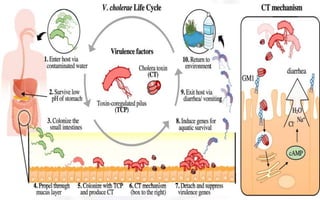
Cholera is an acute diarrheal illness caused by the bacteria Vibrio cholerae. It causes a rapid loss of fluids and electrolytes from the intestines that can lead to dehydration, shock, and even death if untreated. The classic symptoms include painless watery diarrhea and vomiting. Treatment involves oral or intravenous rehydration to replace lost fluids, along with antibiotics to kill the bacteria. Patients are discharged once they can tolerate oral intake and their diarrhea and urinary output returns to normal levels. Cholera remains a global threat, especially in areas with poor sanitation and lack of clean water.