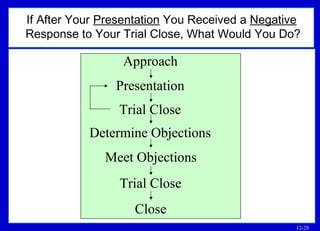
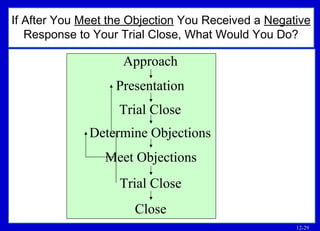
The document discusses techniques for handling objections in sales presentations. It defines objections as opposition or resistance to information or requests from the salesperson. It identifies different types of objections like hidden, stalling, no-need, money, product, and source objections.
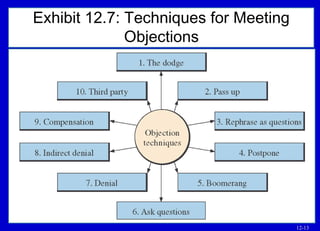
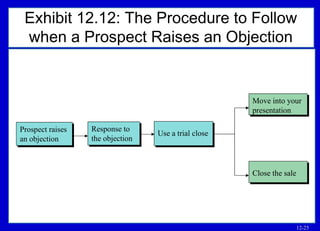
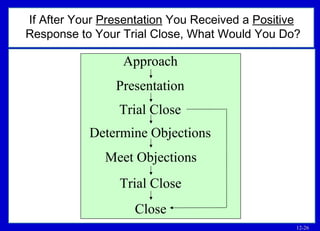
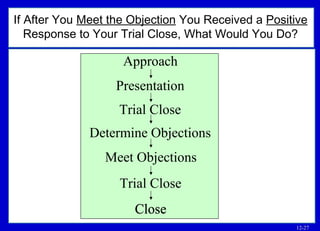
The document outlines basic points to consider when meeting objections like planning for objections, listening to understand the objection, and determining if it is a practical or psychological objection. It describes techniques for meeting objections such as dodging, rephrasing, postponing, sending objections back, and using a five-question sequence.
If an objection cannot be overcome, alternatives include concentrating on other benefits, admitting the limitation and showing how benefits outweigh it, or closing anyway