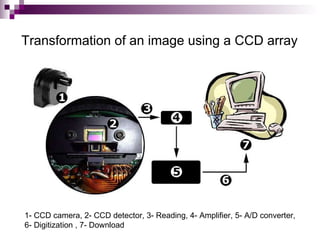
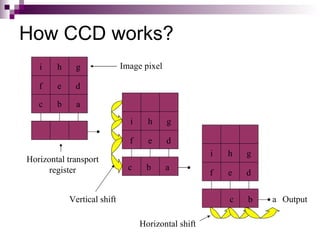
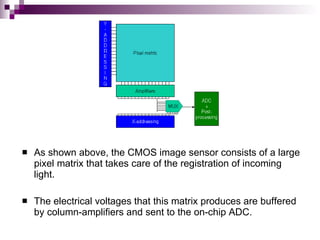
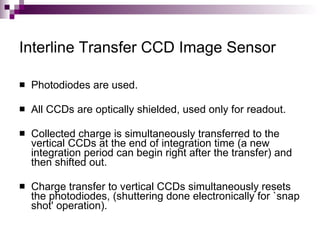
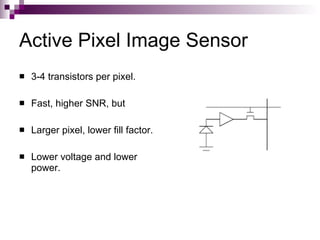
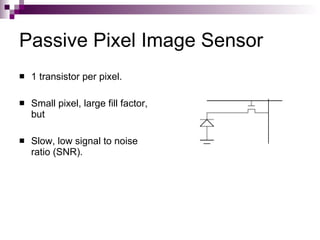
Image sensors contain millions of light-sensitive photosites that record brightness levels and allow digital cameras to capture images. The two main types are CCD and CMOS sensors. CCD sensors transfer the electric charge from each photosite to be converted to a digital signal, while CMOS sensors have transistors at each pixel to individually convert charge to voltage. Both have advantages like CMOS integrating additional processing circuits while CCDs have higher sensitivity. Image sensors are now widely used in applications like digital cameras, camcorders, biometrics, and more due to their small size and low power consumption compared to film.