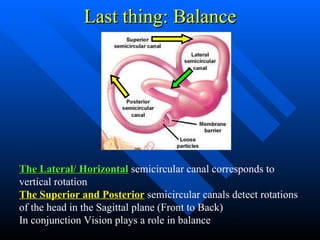
This lecture discusses the anatomy and function of the ear, highlighting critical information about auditory development in infants and the mechanics of hearing. It covers how sound waves travel through the ear structures, including the tympanic membrane and cochlea, ultimately being interpreted by the brain. Additionally, it touches on balance and the protective responses of the ear to loud noises.





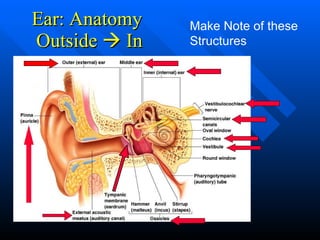
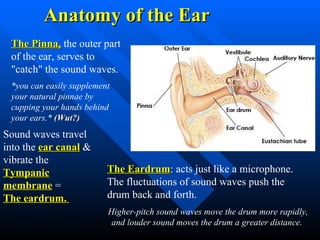
![Anatomy of the Ear The middle ear: The ossicles are the smallest bones in your body. *Don’t write this down* They include: The malleus : the hammer The incus : the anvil The stapes: the stirrup The cochlea: consists of 3 tubes (the membrane so thin we consider it 1 tube) coiled in the shape of a snail shell Endolymph (the fluid inside): stimulates the Auditory Nerve [Cranial Nerve VIII (8)] and the signal travels to the brain and is then interpreted as sound.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8lecture2-111220011430-phpapp02/85/Chapter-8-lecture-2-8-320.jpg)