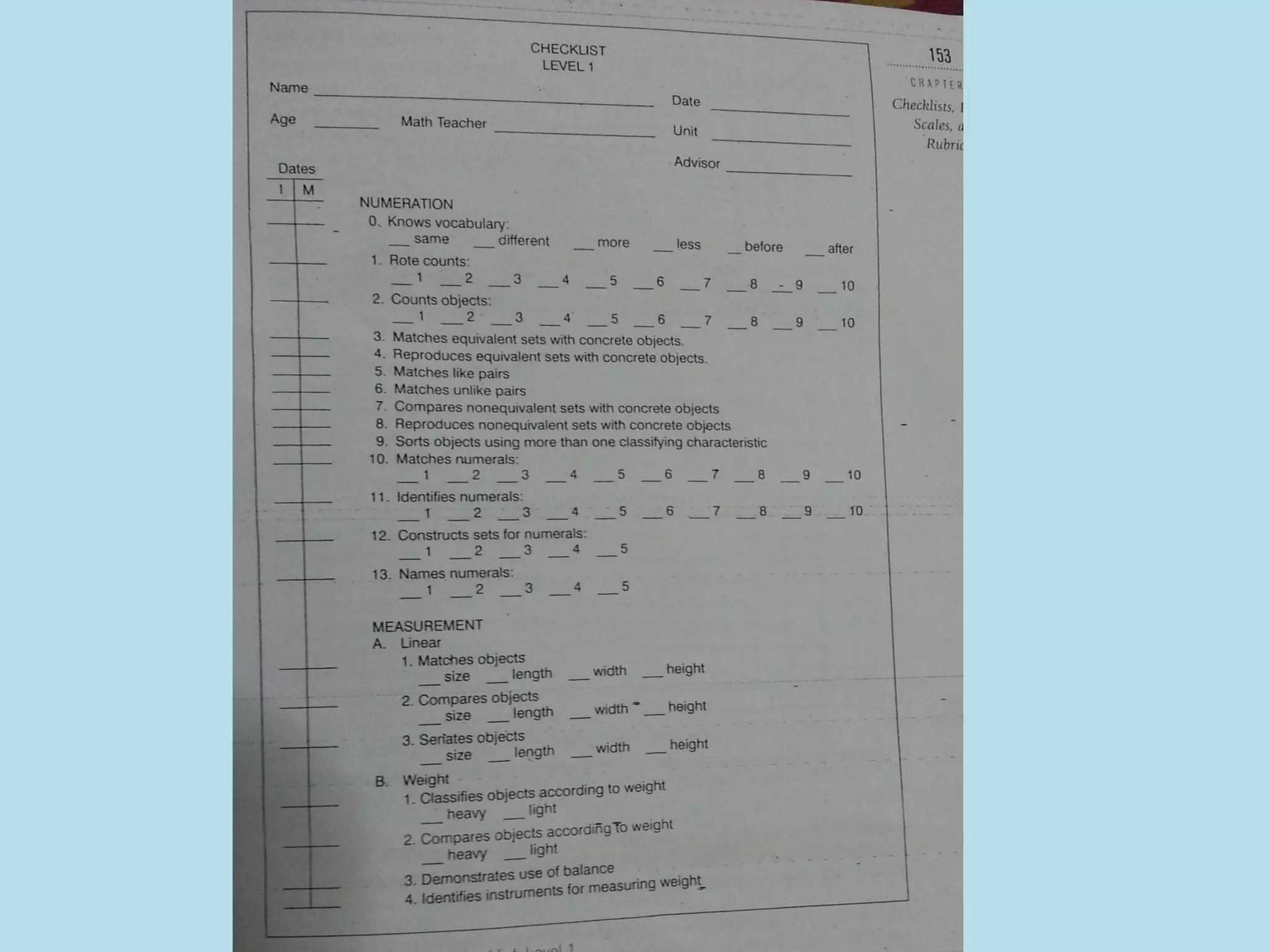
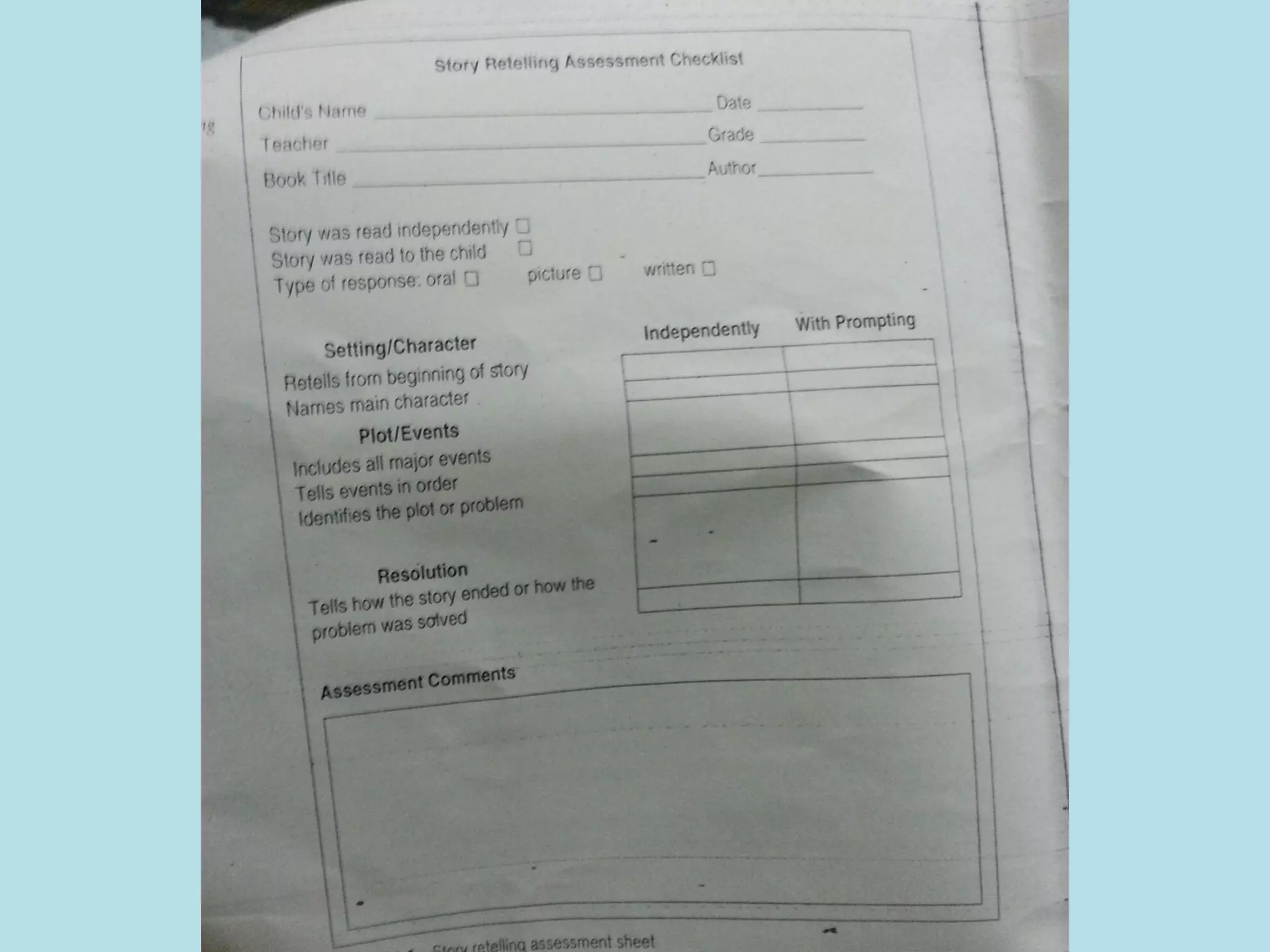
This document discusses checklists, their purposes, uses, and design. Checklists are made up of learning objectives or developmental indicators. They are used to understand development, provide a framework for curriculum, and assess learning. Checklists for infants/toddlers track physical, cognitive, and social development, while those for older children focus more on academics. Checklists can also assess children with delays. Well-designed checklists clearly identify skills, list behaviors separately, organize items by difficulty, and provide a method for recording results.