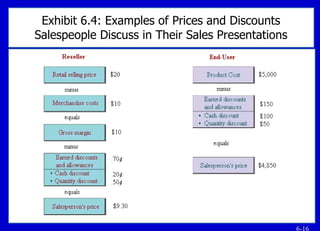
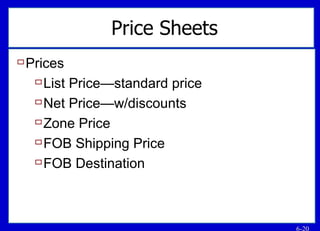
The document provides an overview of key topics related to sales knowledge, including customers, products, technologies, and channels. It discusses the importance of being an expert on products and customers, and how knowledge builds relationships and leads to more sales. Specific areas of sales knowledge covered include the company, products, resellers, advertising, promotions, pricing, competition, technology, and financial metrics. The document emphasizes gaining a thorough understanding across many areas in order to effectively sell to customers.