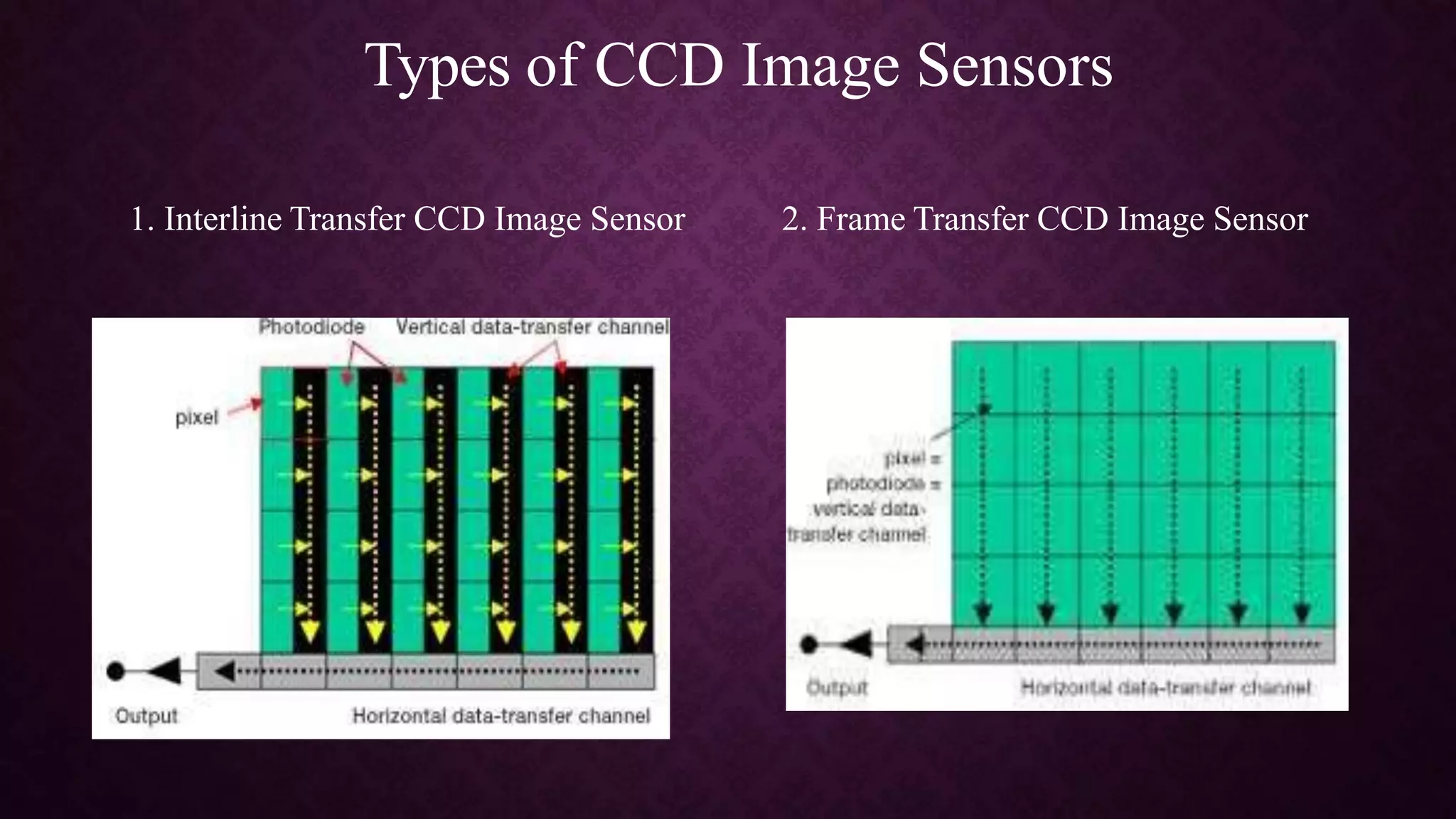
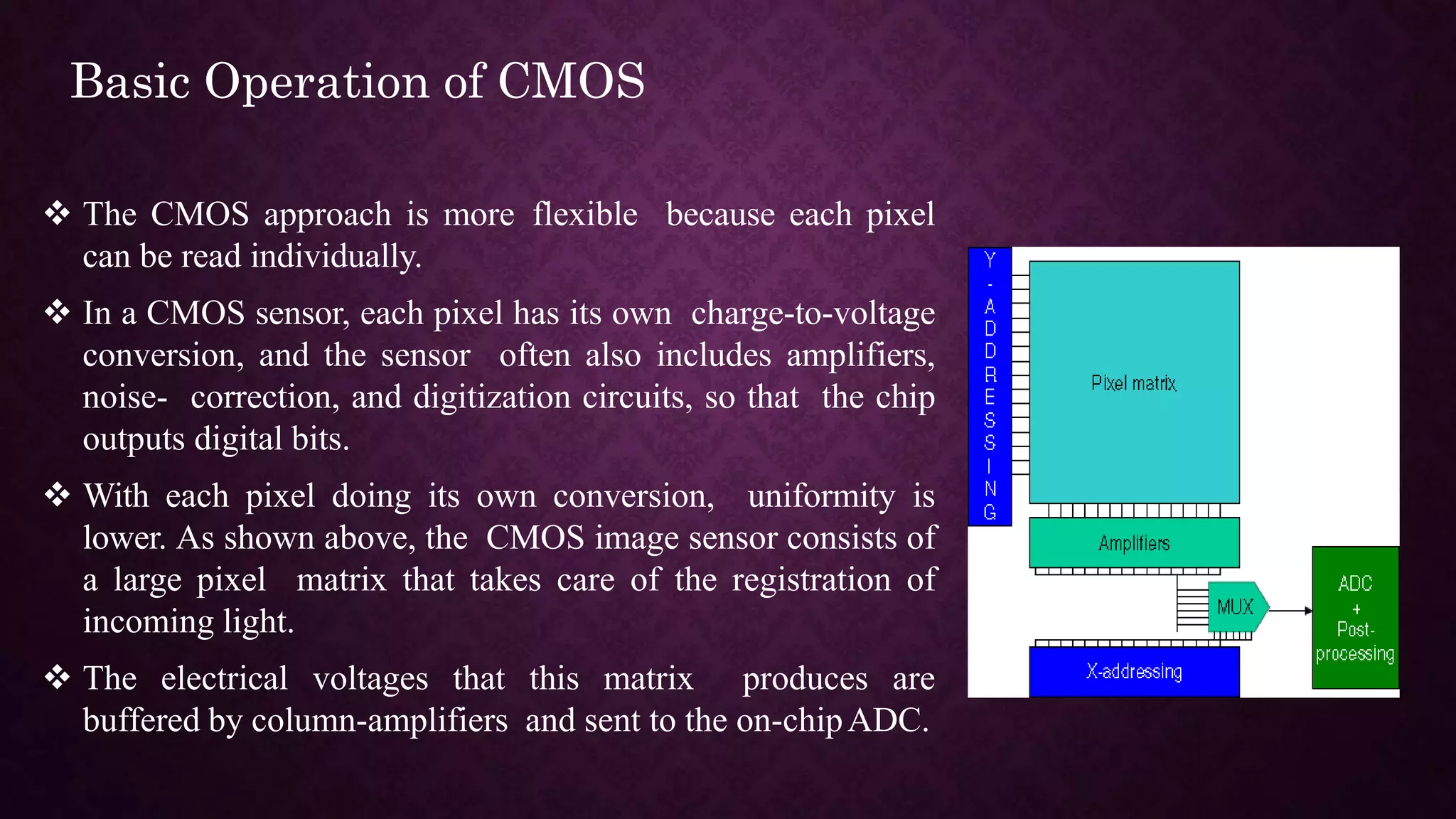
This document discusses CMOS image sensors. It begins by defining an image sensor as a device that converts an optical image into an electrical signal. It then explains the basic operation of CCD and CMOS image sensors, describing how each type works at a pixel level. The document concludes by comparing CCD and CMOS technologies, noting advantages of CMOS such as lower cost and power consumption, while CCD provides better image quality for some applications.