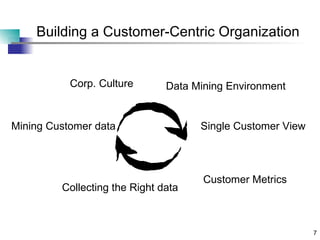
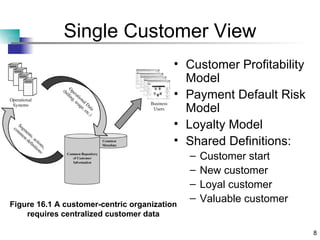
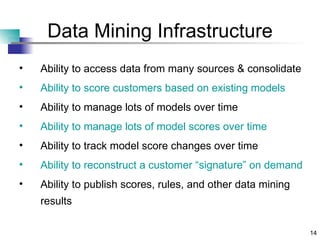
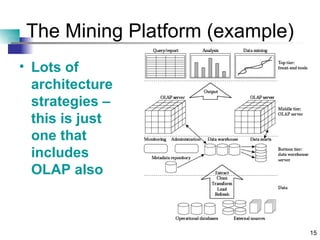
Chapter 16 discusses building an ideal customer-centric organization and data mining environment. It emphasizes establishing a single customer view across the enterprise, collecting the right customer data, and creating a dedicated data mining group and infrastructure. The ideal environment requires consolidating customer data from different sources, being a learning organization that values progress, and making data available for analysis across departments like marketing and sales. However, establishing all of these ideal components at once is challenging.