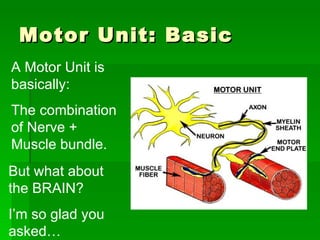
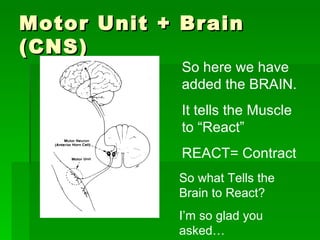
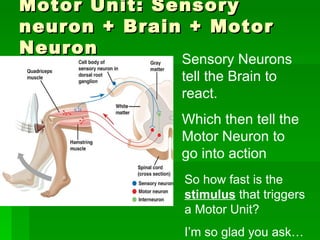
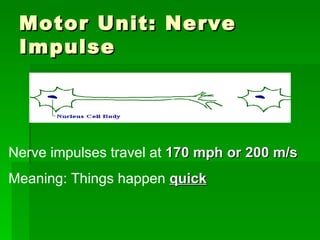
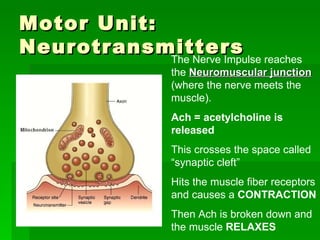
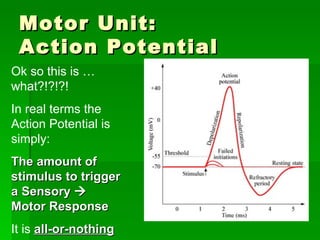
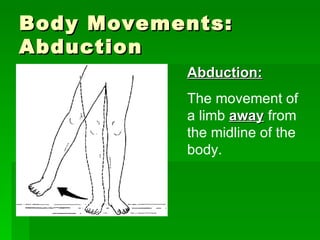
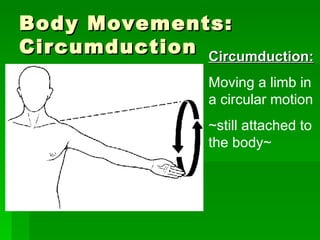
Chapter 6 discusses the muscular system, focusing on motor units, sensory and motor neurons, and their roles in muscle contraction and relaxation. It details the processes involved in muscle movements, including flexion, extension, rotation, adduction, abduction, and circumduction. The chapter emphasizes the importance of understanding nerve impulses and neurotransmitters in triggering muscular responses.