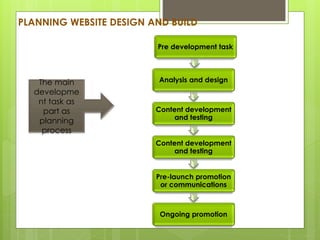
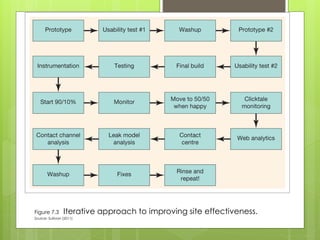
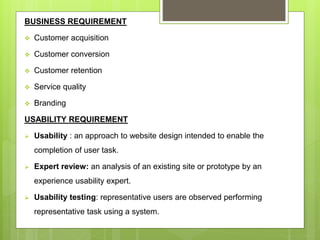
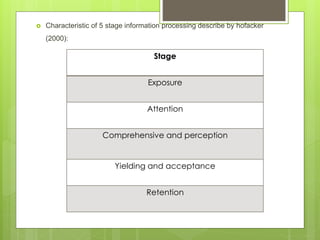
This chapter discusses delivering the online customer experience. It covers planning website design and development, defining requirements, designing the user experience, developing and testing content, online retail merchandising, promoting sites, and ensuring service quality. Key aspects include prototyping, agile development, usability testing, accessibility, localization, information architecture, navigation schemes, and content management systems. The goal is to provide customers a satisfactory online experience that increases conversion rates.