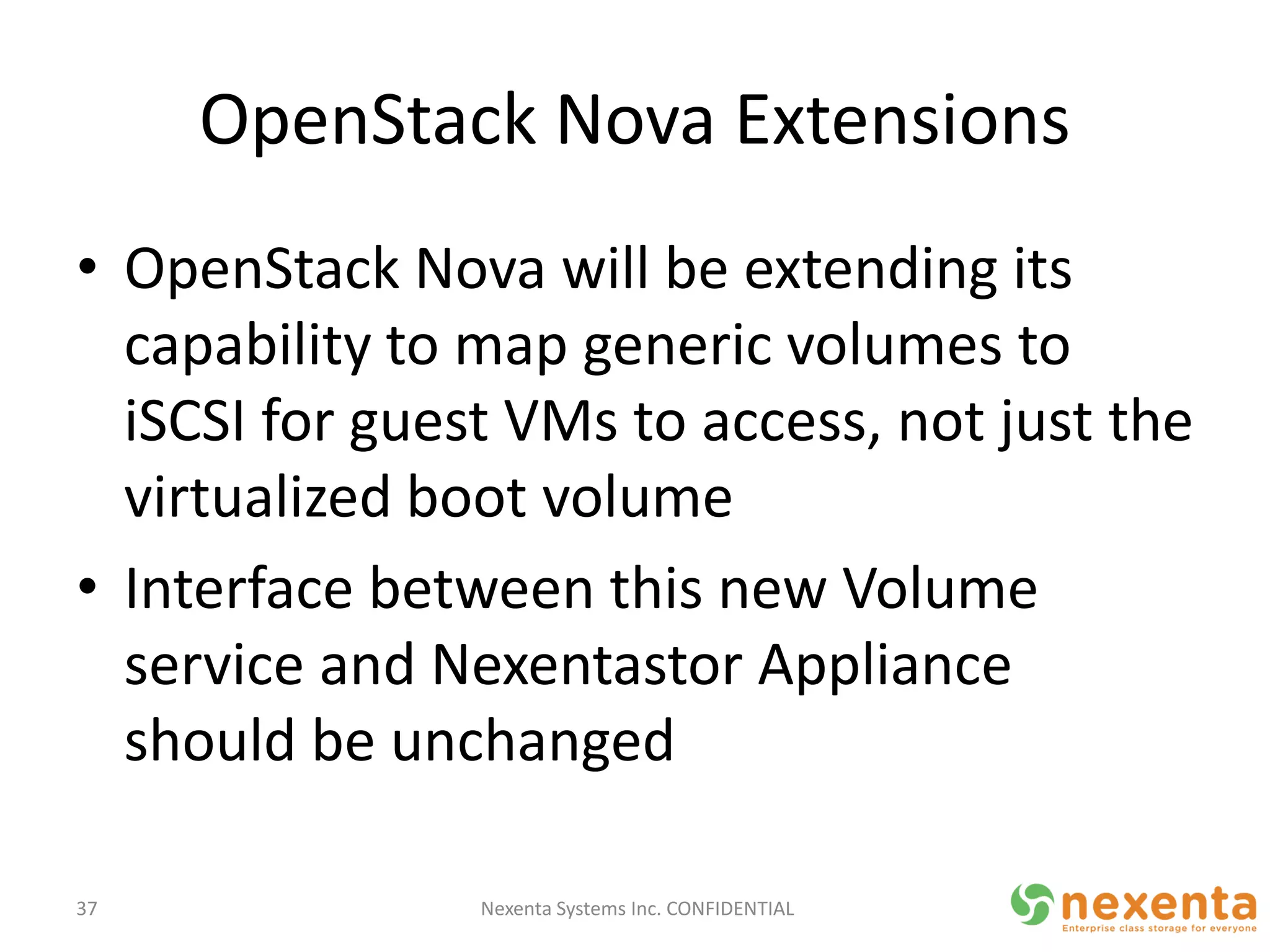
OpenStorage refers to open source storage software that allows for disaggregated hardware components from different vendors. NexentaStor is a leading OpenStorage solution that runs on standard hardware and provides file and block access using protocols like NFS, CIFS, and iSCSI. It offers storage efficiency features like deduplication, compression, and thin provisioning. NexentaStor can also be used with OpenStack Nova to provision volumes and attach them to virtual machines. Nexenta has contributed code to OpenStack Swift to leverage NexentaStor's self-healing capabilities for object storage. OpenStorage is growing with adoption in cloud computing and more integration with projects like OpenStack.