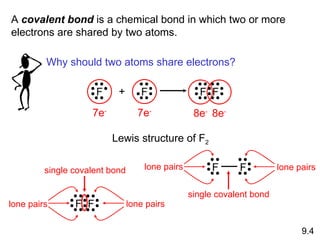
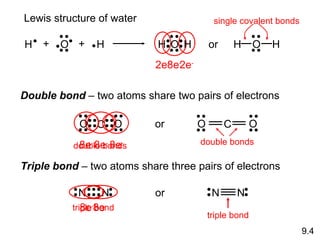
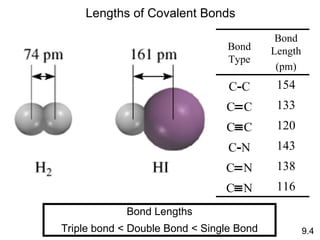
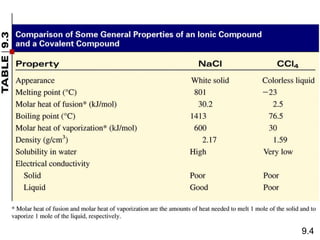
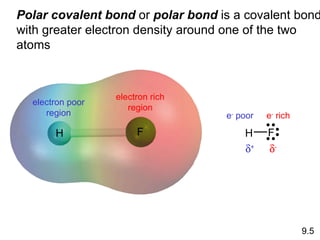
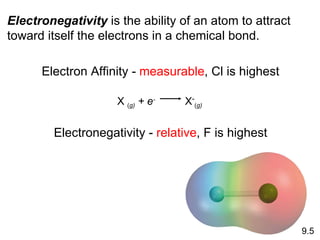
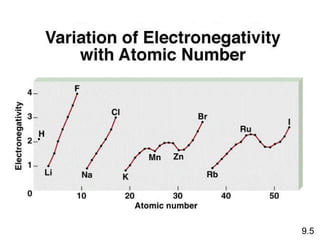
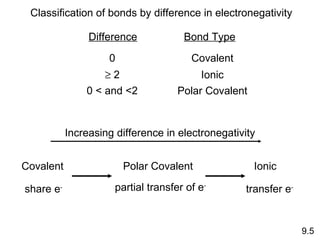
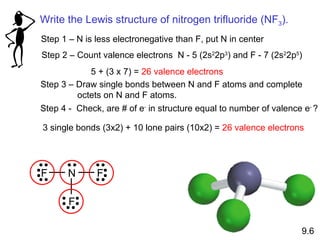
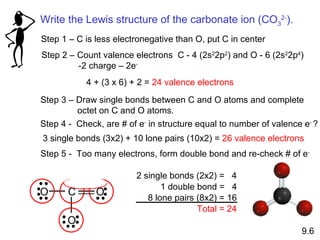
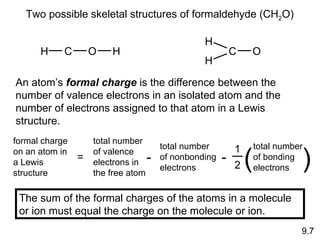
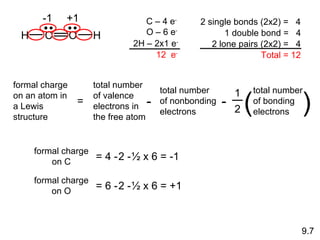
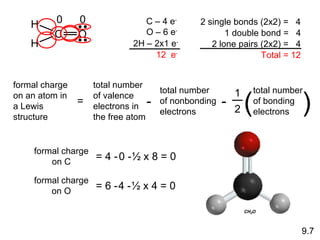
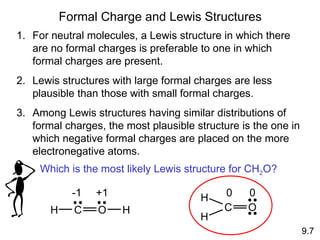
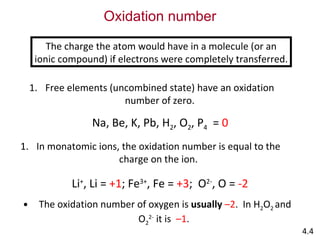
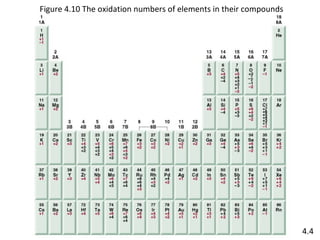
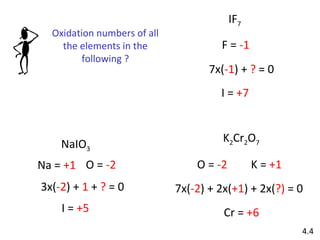
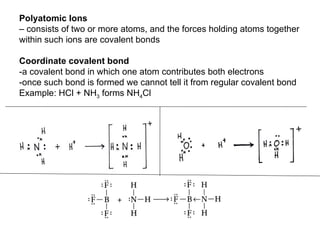
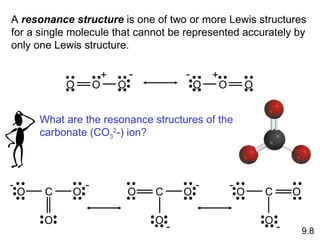
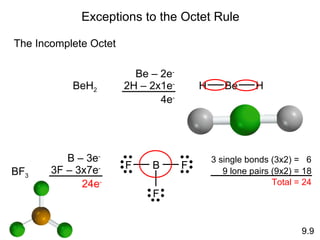
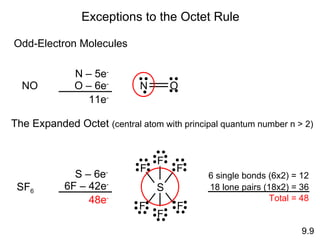
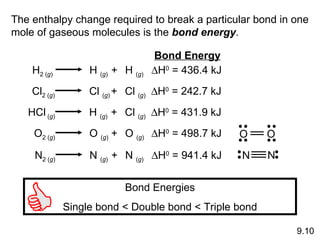
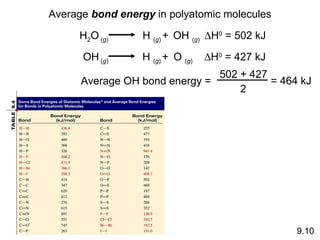
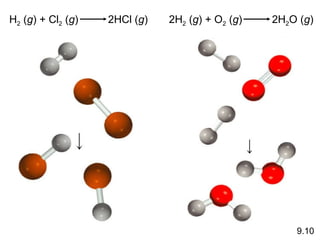
The document discusses various concepts of chemical bonding, emphasizing the role of valence electrons in ionic and covalent bonds. It explains Lewis symbols, structures, formal charges, oxidation numbers, and the importance of electron configurations for stability. Additionally, it covers different types of bonds, bond lengths, and exceptions to the octet rule.



![9.2 The Ionic Bond 1s 2 2s 1 1s 2 2s 2 2p 5 1s 2 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 [He] [Ne] Li + F Li + F - Li Li + + e - e - + F F - F - Li + + Li + F -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfakepathchemicalbondingi-100203115502-phpapp02/85/Chemical-Bonding-I-Basic-Concepts-7-320.jpg)