The document discusses securing Cisco routers. It recommends:
1. Implementing a security policy that protects the physical router, controls access to router management protocols, and filters network traffic.
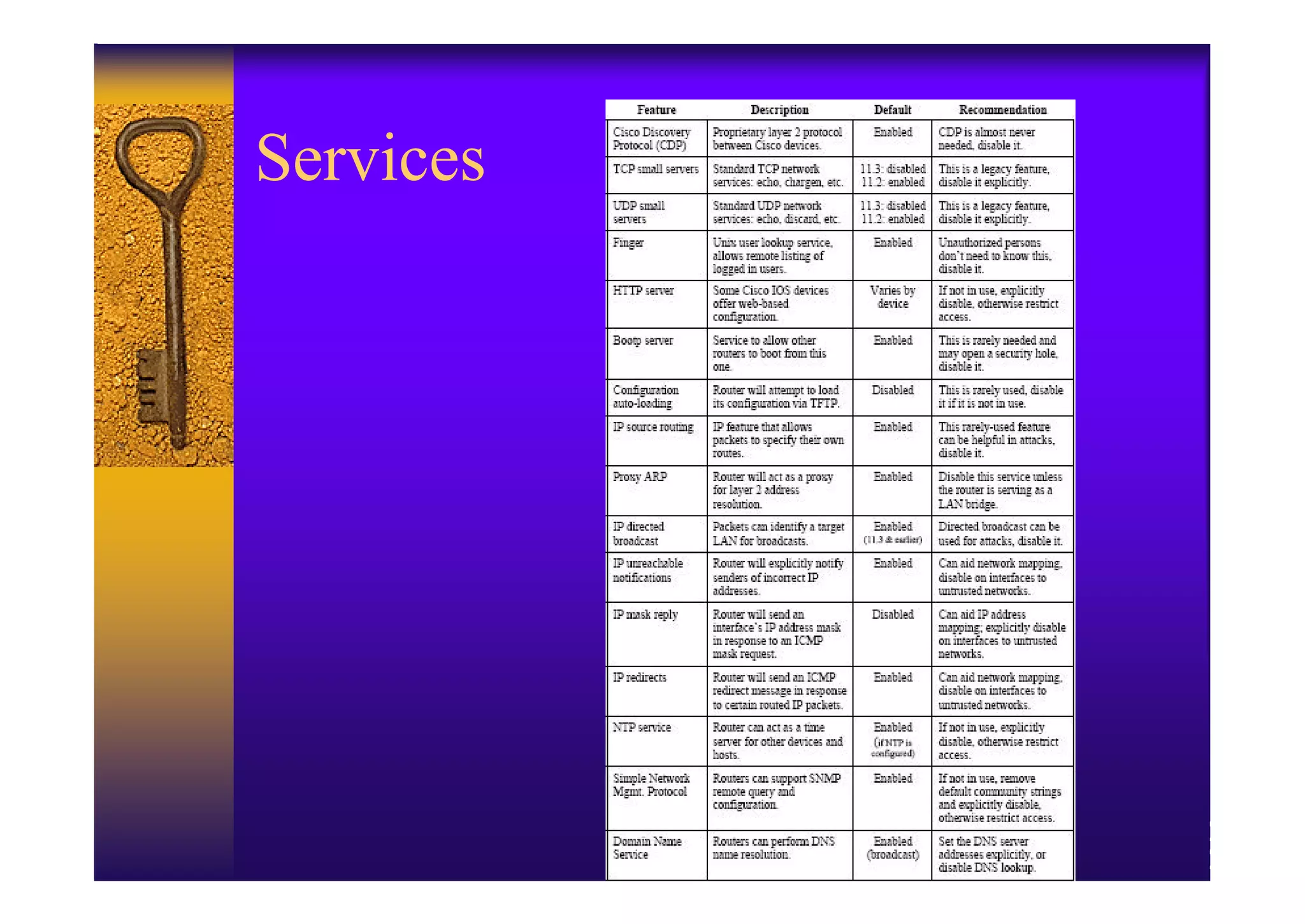
2. Hardening the router by disabling unneeded services, enabling strong authentication like SSH, implementing AAA with centralized authentication, and using access control lists to filter traffic.
3. Monitoring the router for attacks and anomalies using tools like Router Audit Tool (RAT) and implementing countermeasures like rate limiting.


















![Access Control List
♦ access-list list-number {deny | permit} source
[source-wildcard] [log]
♦ access-list list-number {deny | permit} protocol
source source-wildcard source-qualifiers
destination destination-wildcard destination-
qualifiers [ log | log-input]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ciscoequipmentsecurity-130219051534-phpapp02/75/Cisco-Equipment-Security-25-2048.jpg)



![Committed Access Rate
♦ rate-limit {input | output} [access-group [rate-limit] acl]
token-bit-rate burst-normal-size burst-excess-size
conform-action action exceed-action action
♦ north(config)# no access-list 160
north(config)# access-list 160 deny tcp any any established
north(config)# access-list 160 permit tcp any any syn
north(config)# interface eth0/0
north(config-if)# rate-limit input access-group 160
64000 8000 8000
conform-action transmit exceed-action drop
north(config-if)# end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ciscoequipmentsecurity-130219051534-phpapp02/75/Cisco-Equipment-Security-29-2048.jpg)




