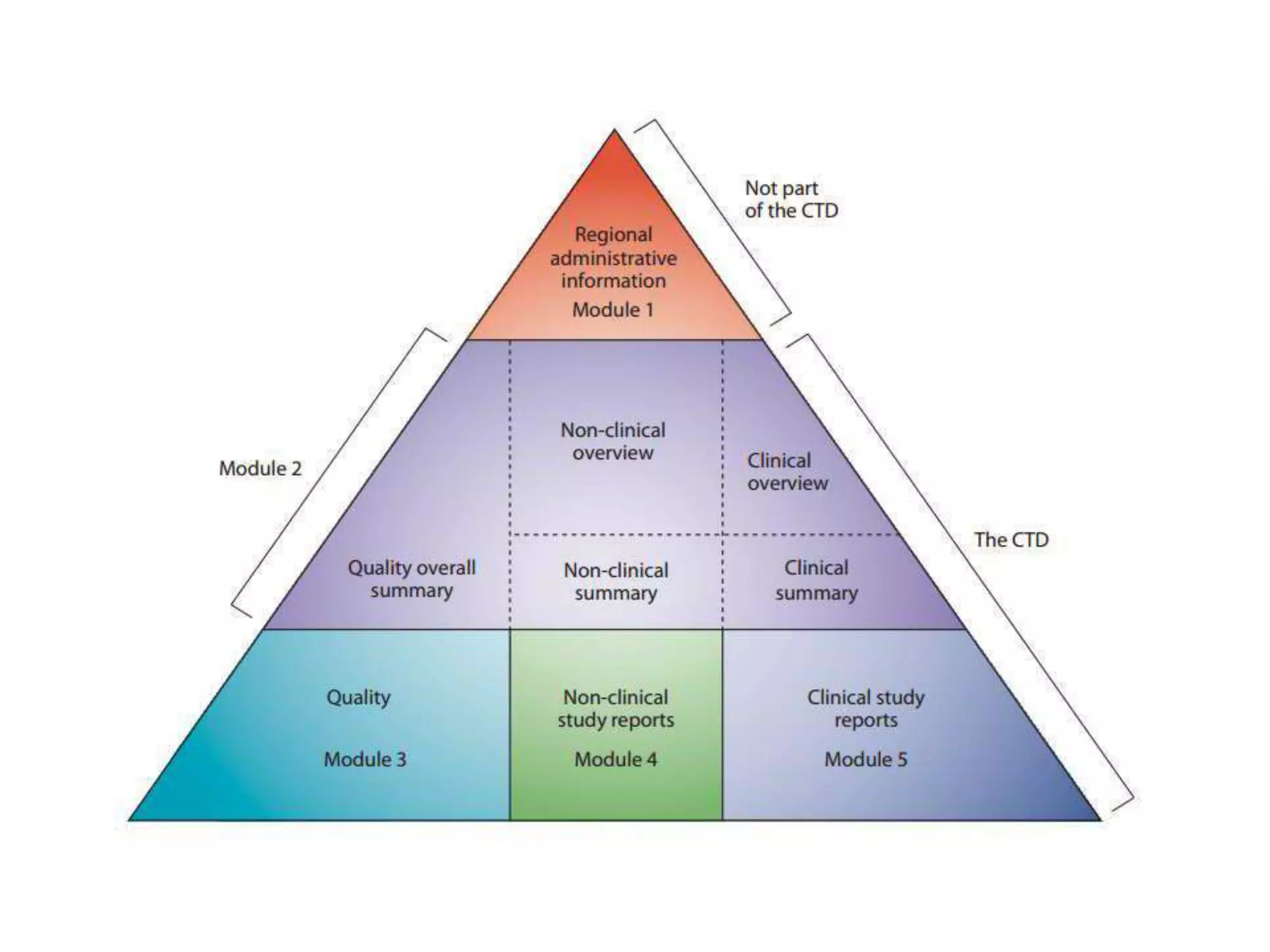
The document discusses the Common Technical Document (CTD) and the Electronic CTD (eCTD), which standardize formats for regulatory submissions in the pharmaceutical industry across major authorities like the EMA, FDA, and MHLW. The CTD aims to improve the efficiency of drug approval processes by providing a harmonized format, while the eCTD enhances submissions through electronic means, improving review accuracy and resource use. The document also details the structure of the CTD's five modules, focuses on submission requirements, and highlights the benefits of transitioning to the eCTD format.









![Module 5: Clinical Study Report
• It explains studies on human and related information.
• Clinical (human study) reports must be presented in order described in the
guidance M4-E.
• 5.1 Table of content of Module 5
• 5.2 Tabular listing of clinical studies
• 5.3 Clinical study reports
• 5.3.1 Reports of biopharmaceutical study [BA-BE]
• 5.3.2 Reports of PK [biomaterial] study
• 5.3.3 Reports of PK studies
• 5.3.4 Reports of PD studies
• 5.3.5 Reports of Efficacy and safety studies
• 5.3.6 Reports of Post marketing experience
• 5.3.7 Case Report forms & Individual patient listings](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/raseminar-221111175004-b0e998e9/75/CTD-and-eCTD-Seminar-pptx-14-2048.jpg)


![• eCTD highly recommended by USFDA for NDAs,
and DMFs, filing.
• From 2010 EU also make compulsory eCTD to all
procedure.
• eCTD composed of 2 types of specification
1.Content specification–As defined by ICH
2.Technical specification-Electronic softwares
• CTD- Table of content [pdf] [paper]
• eCTD -XML Backbone](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/raseminar-221111175004-b0e998e9/75/CTD-and-eCTD-Seminar-pptx-17-2048.jpg)