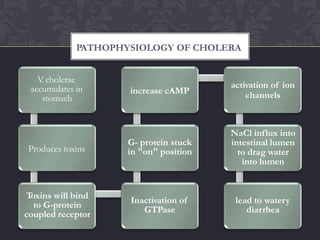
Cholera is an acute diarrheal illness caused by the bacteria Vibrio cholerae. It spreads through contaminated food or water and causes watery diarrhea that can lead to severe dehydration and death if untreated. While rare in developed nations, it remains common in parts of Asia, Africa, and Latin America where sanitation and access to clean water is limited. The primary treatment is oral rehydration therapy to replace fluid losses. Antibiotics may also be used to shorten the illness. Prevention relies on access to safe water, basic hygiene practices, and vaccination in at-risk populations.