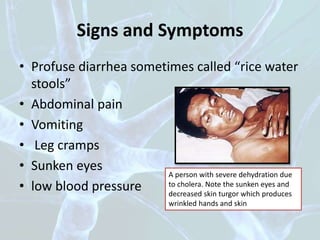
Cholera is an infection of the intestines caused by the bacterium Vibrio cholerae that causes severe watery diarrhea and dehydration. It spreads primarily through contaminated water supplies but can also be transmitted through foods like raw seafood, fruits, and vegetables. Cholera bacteria live naturally in coastal waters and attach to crustaceans, spreading globally through their movements and growth of algae fueled by sewage runoff. Preventing cholera involves excluding infected individuals until symptoms cease, thorough hand washing, and isolating severely ill patients.