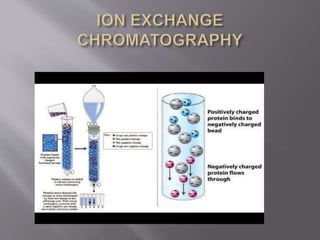
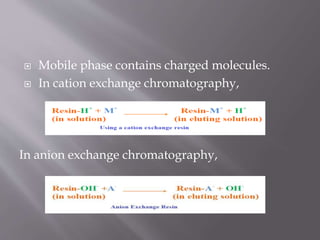
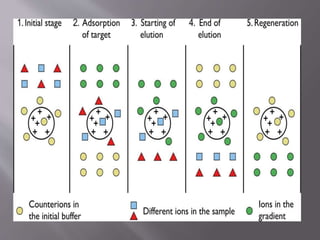
Ion exchange chromatography is a technique used to separate charged molecules based on their interaction with oppositely charged groups on a resin. It works by reversible exchange of ions between the ions in a sample and those on an ion exchange resin. There are two types of resins - cation exchange resins which interact with positively charged ions, and anion exchange resins which interact with negatively charged ions. The process involves equilibrating the resin, applying the sample, washing unbound molecules, and then eluting the bound molecules using an increasing salt gradient. Ion exchange chromatography is widely used to purify proteins and analyze ions in applications like biochemistry, water quality testing, and metal purification.