Embed presentation
Download as PPSX, PPTX



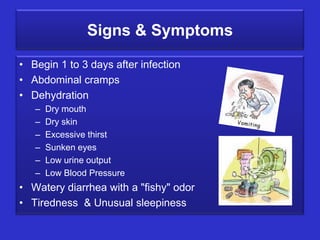
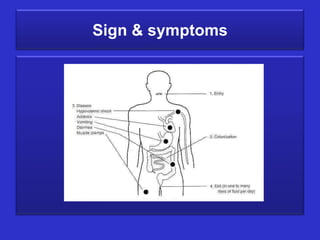

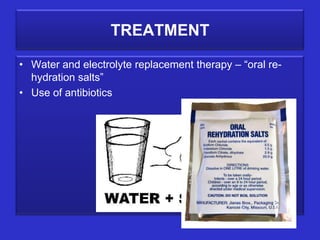

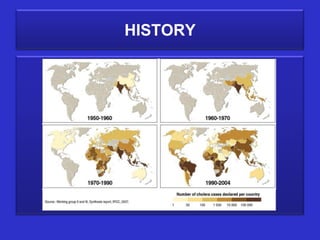


The document summarizes cholera, a deadly waterborne disease caused by the Vibrio cholerae bacteria. It is spread through contaminated food or water due to poor hygiene. Symptoms include abdominal cramps, watery diarrhea, dehydration, and exhaustion. Diagnosis involves examining stool samples microscopically or testing for cholera enterotoxin. Treatment focuses on oral rehydration and antibiotics while prevention emphasizes drinking boiled water, avoiding raw food, and proper sanitation.










