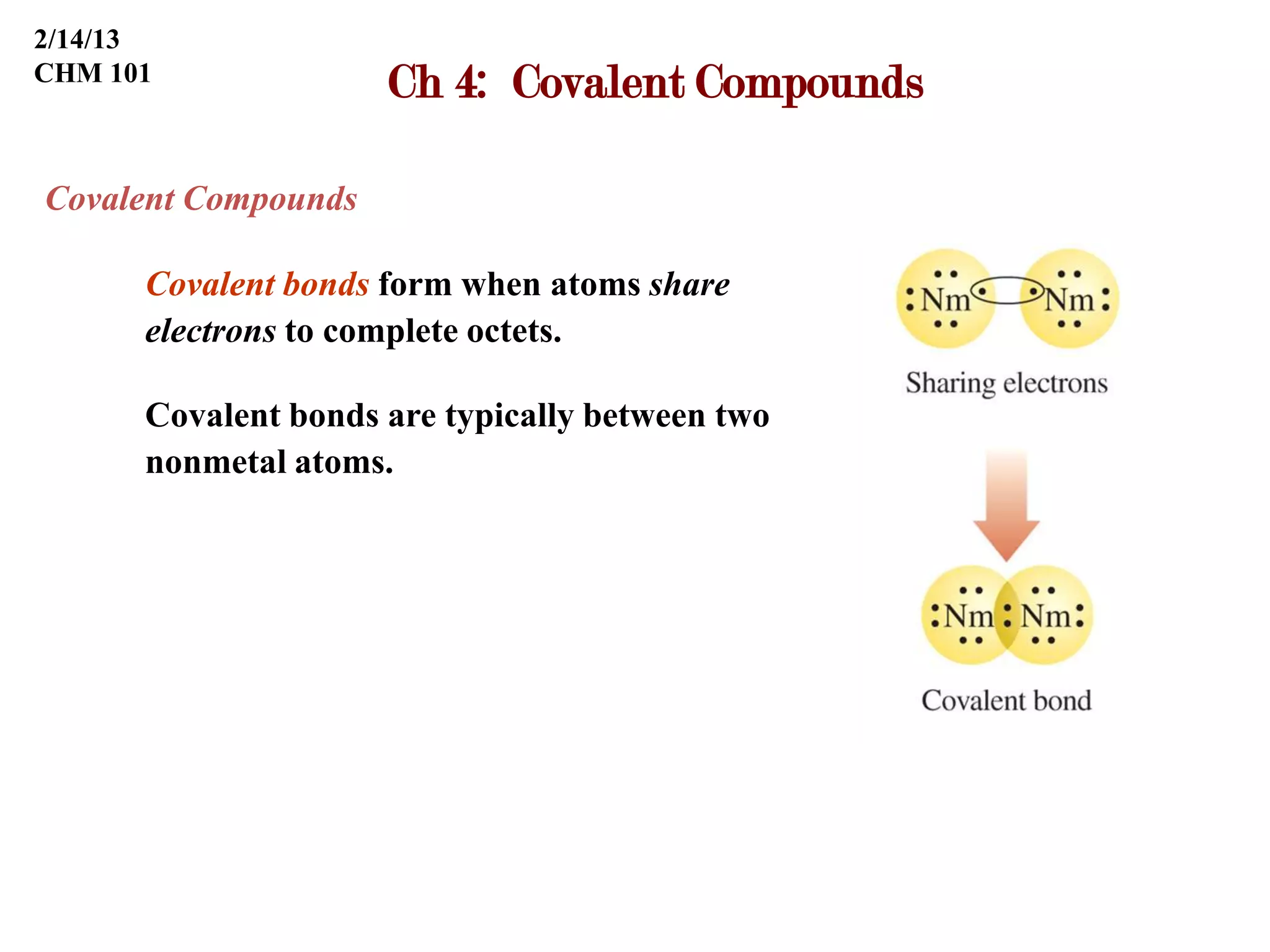
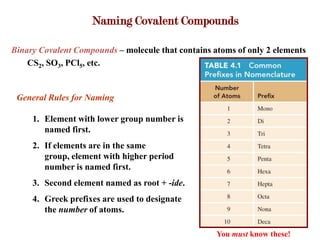
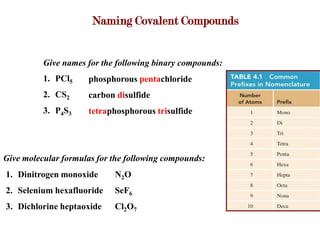
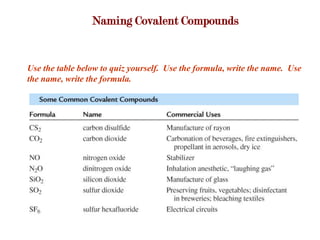
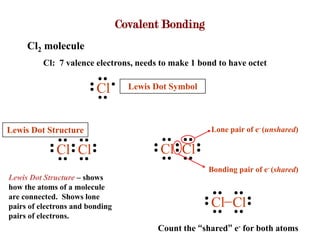
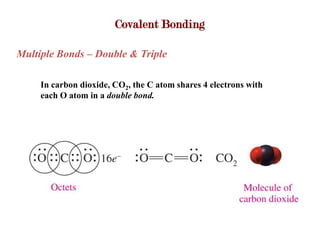
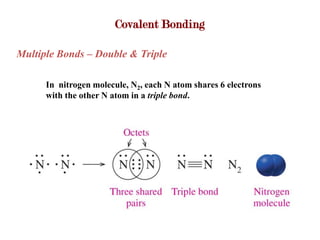
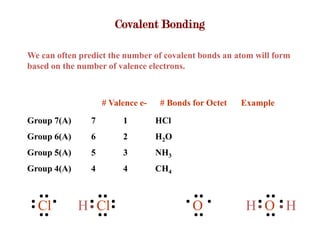
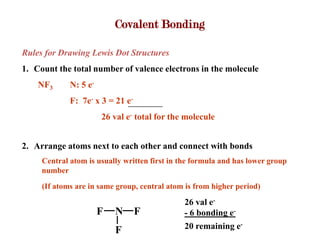
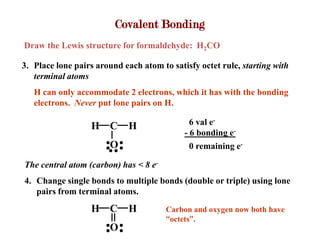
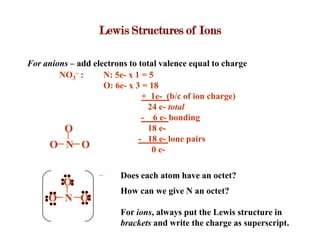
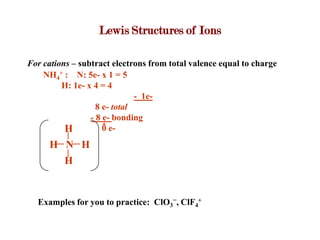
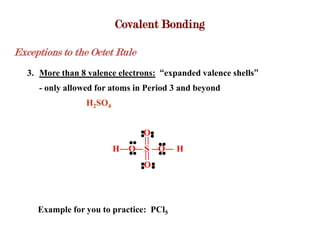
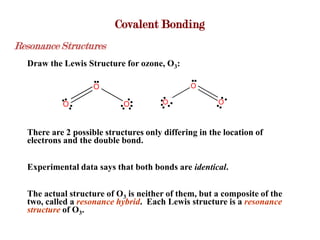
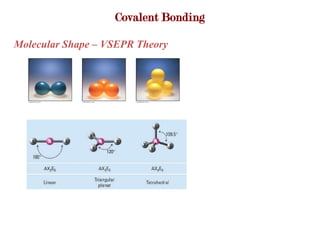
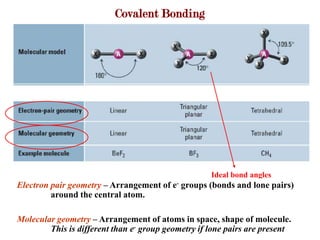
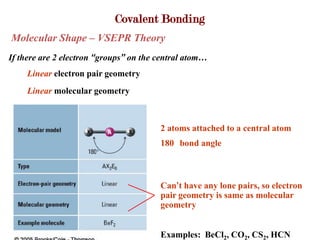
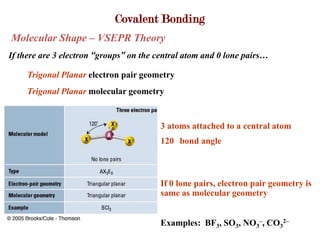
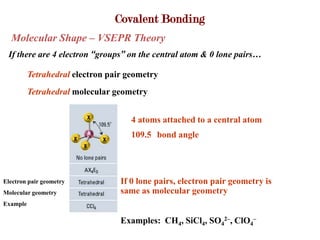
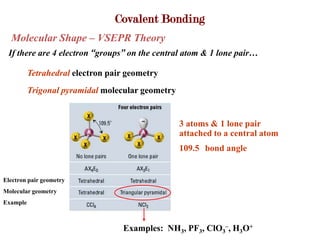
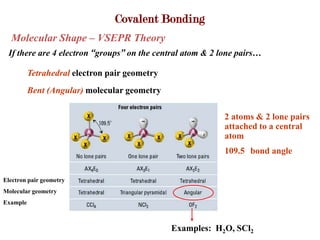
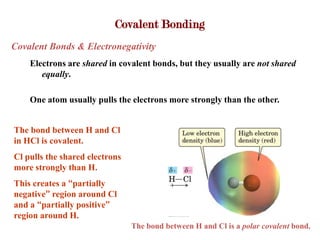
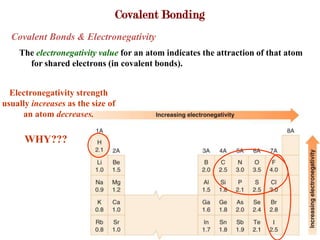
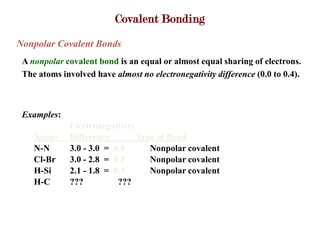
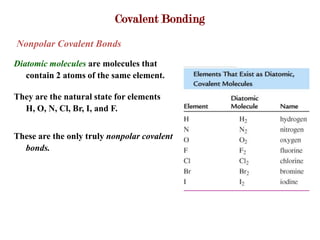
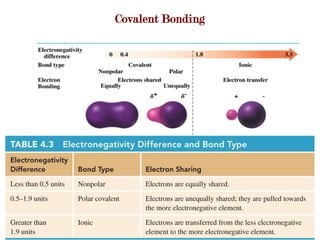
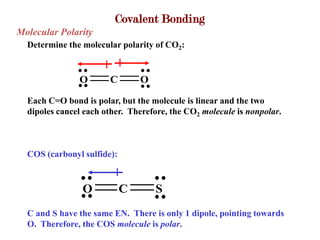
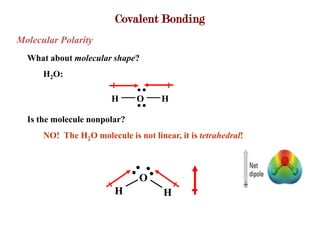
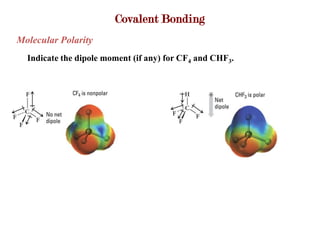
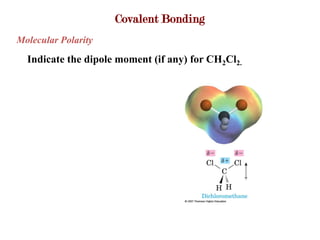
Covalent bonds form when atoms share electrons to complete their outer electron shells. Covalent compounds are typically made of nonmetal atoms. Binary covalent compounds contain only two elements. Their names follow specific rules based on element position in the periodic table. Molecular shape is determined by VSEPR theory, which predicts the geometry that minimizes electron pair repulsions. Polar covalent bonds result from unequal electron sharing between atoms of different electronegativity. Molecular polarity depends on both bond polarity and molecular geometry.