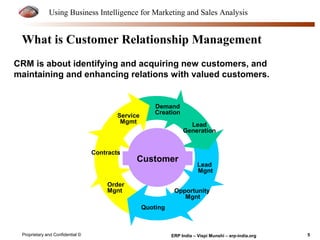
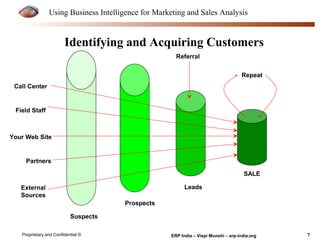
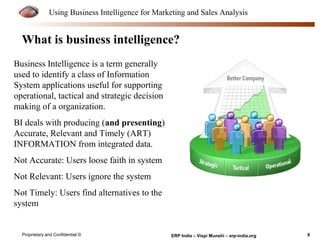
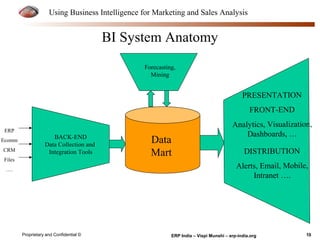
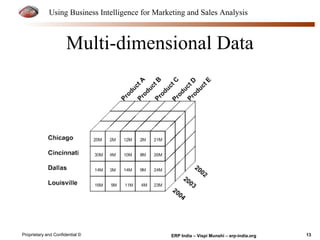
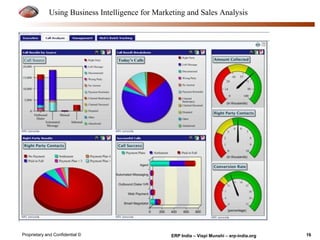
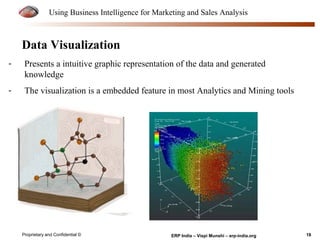
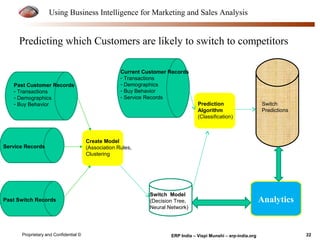
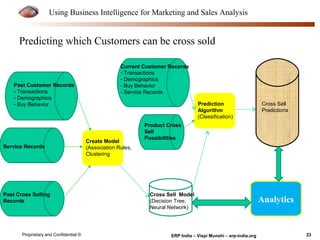
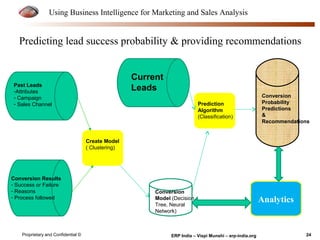
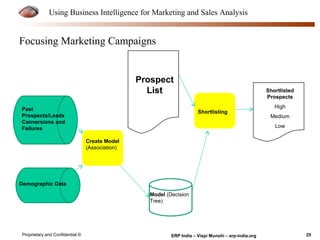
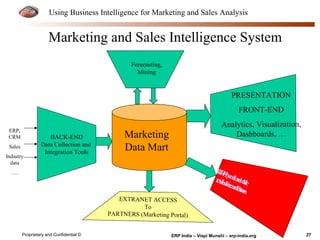
The document provides an overview of using business intelligence (BI) for enhancing marketing and sales analysis, including definitions and applications of BI, data analytics, and predictive analytics. It outlines key marketing and sales functions, the anatomy of a BI system, and various tools and techniques for data mining and visualization. Examples demonstrate how BI can be used to predict customer behavior and optimize marketing efforts, while also discussing metrics for measuring campaign and sales performance.