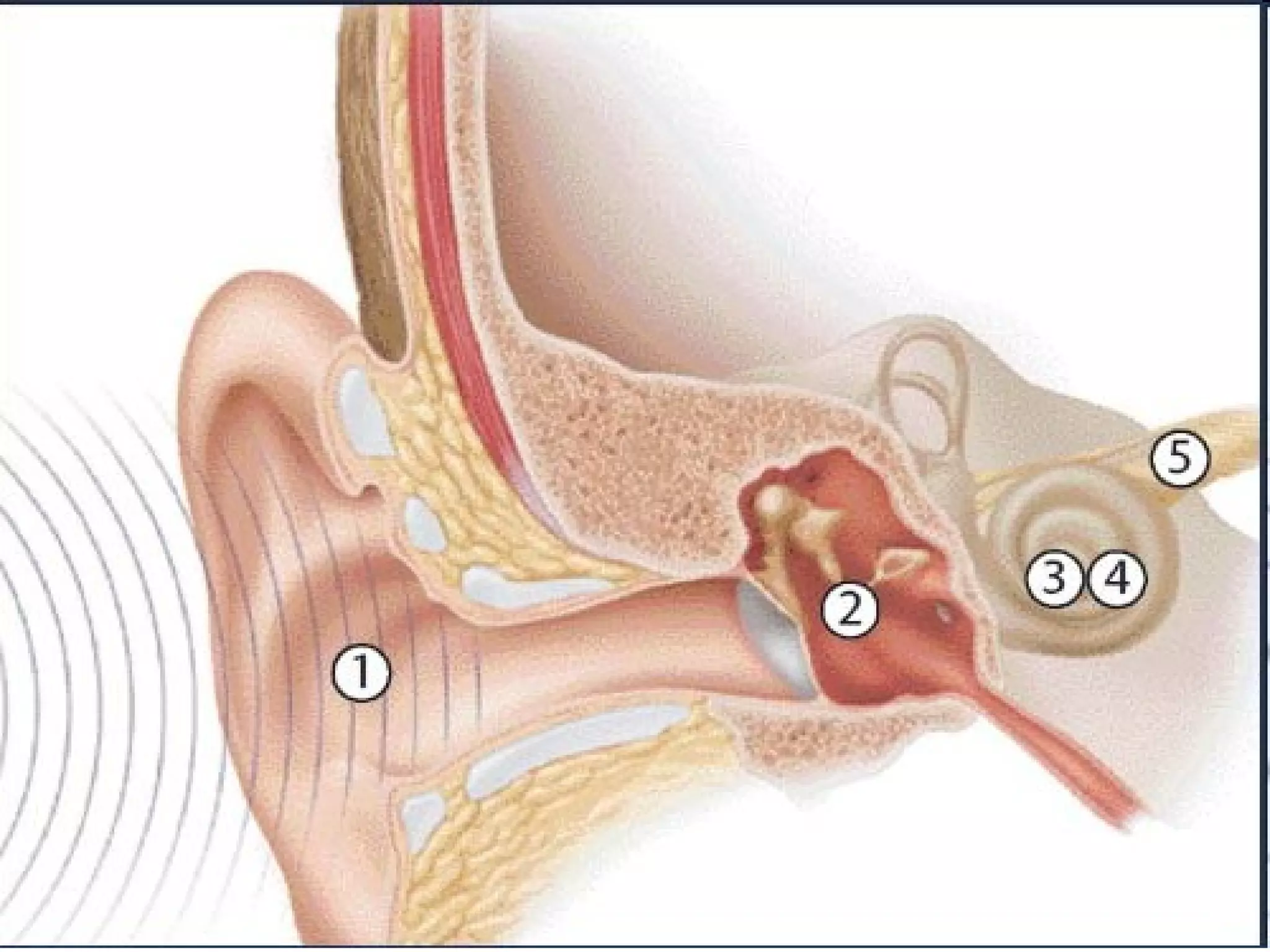
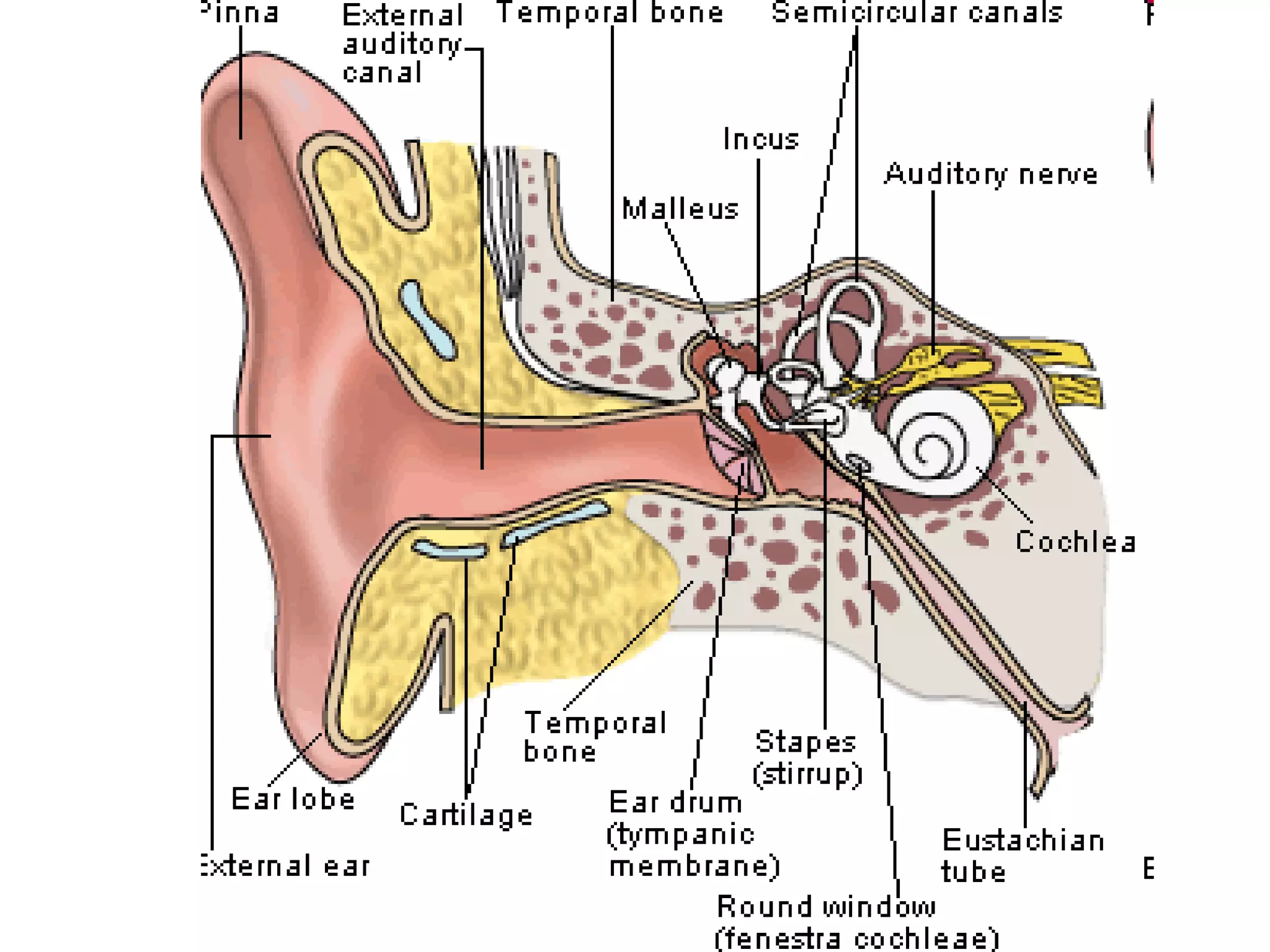
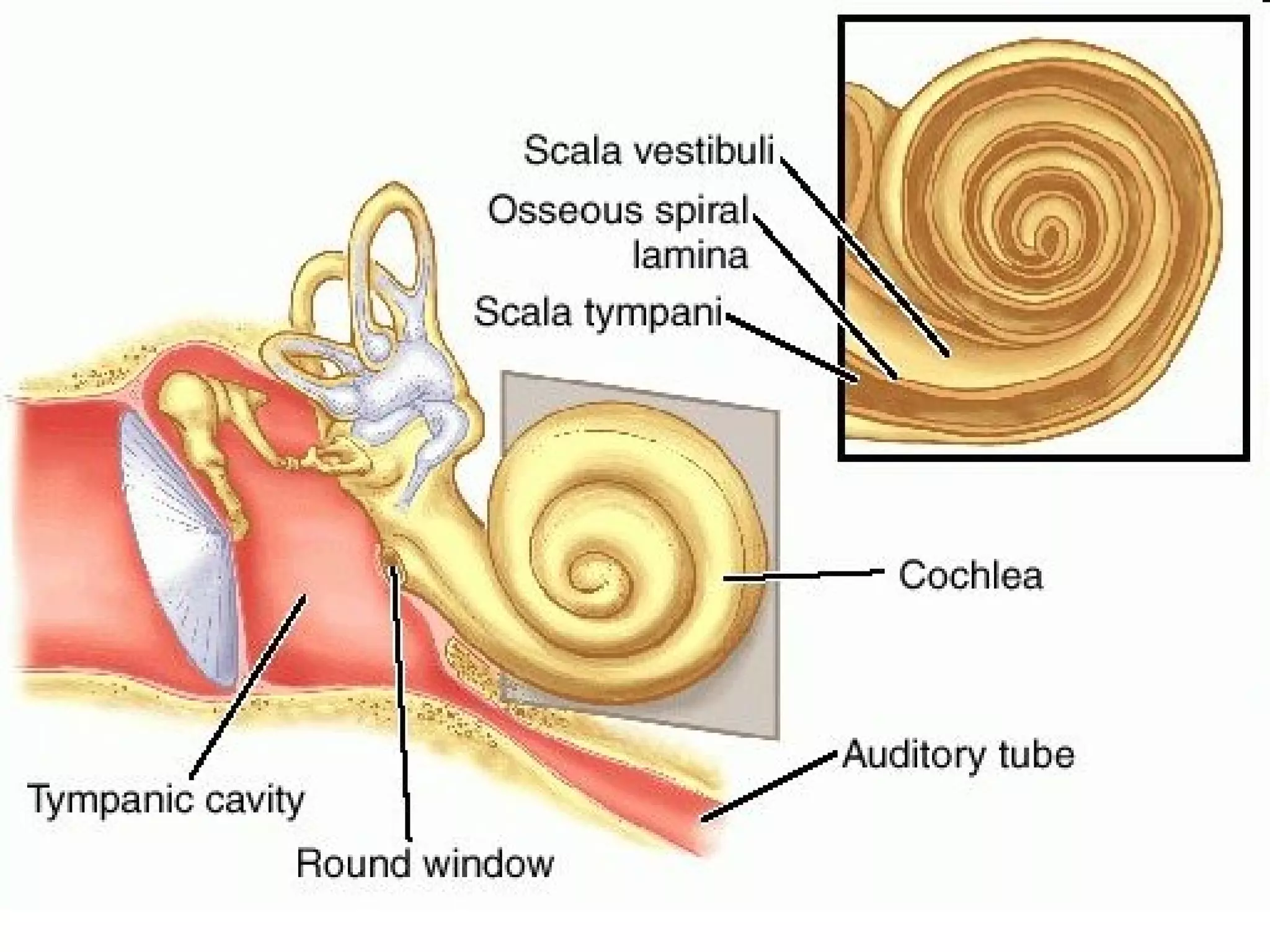
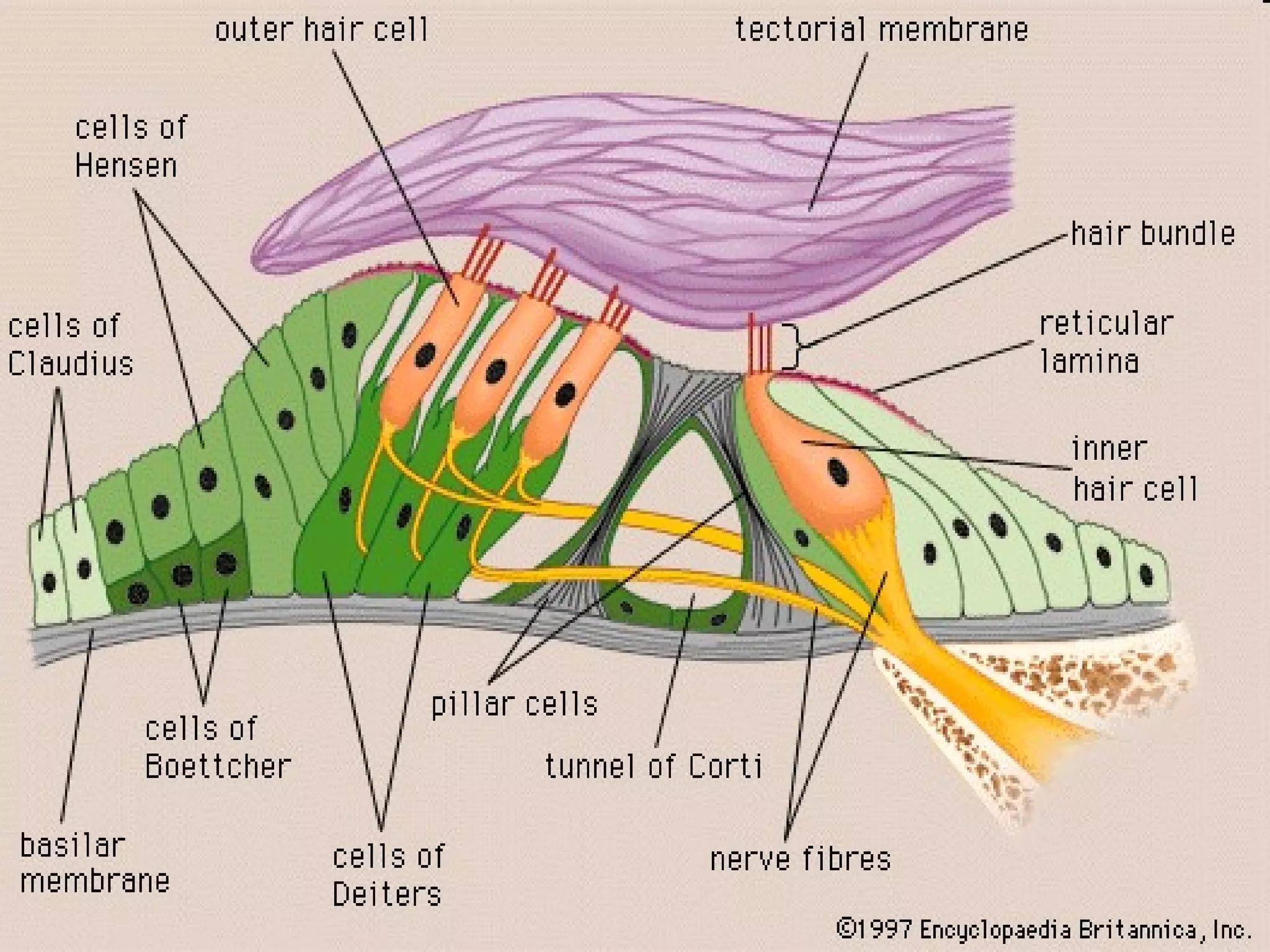
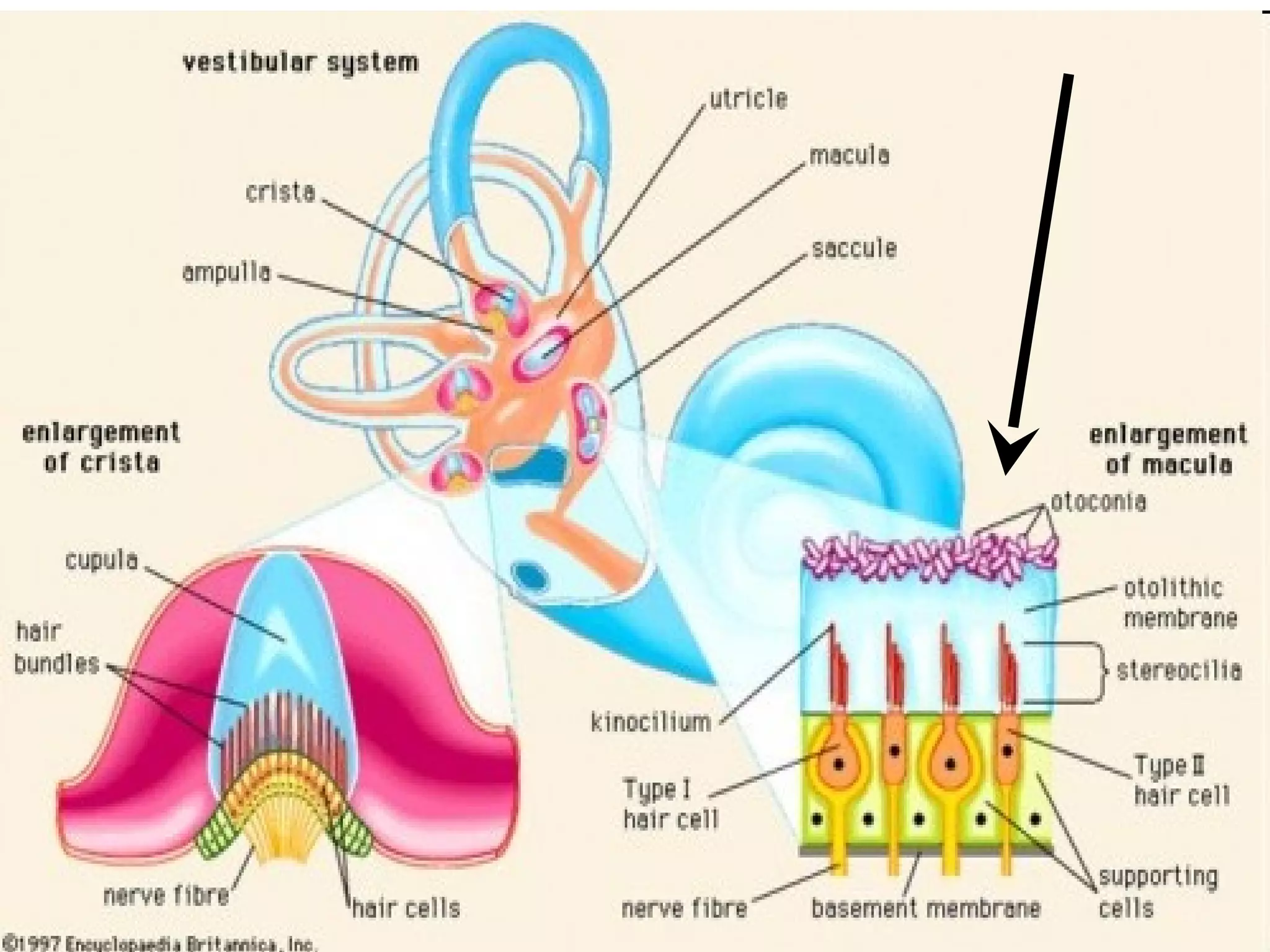
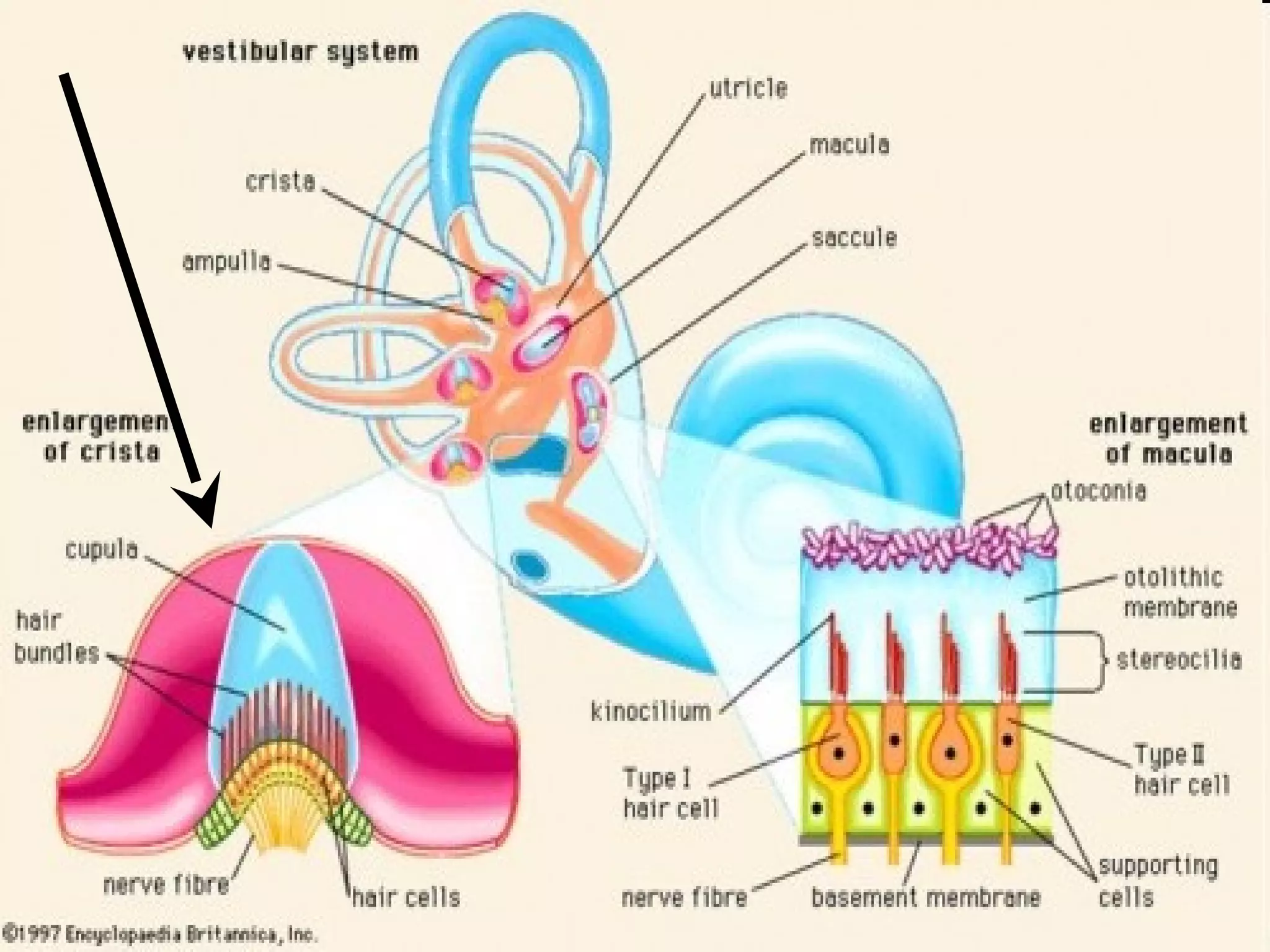
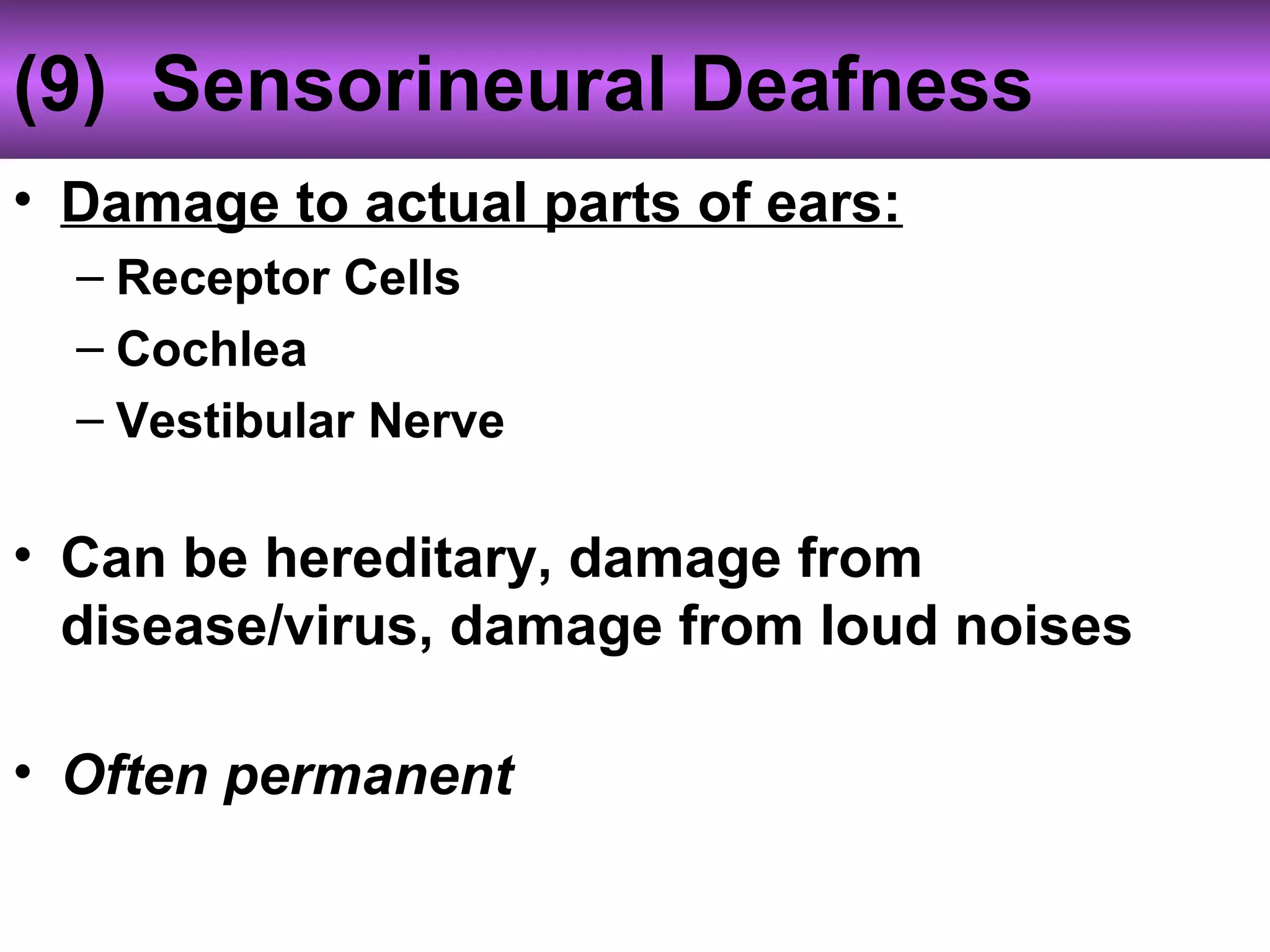
The ear is designed like a funnel to channel sound waves into the auditory canal and cause the ear drum to vibrate. Inside the ear, the vibrations are transmitted through three small bones to the cochlea, where fluid carries the signal to receptors. The cochlea contains receptors for both hearing and balance. Two types of equilibrium receptors in the cochlea, called the vestibular apparati, help the brain monitor the position of the head. Static equilibrium receptors identify basic positions like up and down, while dynamic equilibrium receptors detect more detailed movement and rotations through fluid in the semicircular canals. Damage to different parts of the ear can cause either conduction or sensorineural deafness.