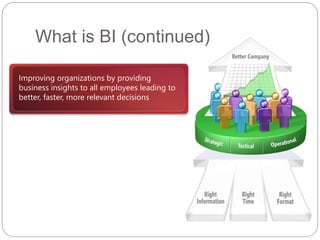
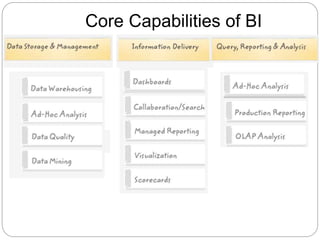
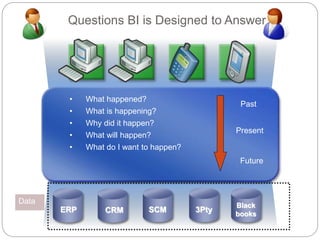
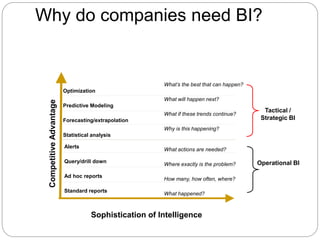
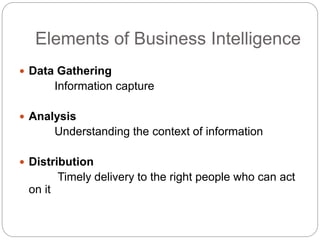
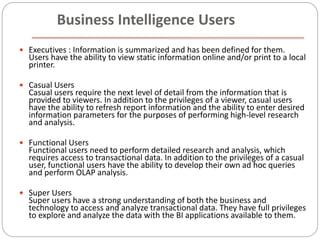
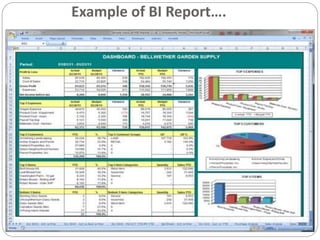
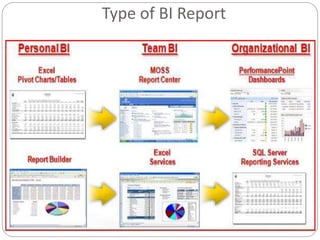
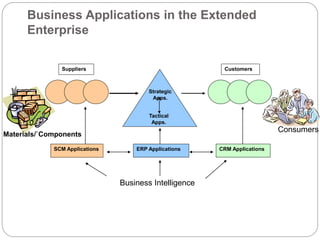
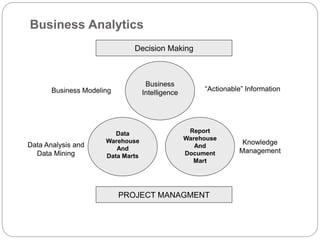
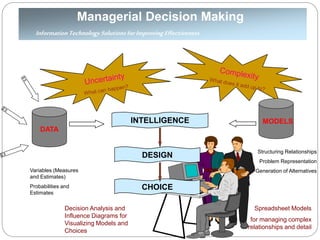
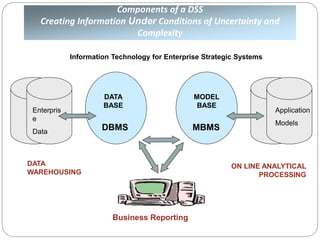
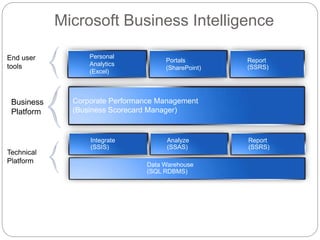
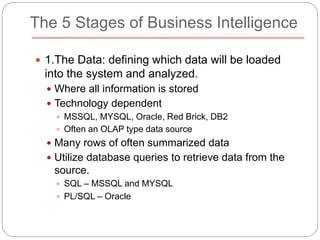
The document provides an overview of Business Intelligence (BI), detailing its definition, core capabilities, and the benefits it offers to organizations, including improved decision-making and operational efficiency. It outlines the five stages of BI, from data collection to presentation, emphasizing the importance of accurate and timely information. Additionally, it discusses the roles of different BI users and the significance of analytics in transforming raw data into actionable insights.