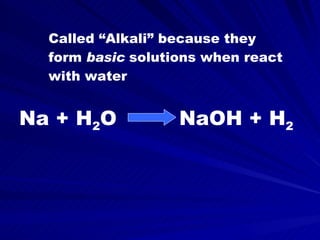
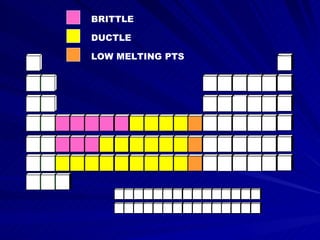
The document discusses various chemical groups and families, including their properties and common uses. It covers the alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, inner transition metals (lanthanides and actinides), and other nonmetal groups such as carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, halogens, noble gases, and hydrogen. For each group, it highlights some of the most abundant elements, their physical and chemical characteristics, and important commercial applications.