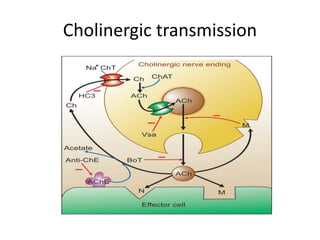
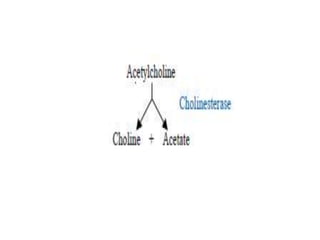
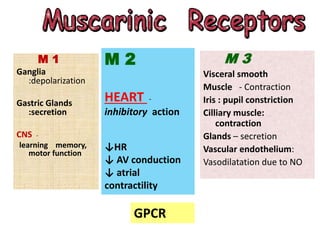
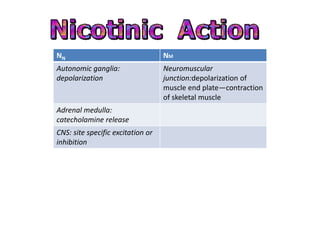
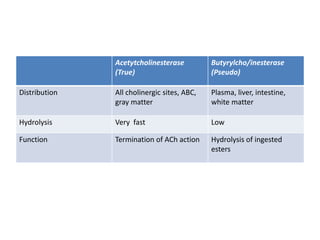
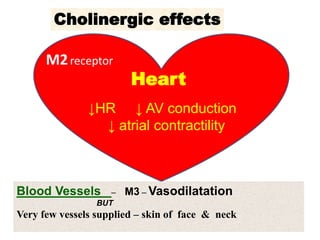
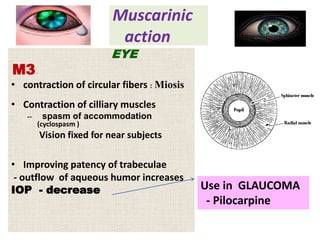
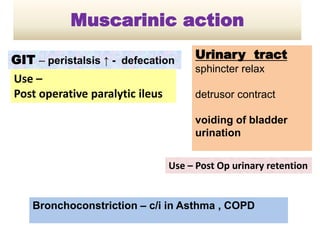
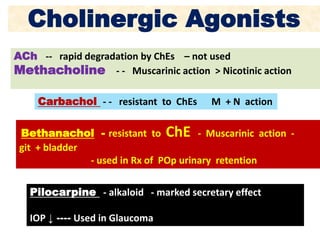
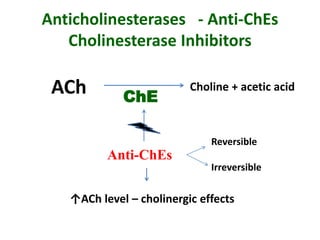
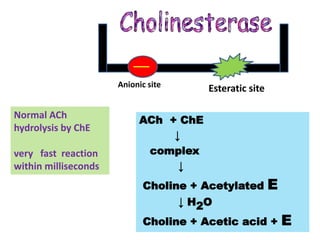
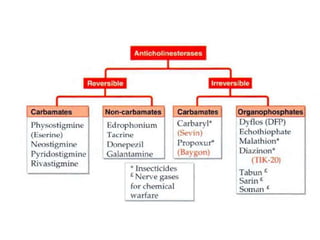
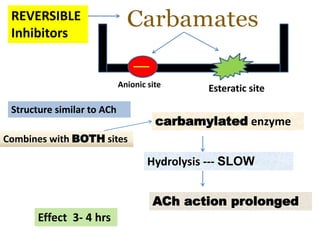
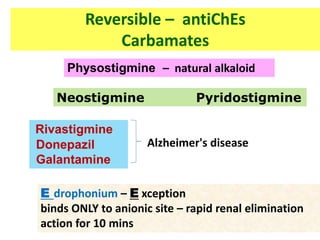
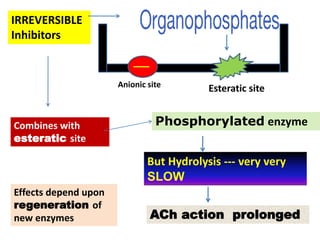
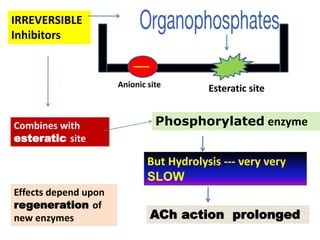
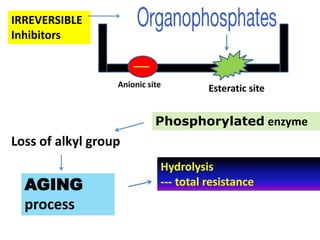
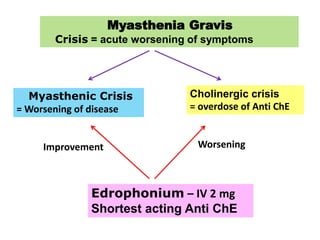
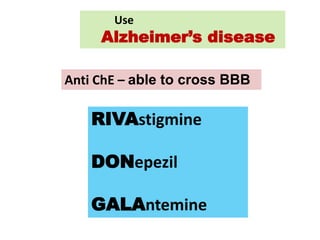
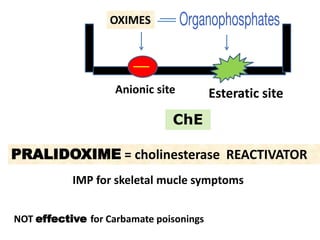
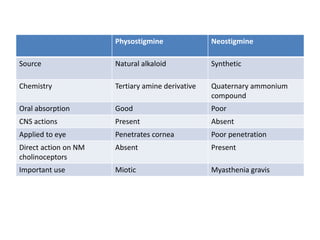
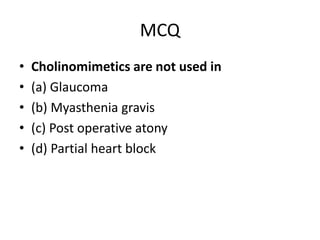
Cholinergic drugs act at cholinergic receptors in the autonomic nervous system and central nervous system. They include acetylcholine and cholinomimetics that act as agonists at muscarinic and nicotinic receptors. Anticholinesterases inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase and increase the level and duration of action of acetylcholine. They are used to treat myasthenia gravis and Alzheimer's disease. Organophosphate poisoning causes inhibition of acetylcholinesterase and cholinergic excess that is treated with atropine and pralidoxime. Pilocarpine is used as a miotic in glaucoma by stimulating muscarinic receptors in the eye