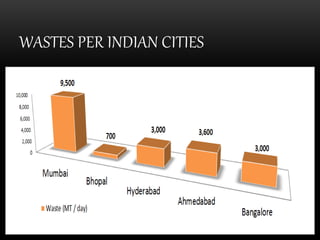
This document presents information on solid waste management. It defines solid waste and discusses its types and sources. The effects of solid waste are also addressed. The concepts of the 3Rs - reduce, reuse, recycle - for waste management are introduced. Methods of solid waste management include storage, collection, transport, recycling, and disposal. Storage methods include dust bins and paper sacks. Collection occurs through house-to-house pickup or from public bins. Transportation moves waste to disposal sites. Recycling recovers materials for new products. Disposal methods consist of dumping, landfilling, incineration, composting, and burial.