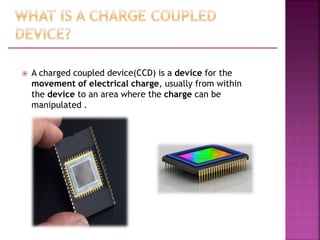
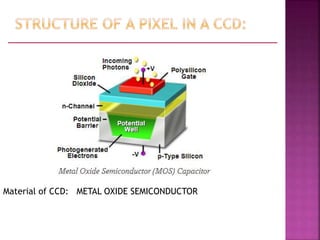
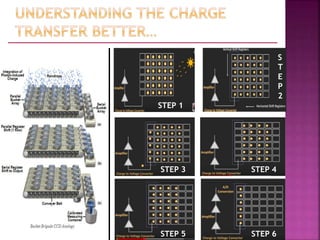
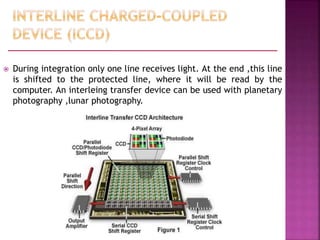
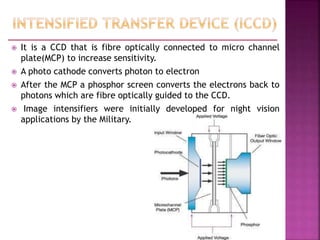
A Charged Coupled Device (CCD) is an electronic component used for converting light into electrical charge, structured in pixels, and primarily utilized in digital cameras and imaging devices. The four key stages of image generation in a CCD include charge generation, storage, transfer, and measurement, while various types of CCDs such as interline and full frame cater to specific photographic needs. CCDs offer advantages like high sensitivity and image quality but are also costly, power-hungry, and can suffer from issues like vertical smear under bright light.