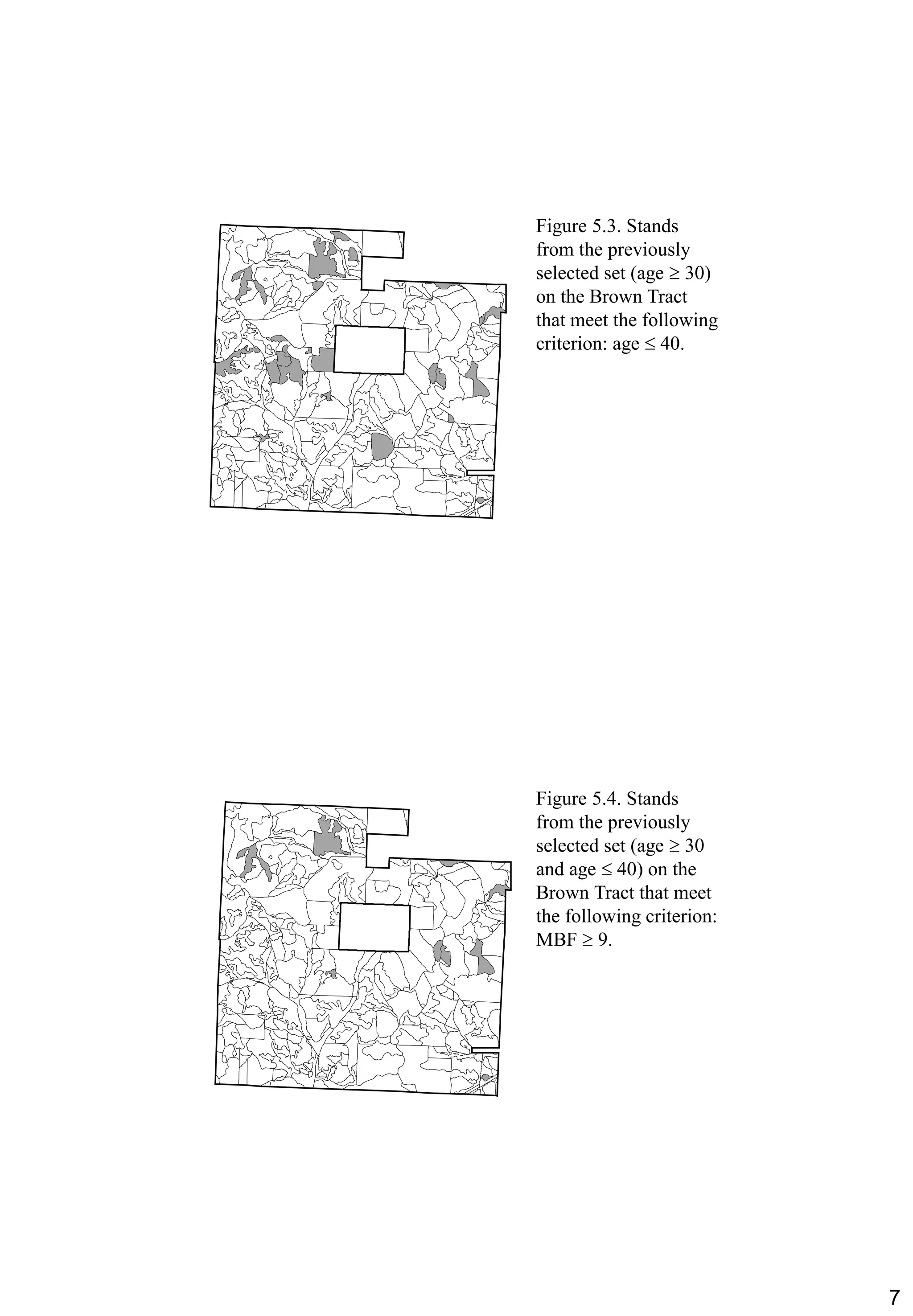
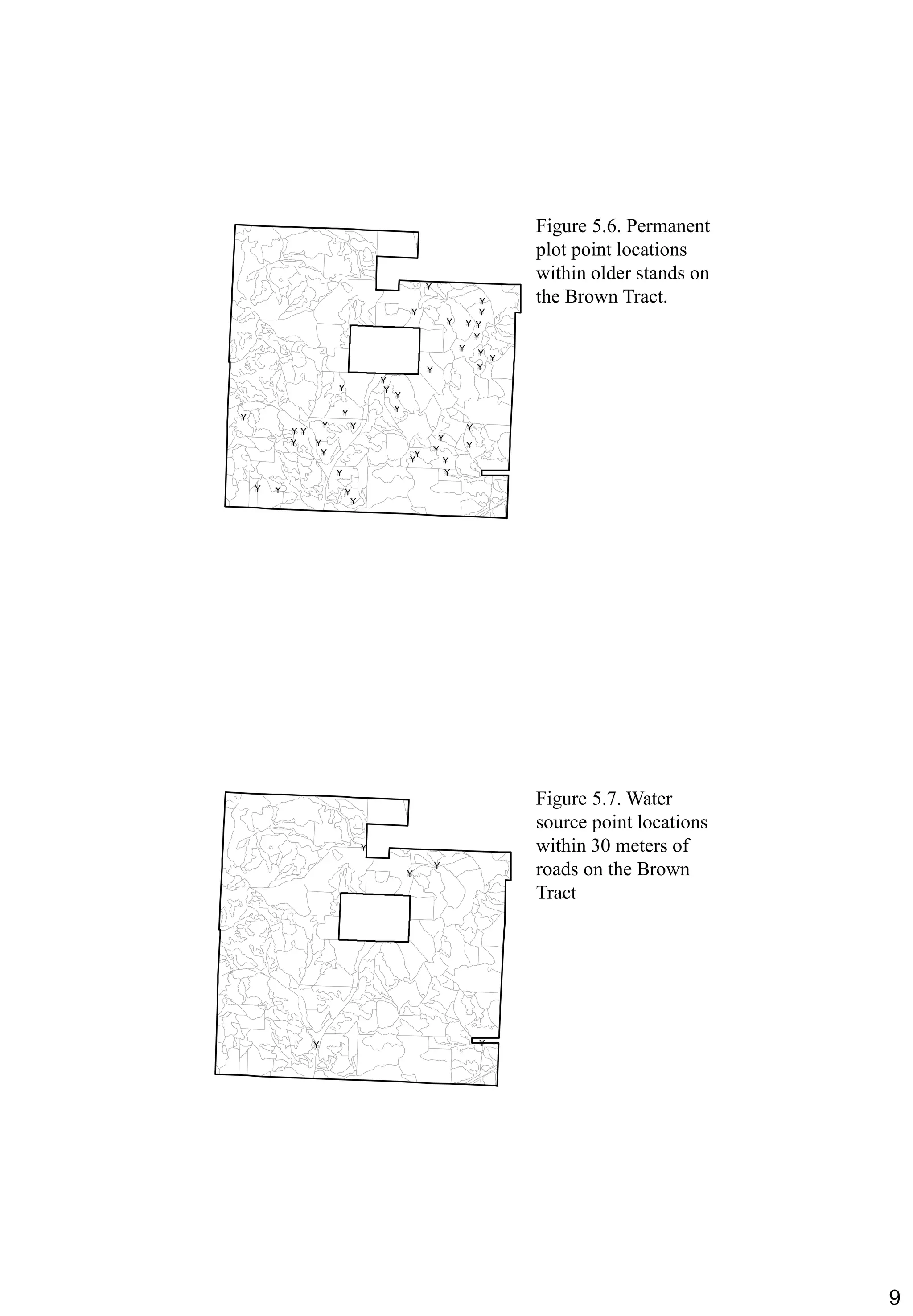
Chapter 5 of the book discusses methods for selecting landscape features from a GIS database, including manual and automatic selections based on specific criteria. It explains the concept of queries used to retrieve information about resources and highlights potential issues with query operations, such as syntax errors. The chapter also includes practical examples and considerations for effective feature selection and querying.