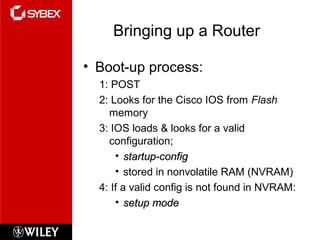
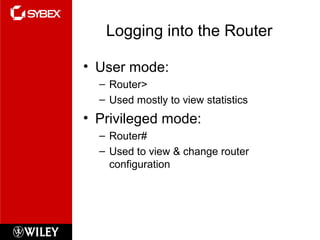
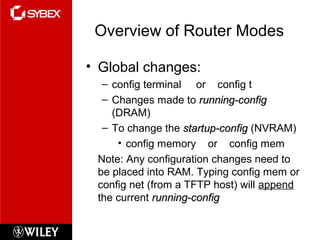
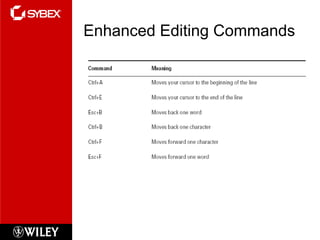
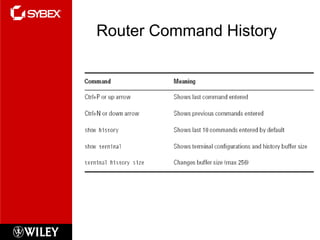
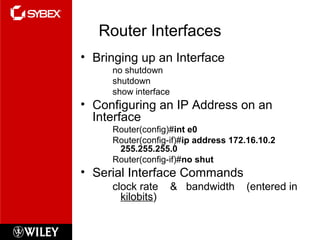
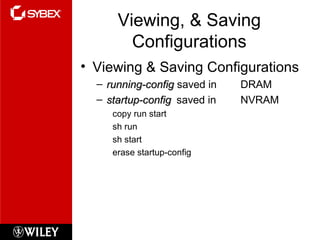
The document discusses Cisco router configuration and administration. It covers topics like the Cisco IOS, connecting to routers, router modes, editing features, administrative functions like hostnames, banners, and passwords, interface configuration, and verifying configurations. Administrative functions allow configuration of items like hostnames, banners to display messages, and passwords to control access. The Cisco IOS is loaded during boot-up and configurations can be viewed and saved.