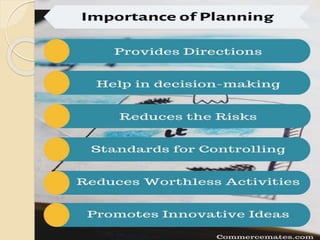
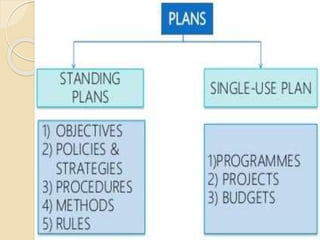
The document discusses the concept and importance of planning in management, highlighting its role in setting objectives, decision-making, and shaping organizational direction. It outlines the characteristics of effective planning, its benefits, limitations, and various types of plans including single-use and standing plans. Additionally, the document elaborates on the planning process, which involves setting objectives, developing premises, identifying and evaluating alternatives, and implementing plans to achieve organizational goals.