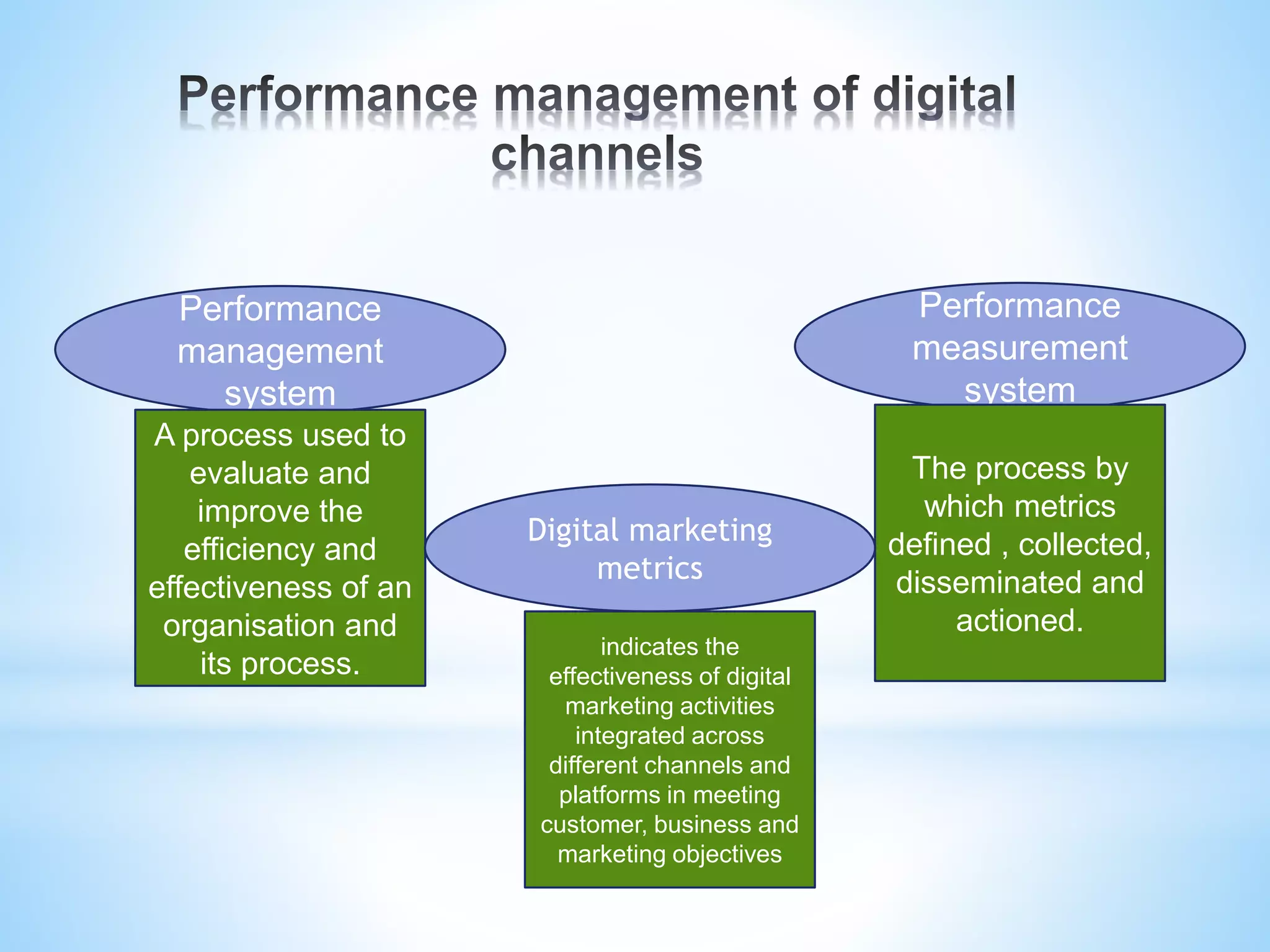
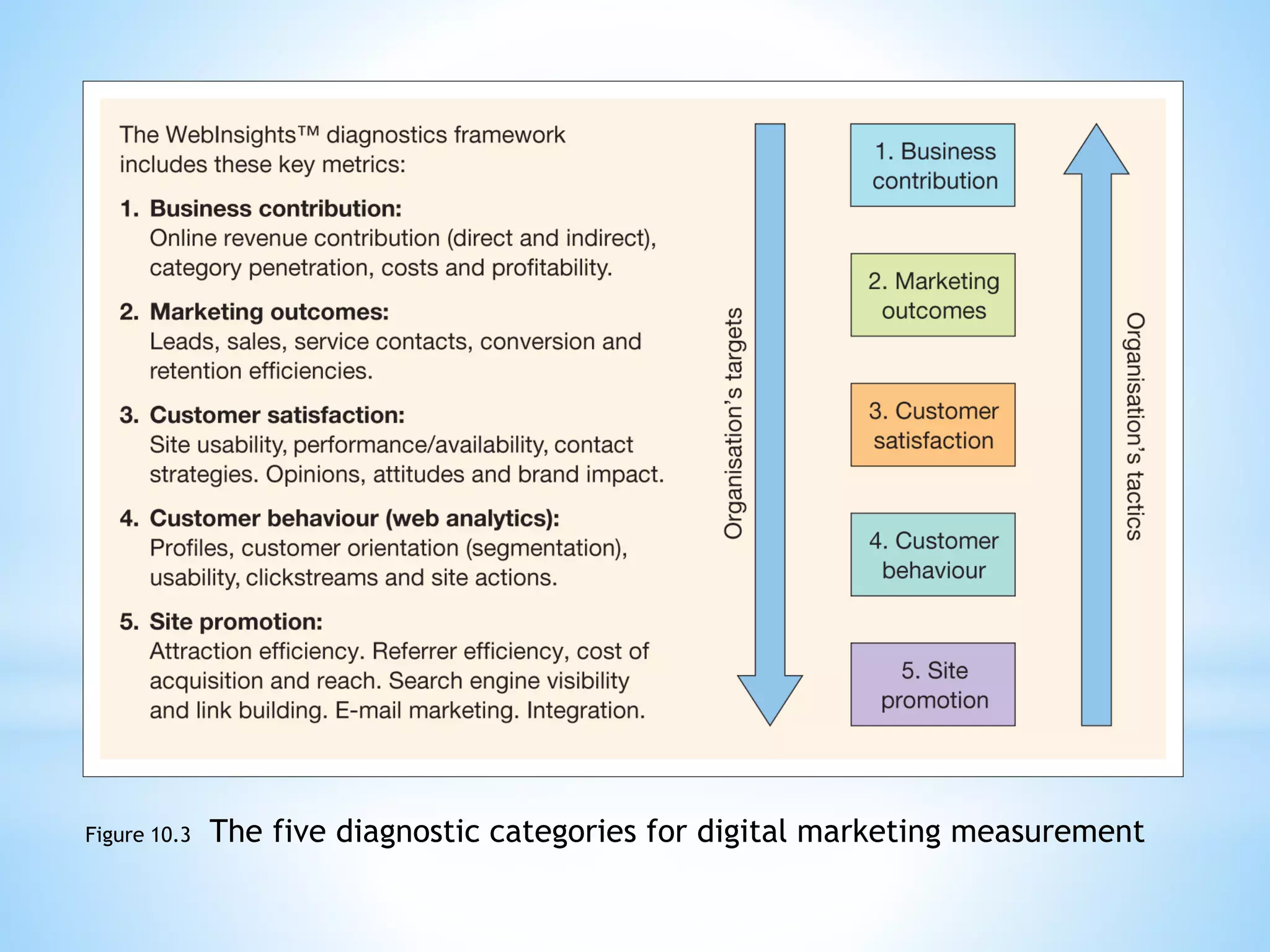
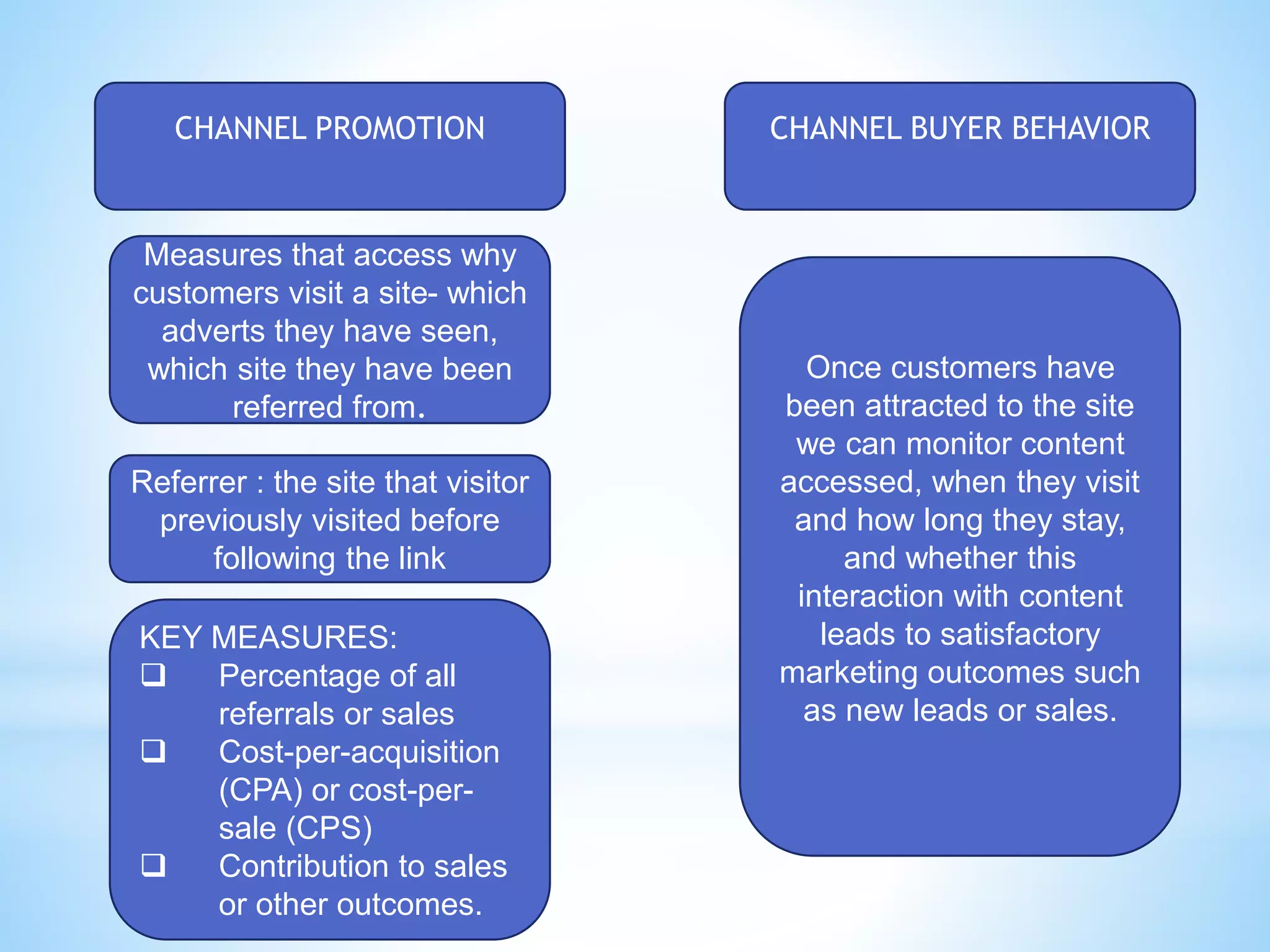
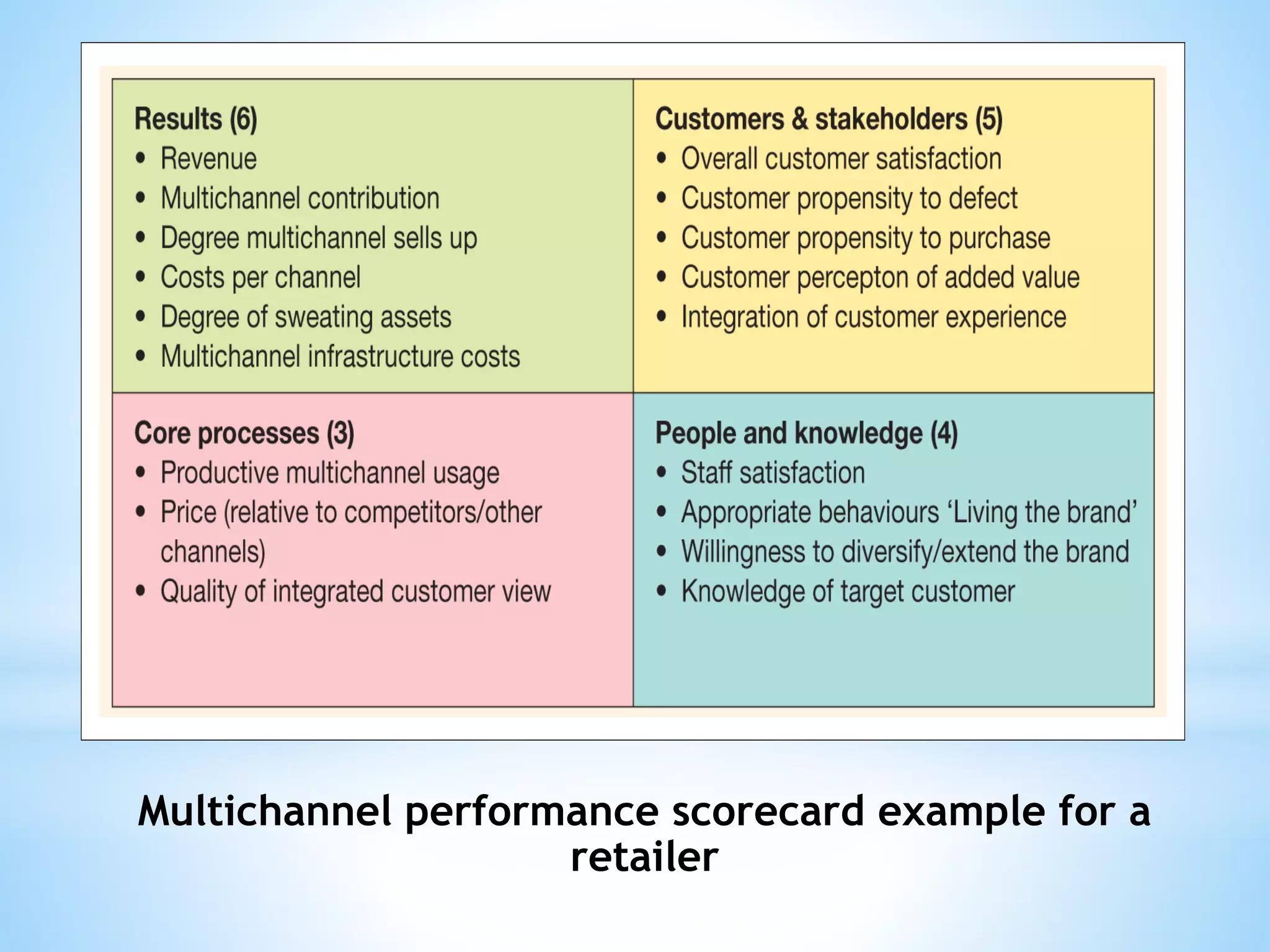
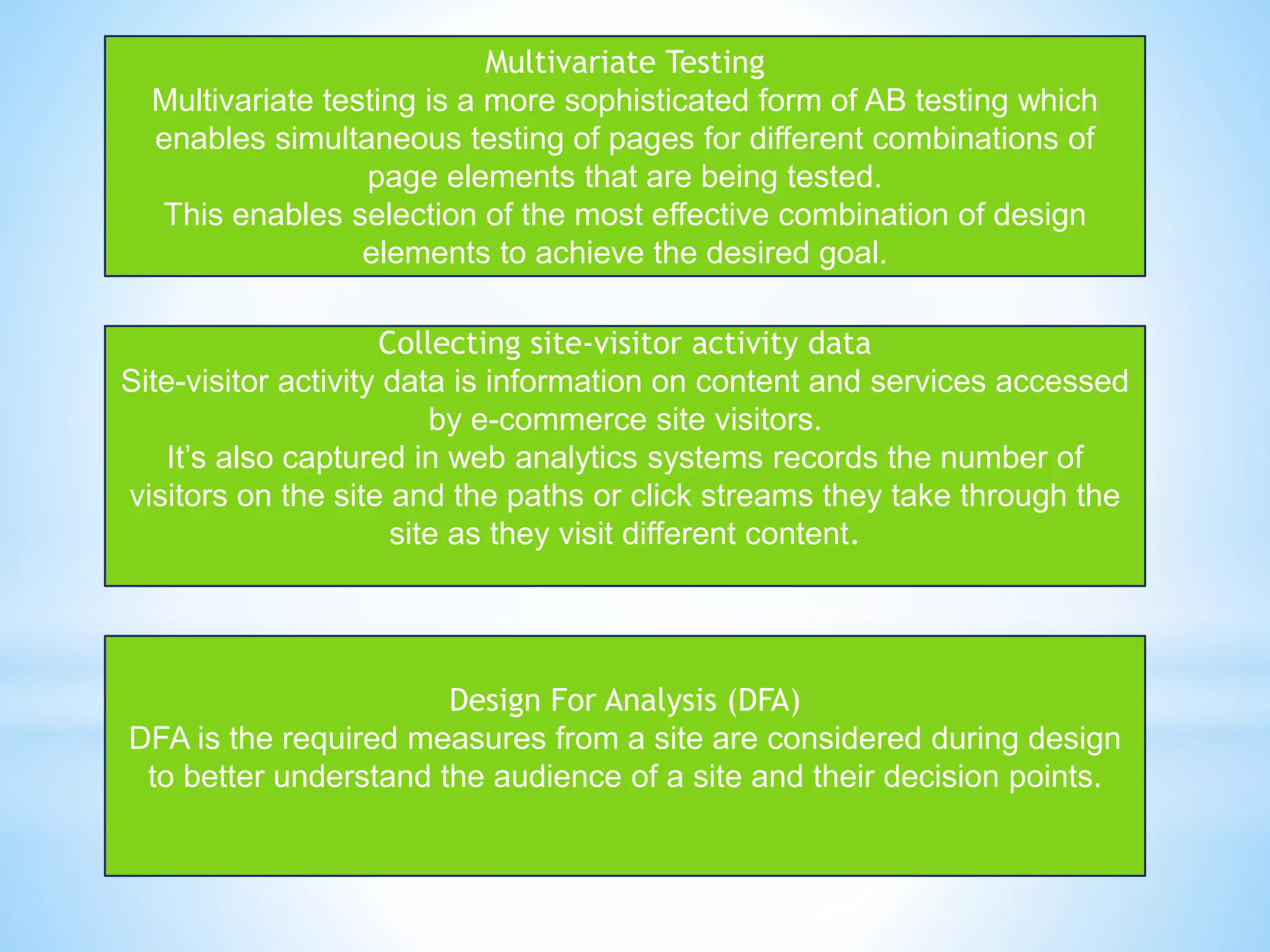
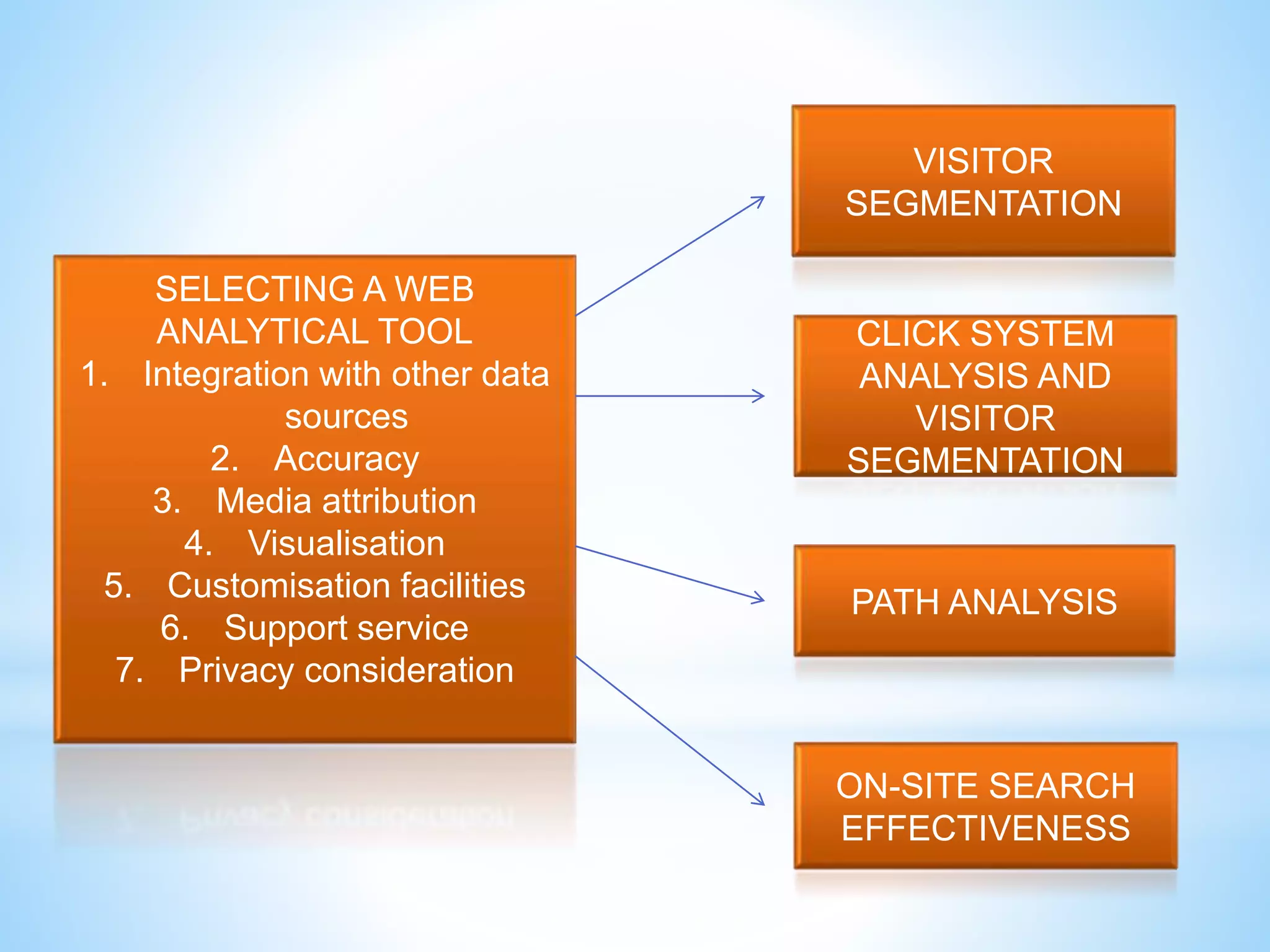
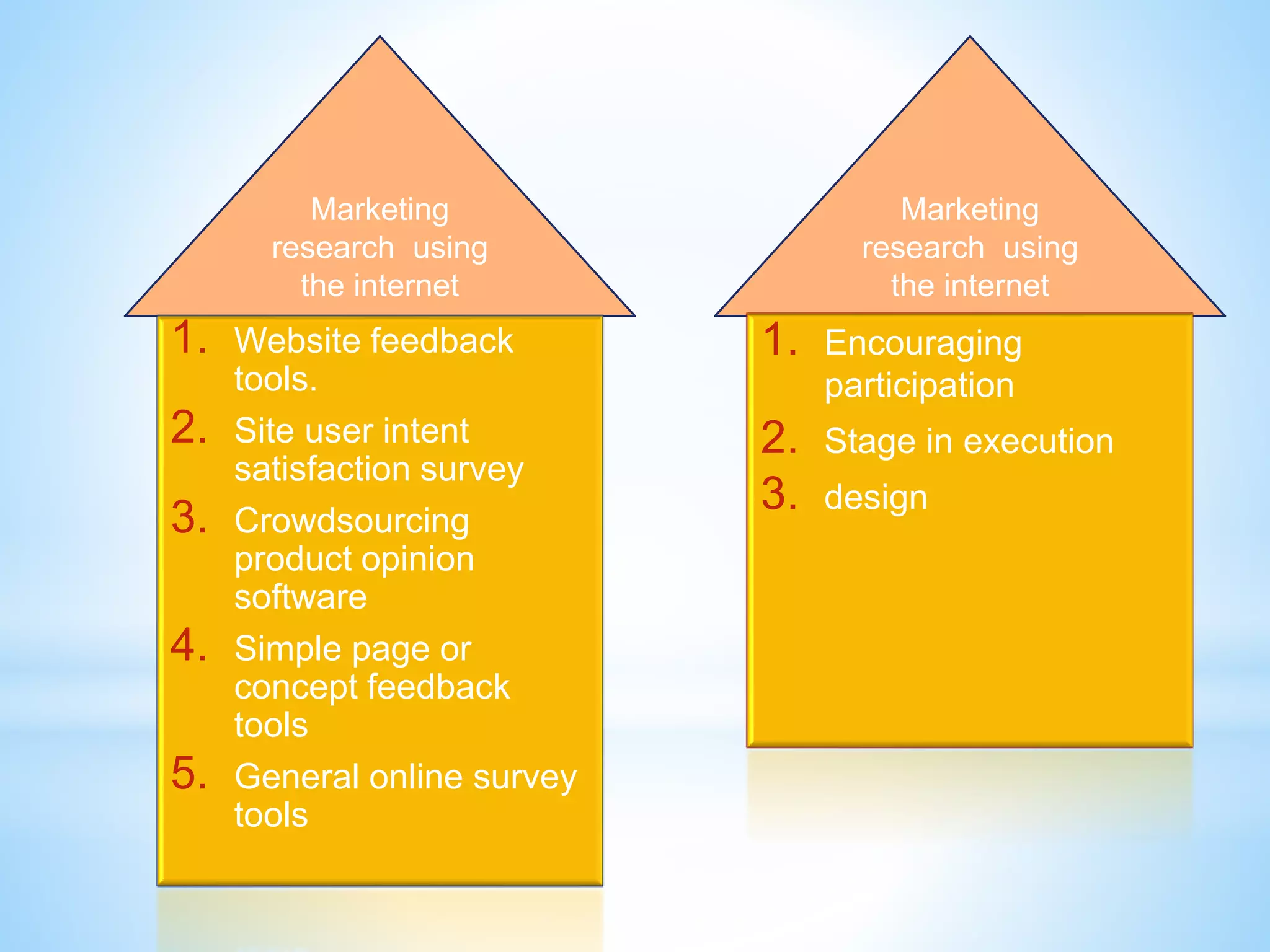
The document discusses performance management for digital channels. It defines key terms like web analytics, performance management systems, and digital marketing metrics. It explains that performance management aims to analyze and drive business performance through digital marketing approaches. Various metrics are identified to measure effectiveness, efficiency, and the contribution of digital marketing at different levels like strategic, profitability, and efficiency control. The document also discusses site management processes, responsibilities, and technologies used for website maintenance.