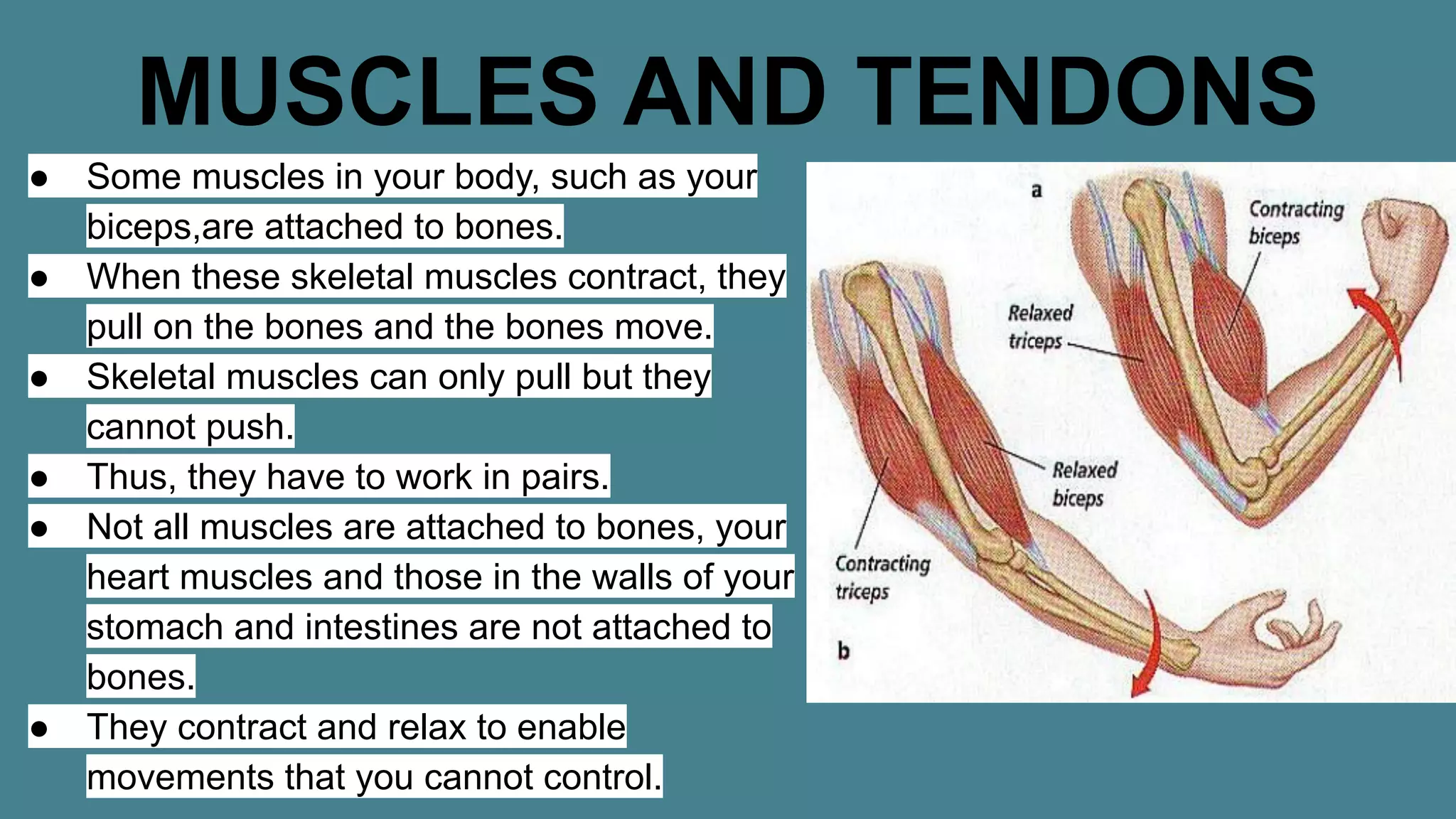
The document discusses the human skeleton, which consists of 206 bones in adults and provides structure, support, and protection for vital organs. It also covers types of joints and their functions, as well as the role of muscles and tendons in enabling movement. Notably, it explains how muscles attach to bones via tendons, with the Achilles tendon being highlighted for its significance.