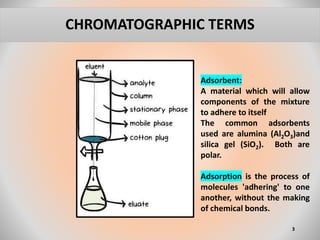
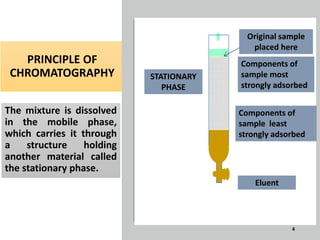
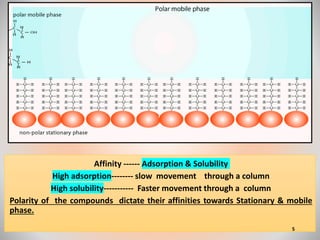
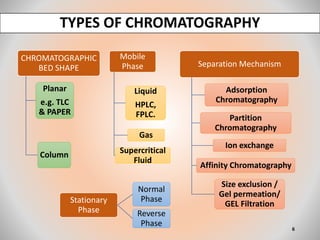
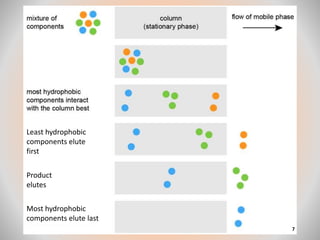
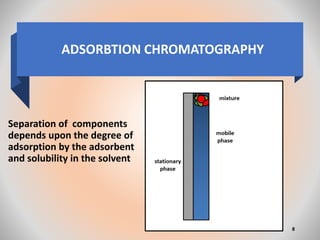
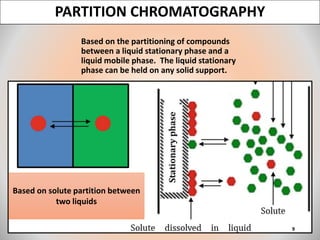
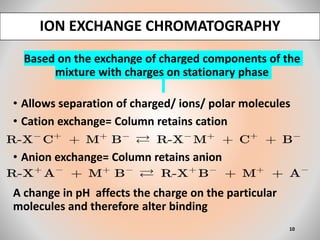
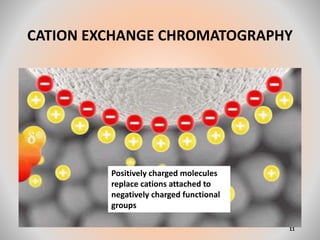
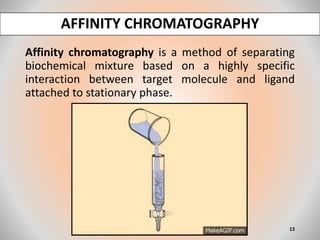
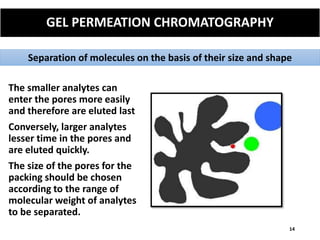
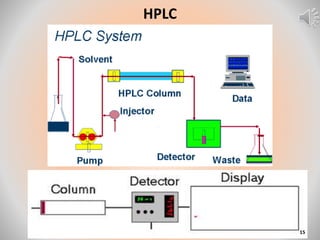
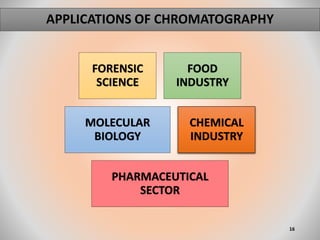
The document provides an overview of chromatography, a separation technique first coined by Mikhail Tsvet in 1906 and further developed in the mid-20th century. It explains key terminology, principles, types of chromatography like affinity and ion exchange, and applications across various fields such as forensic science and pharmaceuticals. The content emphasizes how different chromatographic methods separate components based on properties like adsorption, solubility, and size.