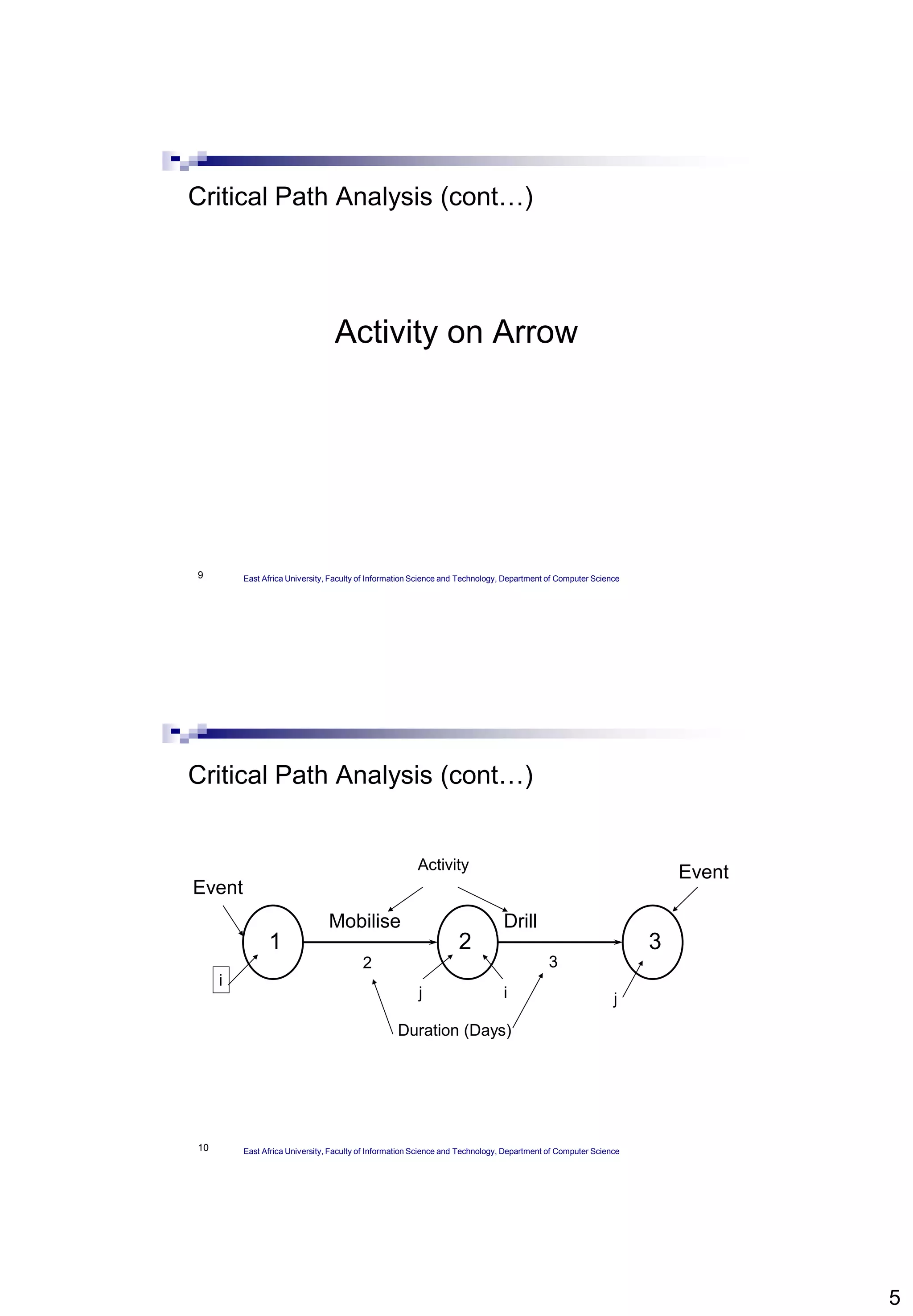
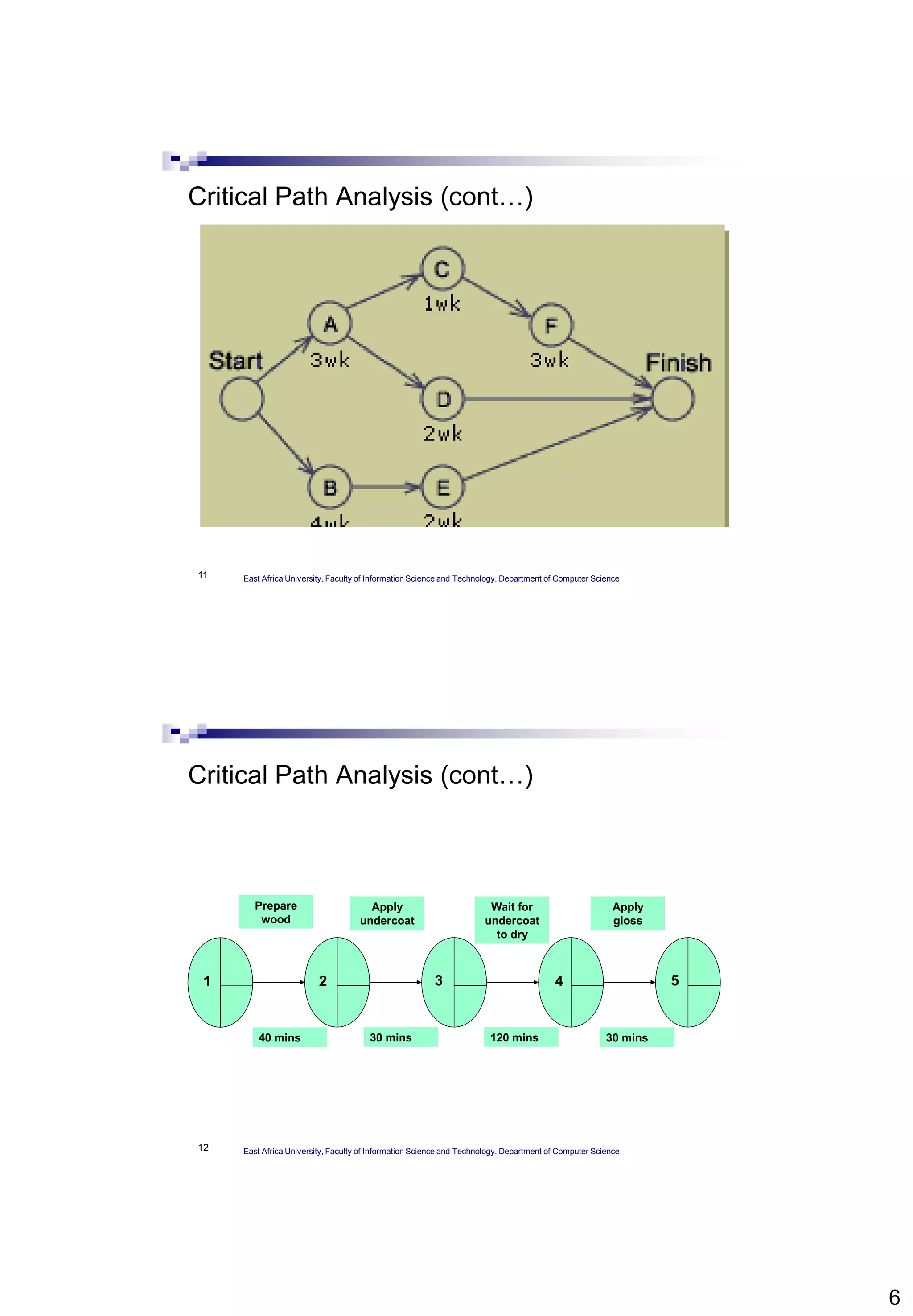
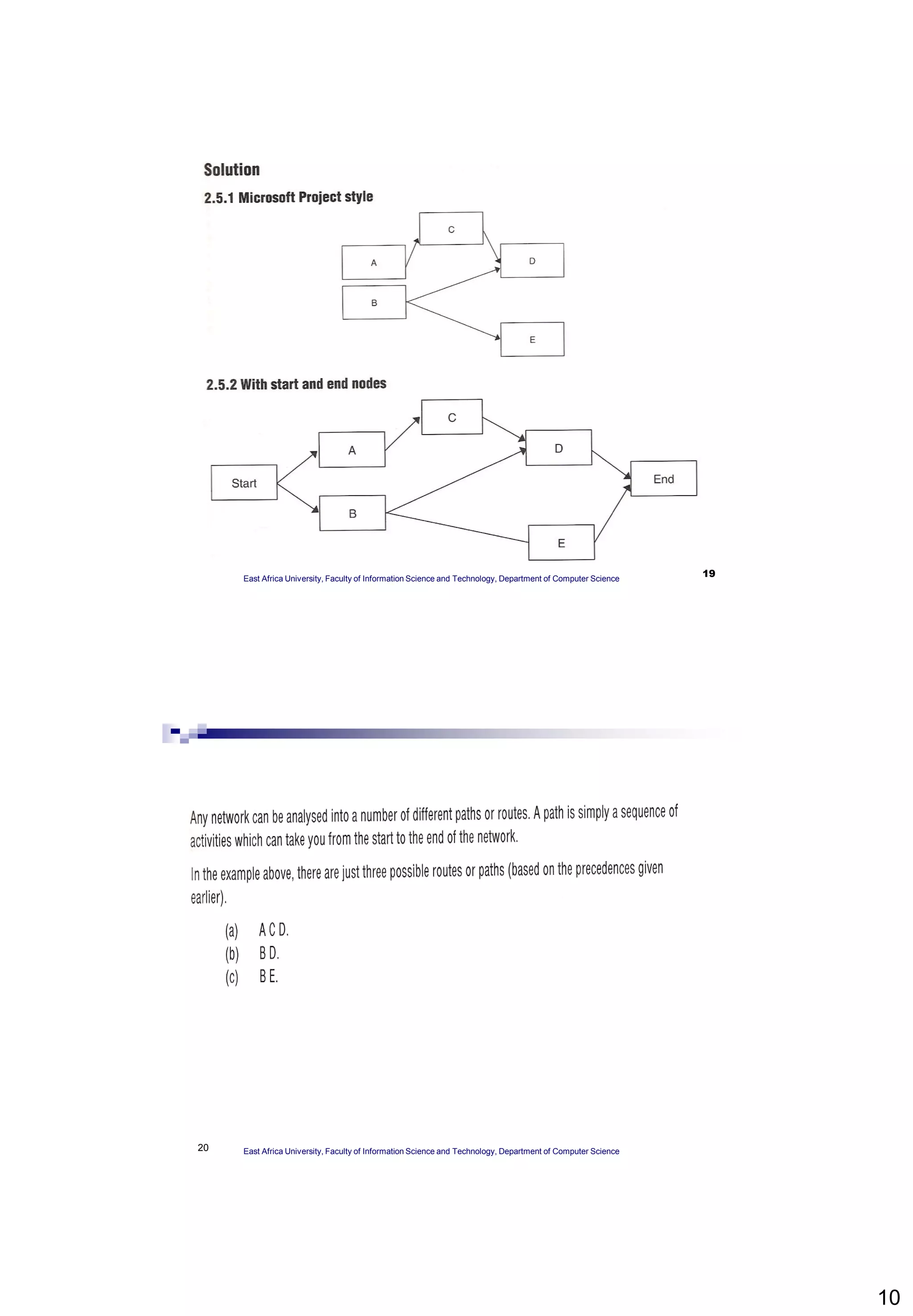
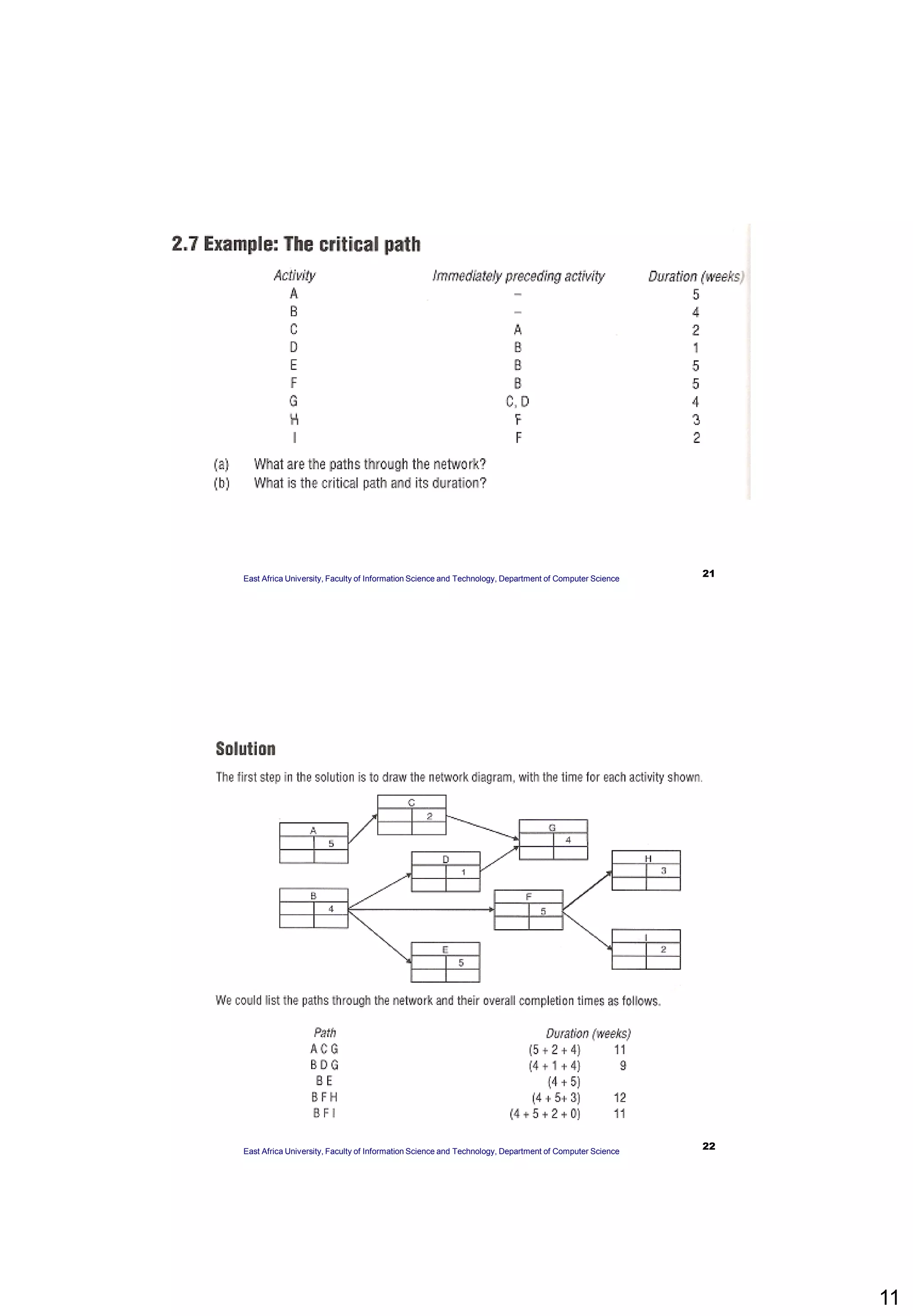
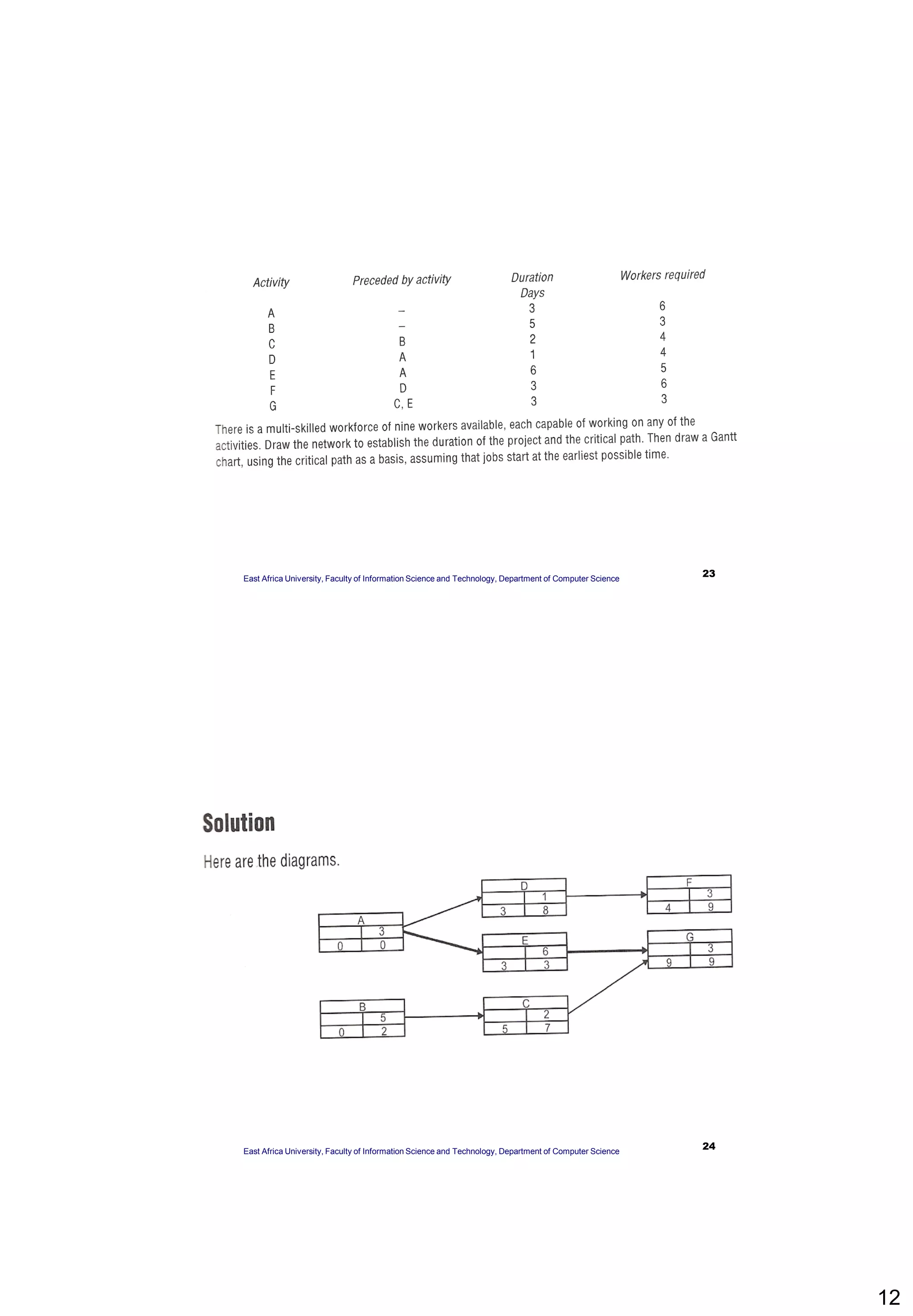
The document provides an overview of Critical Path Analysis (CPA), a project management tool that helps identify the sequence and timing of tasks within a project to optimize completion time. It explains how CPA is applied, including the calculation of early and late start/finish dates, and emphasizes the significance of the critical path where delays directly impact the project completion. Additionally, it outlines the concepts of float, critical activities, and the need for task scheduling and resource allocation.