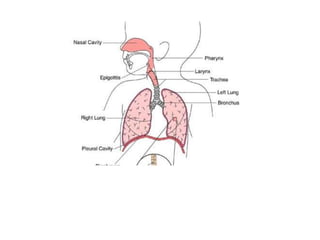
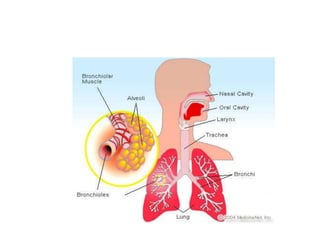
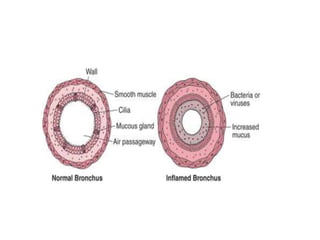
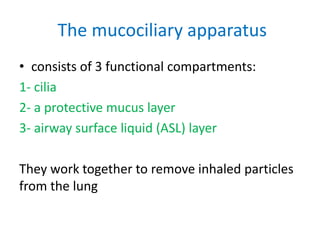
Chronic bronchitis in children is defined as recurring inflammation and degeneration of the bronchial wall that may be associated with active infection. It is often part of an underlying disease like asthma. Common causes include repeated acute bronchitis infections, cigarette smoke exposure, gastroesophageal reflux, and fungal or viral infections. Mucociliary clearance dysfunction is also a common feature. Treatment focuses on managing underlying conditions through bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, and antibiotics if needed. Proper diagnosis and management of chronic bronchitis or underlying diseases is important to prevent chronic lung damage.