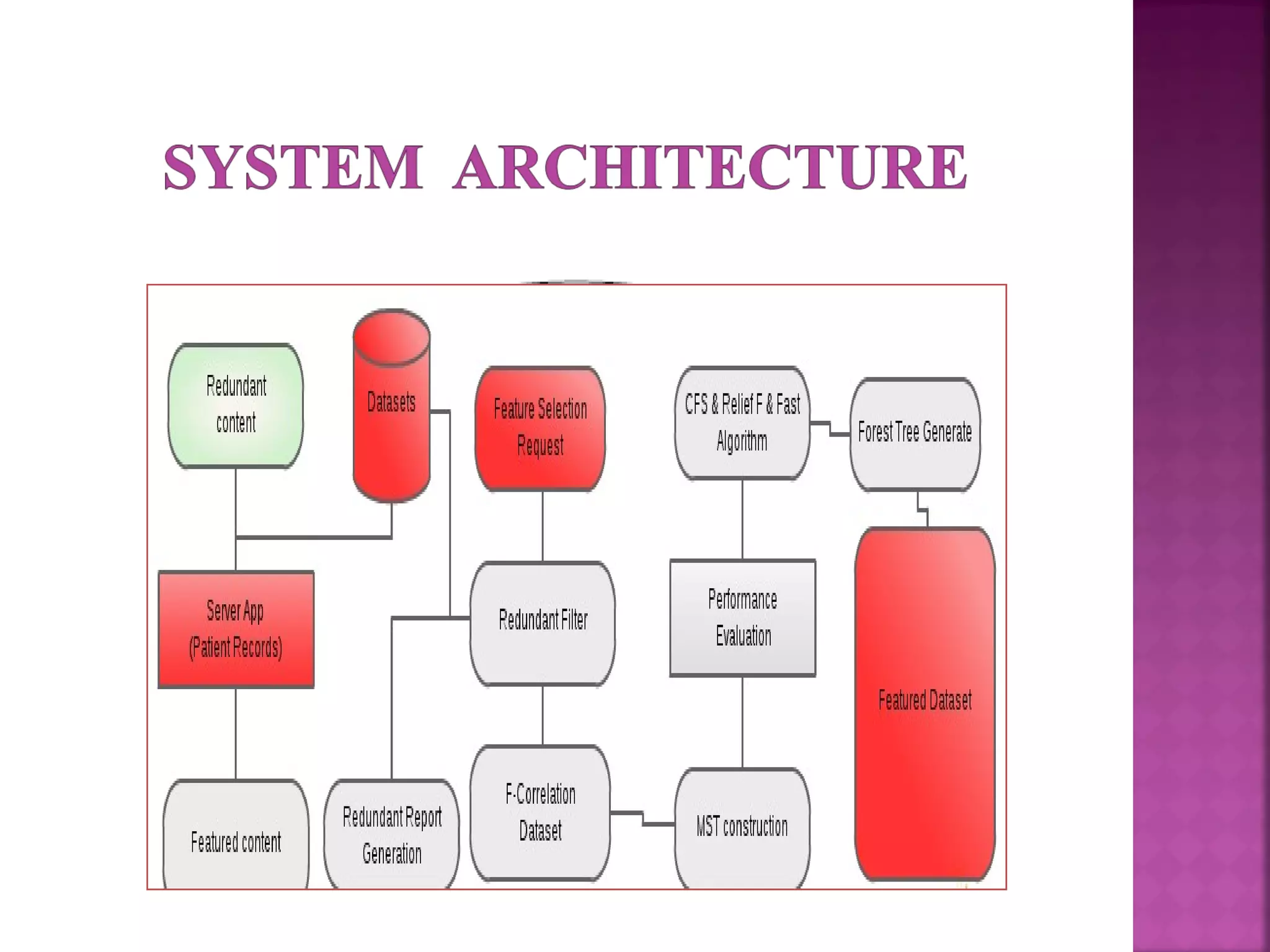
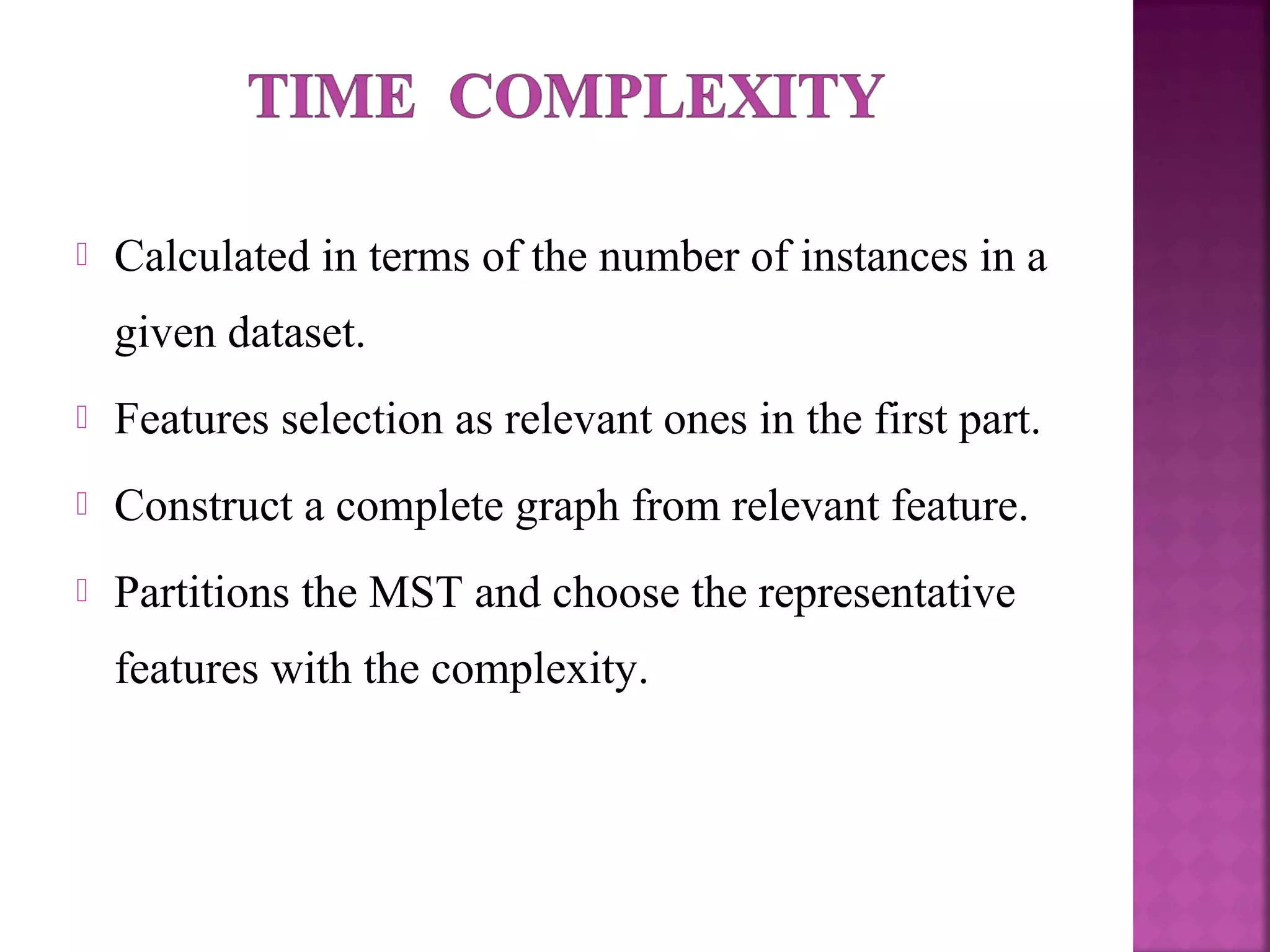
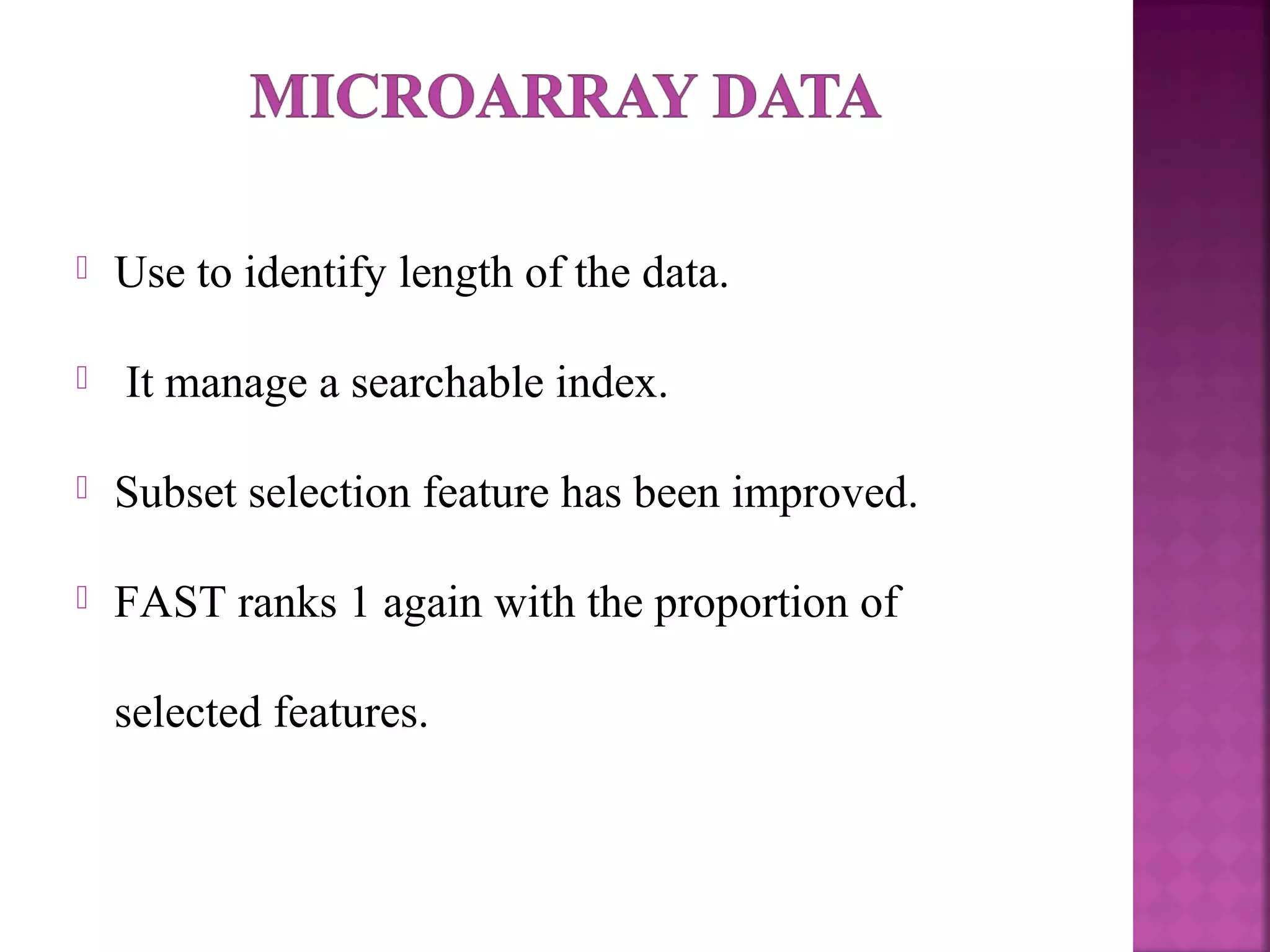
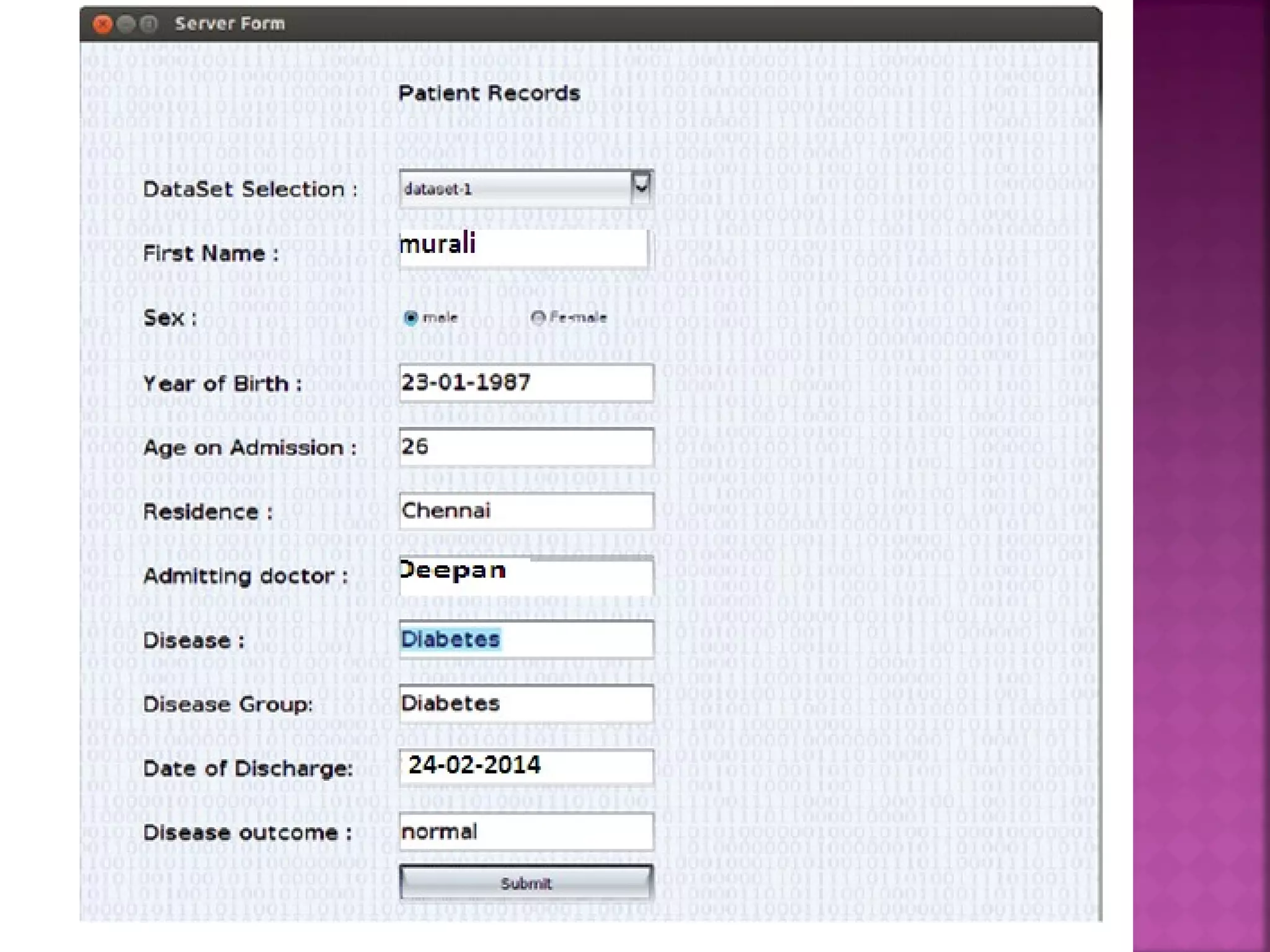
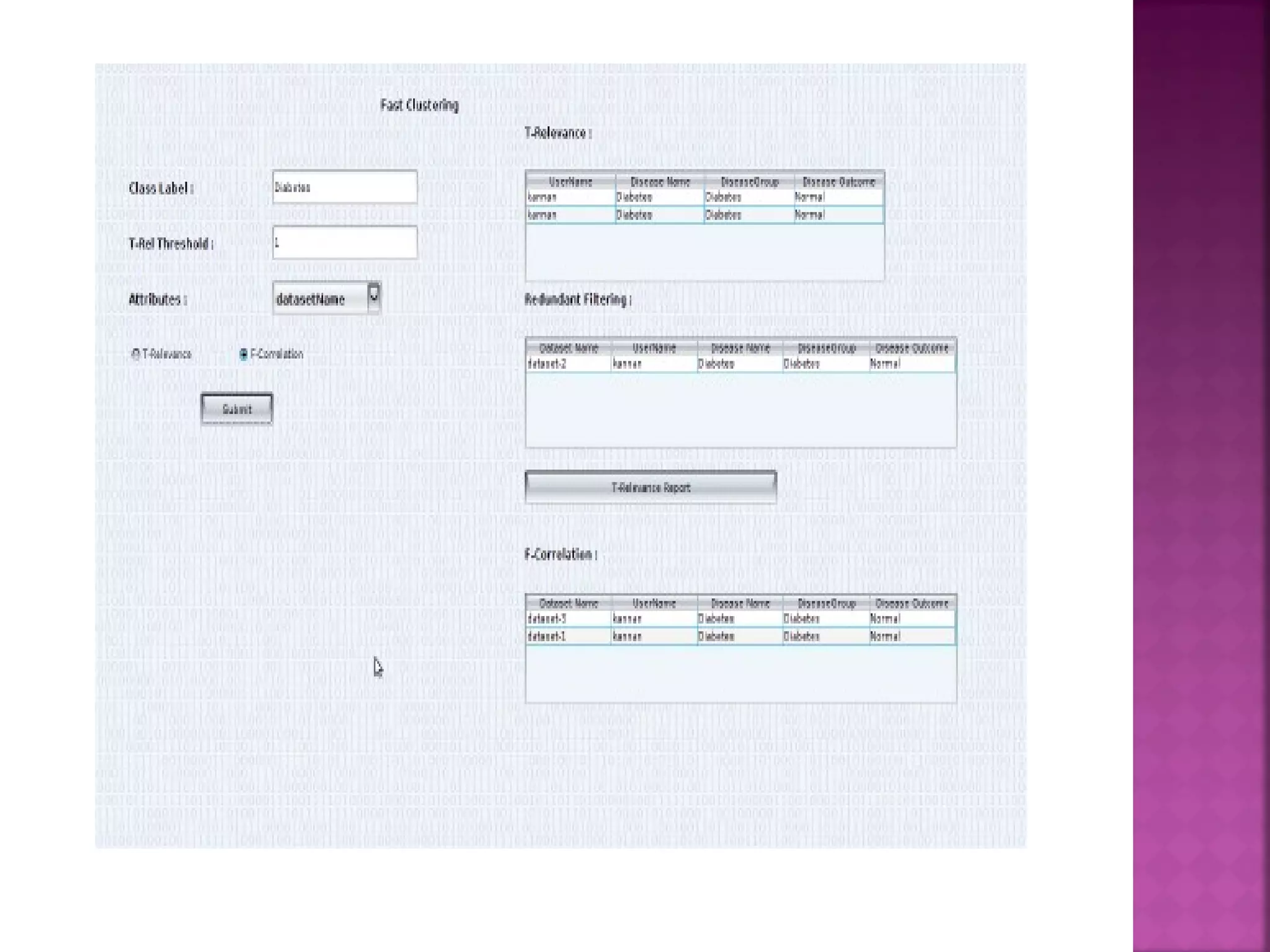
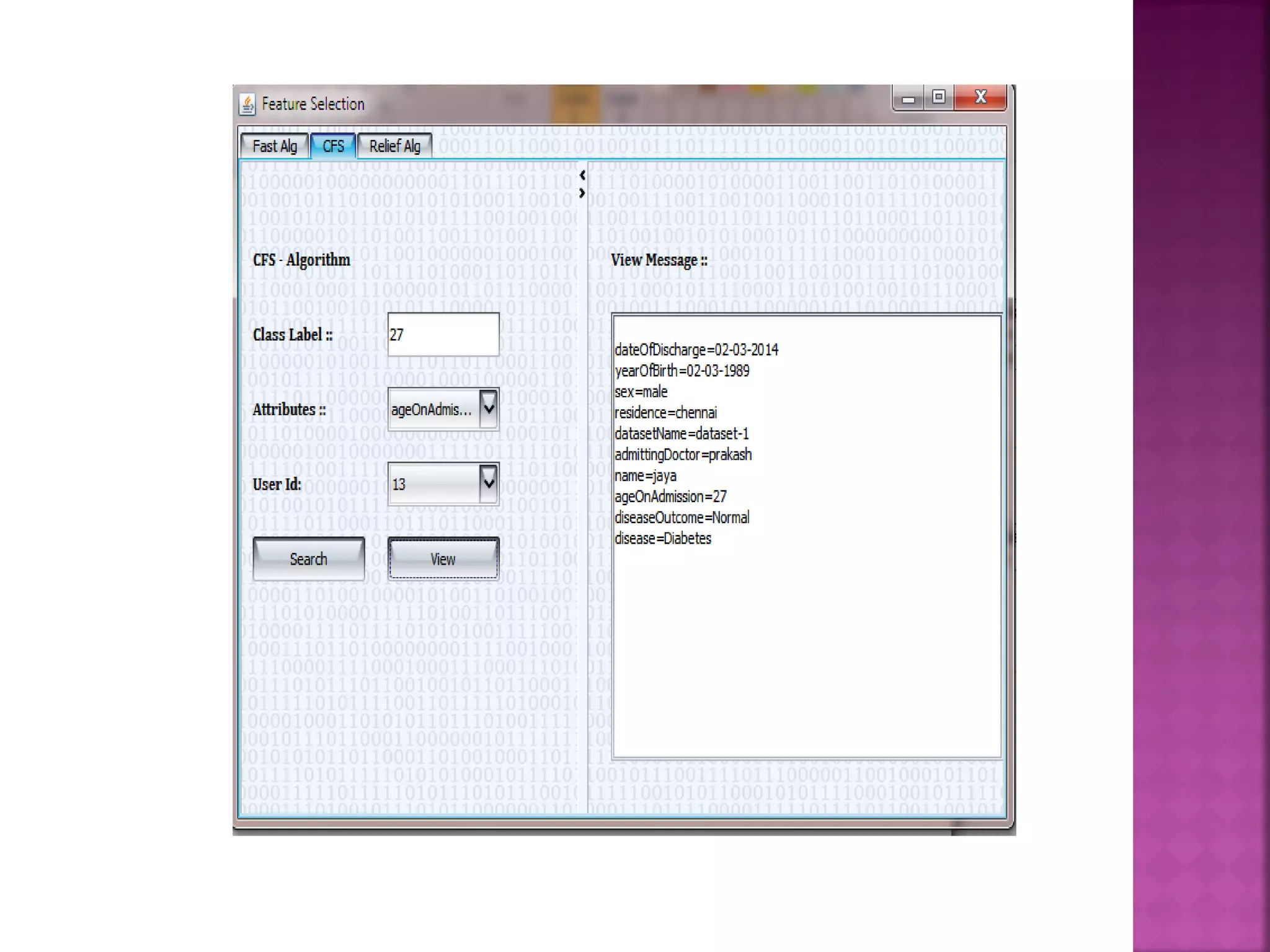
The document presents a feature selection algorithm called FAST (Fast clustering-based feature selection algorithm). FAST uses minimum spanning trees and clustering to identify relevant feature subsets while removing irrelevant and redundant features. This achieves dimensionality reduction and improves the accuracy of learning algorithms. The algorithm was experimentally evaluated on datasets with over 10,000 features and was shown to outperform other feature selection methods in terms of time complexity and selected feature proportions.











![ [1] H. Almuallim and T.G. Dietterich, (1994), ““Algorithms for
Identifying Relevant Features,” Artificial Intelligence, vol. 69,
nos. 1/2, pp. 279-305.
[2] L.D. Baker and A.K. McCallum, (1998), “ Learning boolean
concepts in the presence of many irrelevant features,” Proc. 21st
Ann. Int’l ACM SIGIR Conf. Research and Development in
information Retrieval, pp. 96-103.
[3] Arauzo-Azofra, J.M. Benitez, and J.L. Castro, (2004), “A
Feature Set Measure Based on Relief,” Proc. Fifth Int’l Conf.
Recent Advances in Soft.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/techpres1ppt-150210192912-conversion-gate02/75/High-dimesional-data-FAST-clustering-ALG-PPT-20-2048.jpg)
