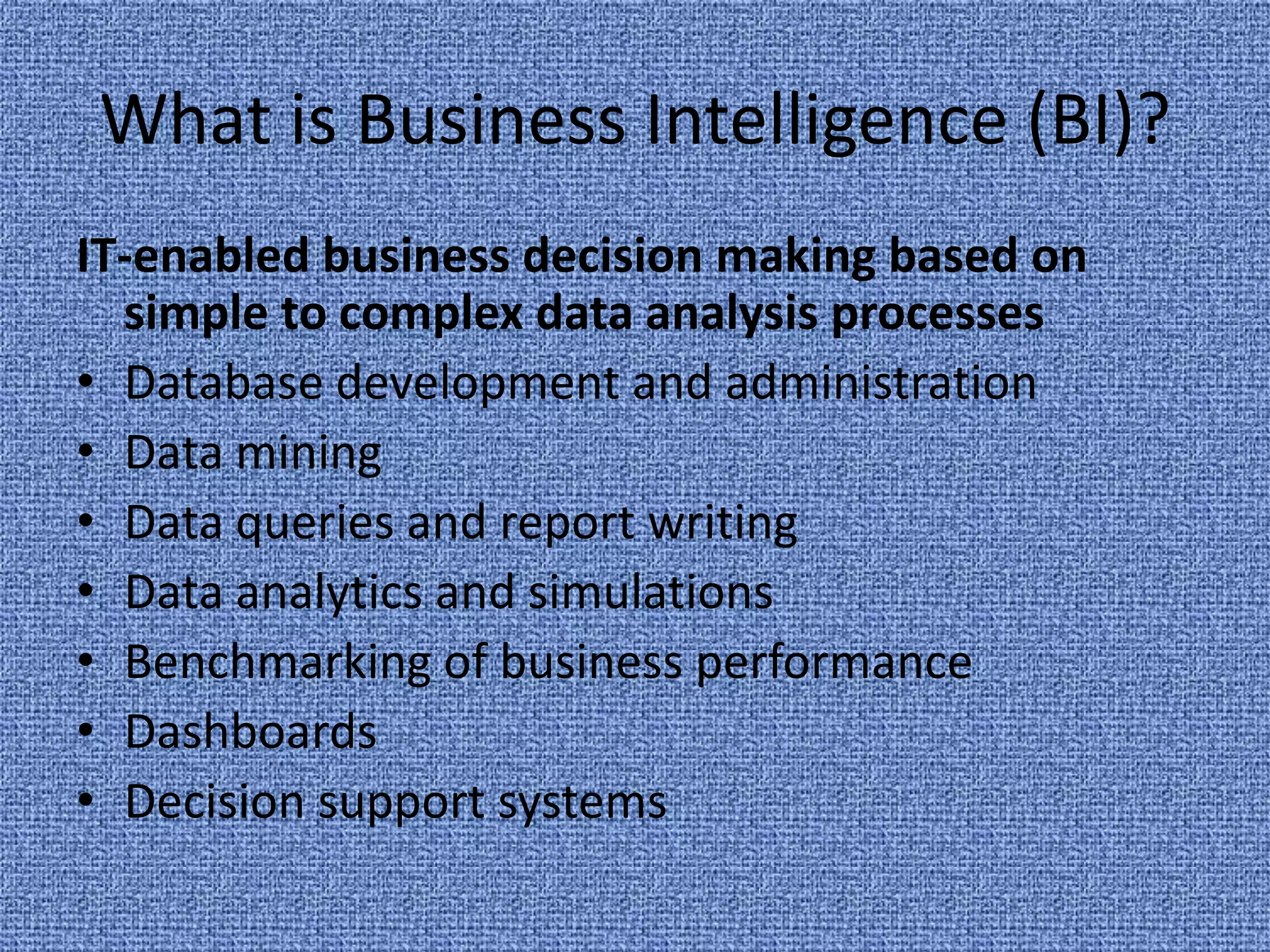
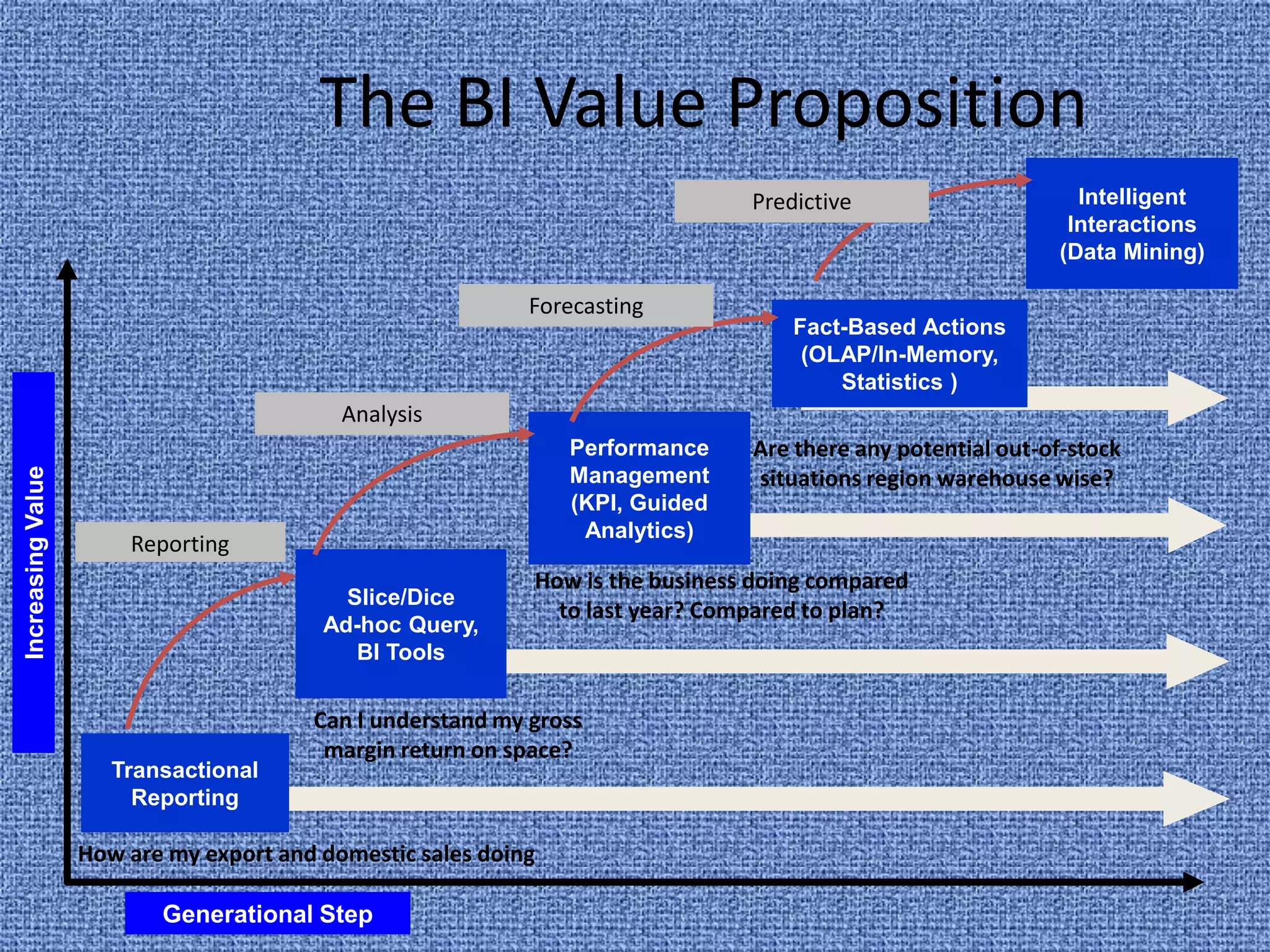
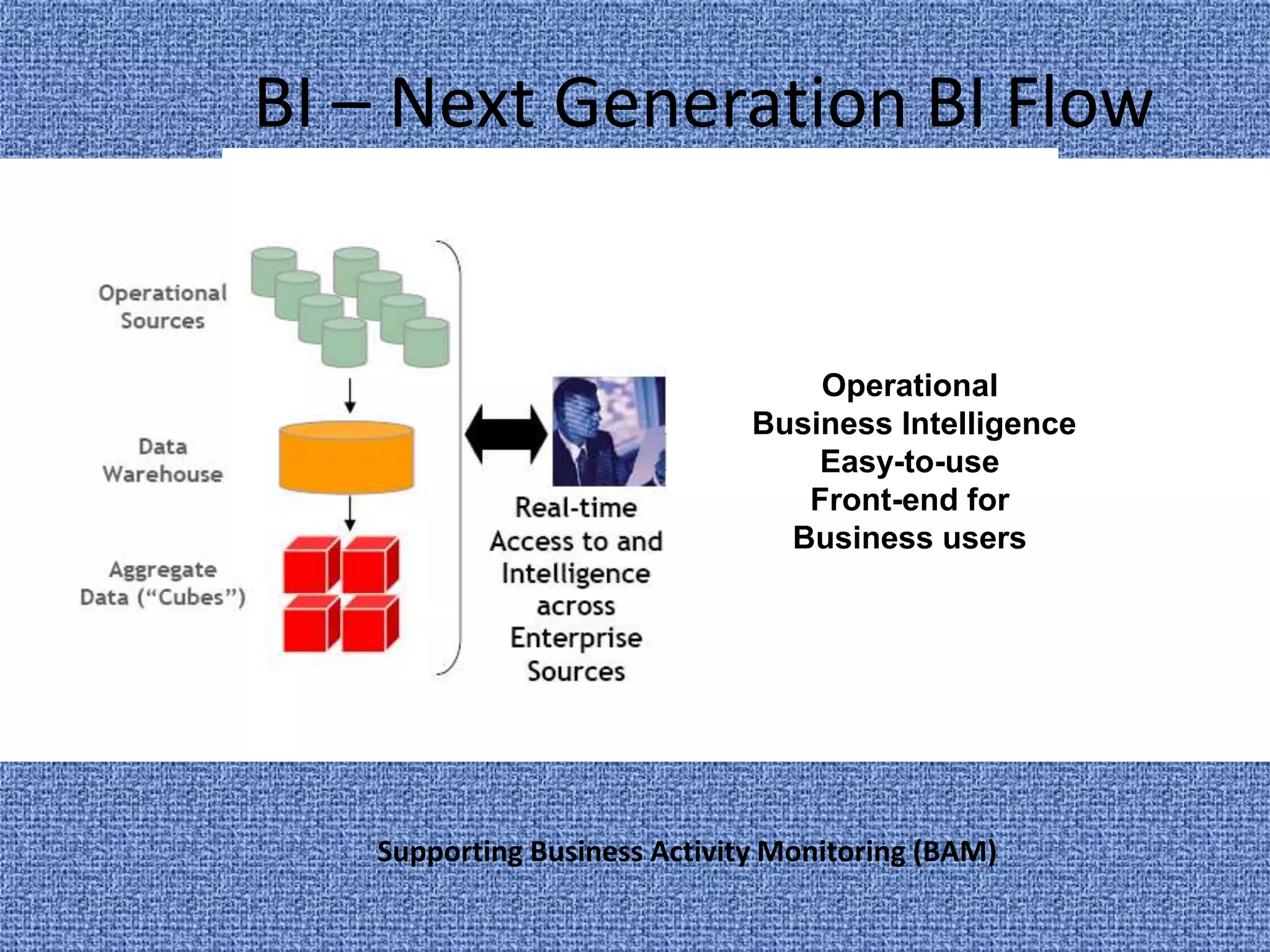
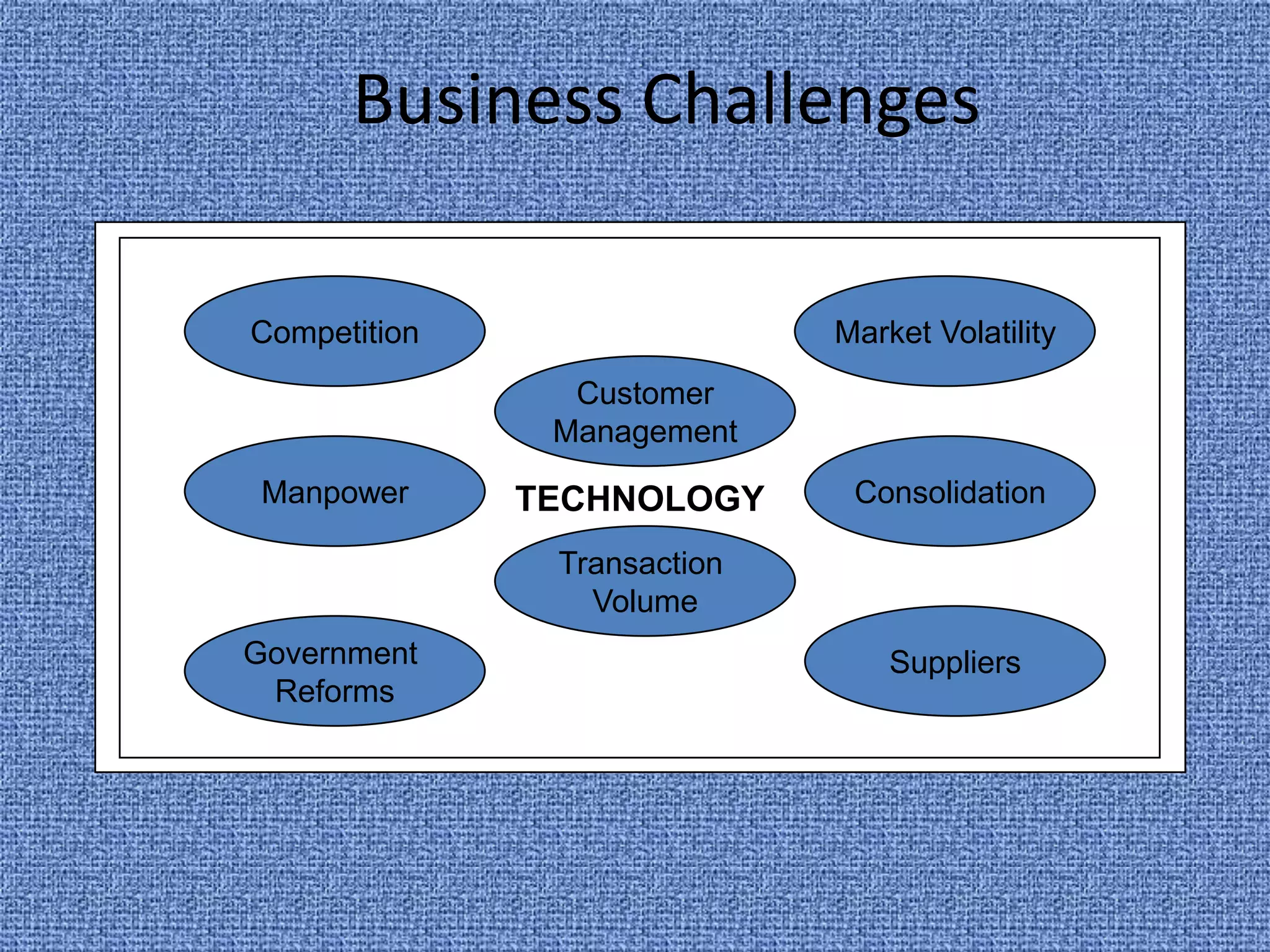
Business intelligence (BI) refers to technologies and applications used to analyze data and present information to help make business decisions. BI evolved from systems in the 1970s and 1980s that provided executives with key performance data. It grew to include data mining, querying, reporting, analytics and more. BI helps businesses make more informed decisions through competitive analysis, customer behavior analysis, targeted strategies, scenario planning, and optimization. Real-time BI that provides constantly updated information is an emerging trend to meet the needs of businesses that want timely data. However, integrating disparate data sources and accounting for constantly changing business structures makes true real-time BI challenging to achieve.




![objectivesIdentify market opportunitiesKnow where market share is unsatisfactoryBetter understand their profitability driversIdentify unacceptable cost areasGain an accurate view of sale and/or distribution costs, per channel, per customer, per transaction, per dayRecognize business areas of high performanceIdentify the key performance indicators [KPI's] to use to measure capabilityCalculate sales commissions, number of sales closed, highlight good and poor performersTrack whether strategies for certain markets or customers are working and driving business valueGet instant insight to the exact profit by company of each sale](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation2-110924221040-phpapp01/75/bi-8-2048.jpg)