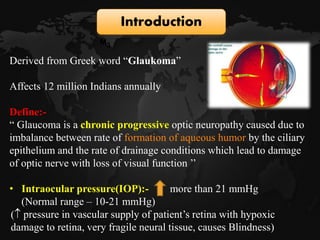
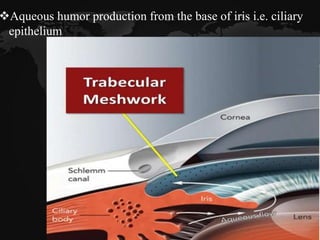
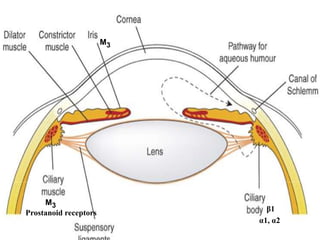
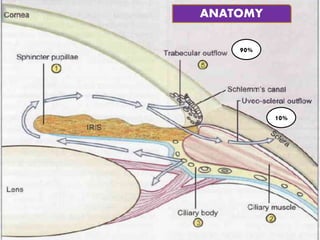
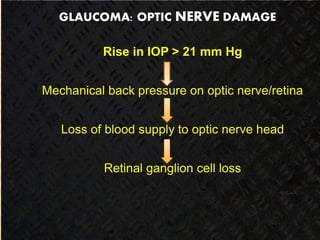
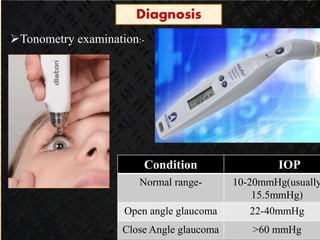
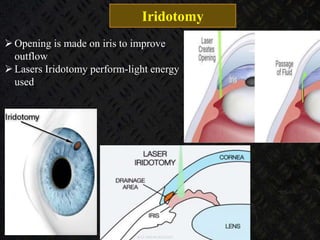
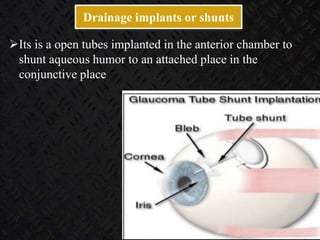
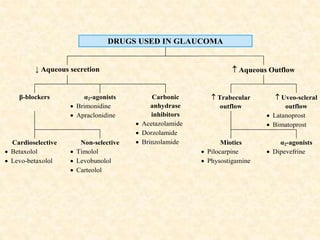
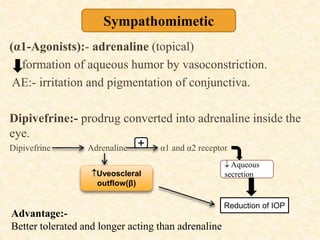
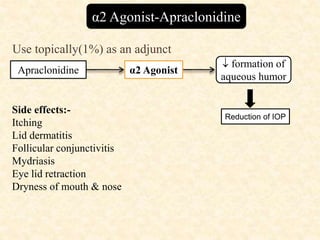
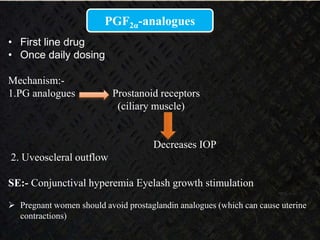
Glaucoma is a chronic progressive optic neuropathy caused by an imbalance between the rate of aqueous humor formation and drainage, leading to damage of the optic nerve and loss of vision. It is defined as an intraocular pressure of over 21 mmHg. The aqueous humor is produced by the ciliary epithelium and normally drained through two routes - the conventional trabecular route which drains around 90% and the uveoscleral pathway which drains around 10%. Glaucoma is diagnosed by tonometry and treated through lifelong drug therapy, laser treatment, or surgery to lower intraocular pressure and prevent further vision loss.