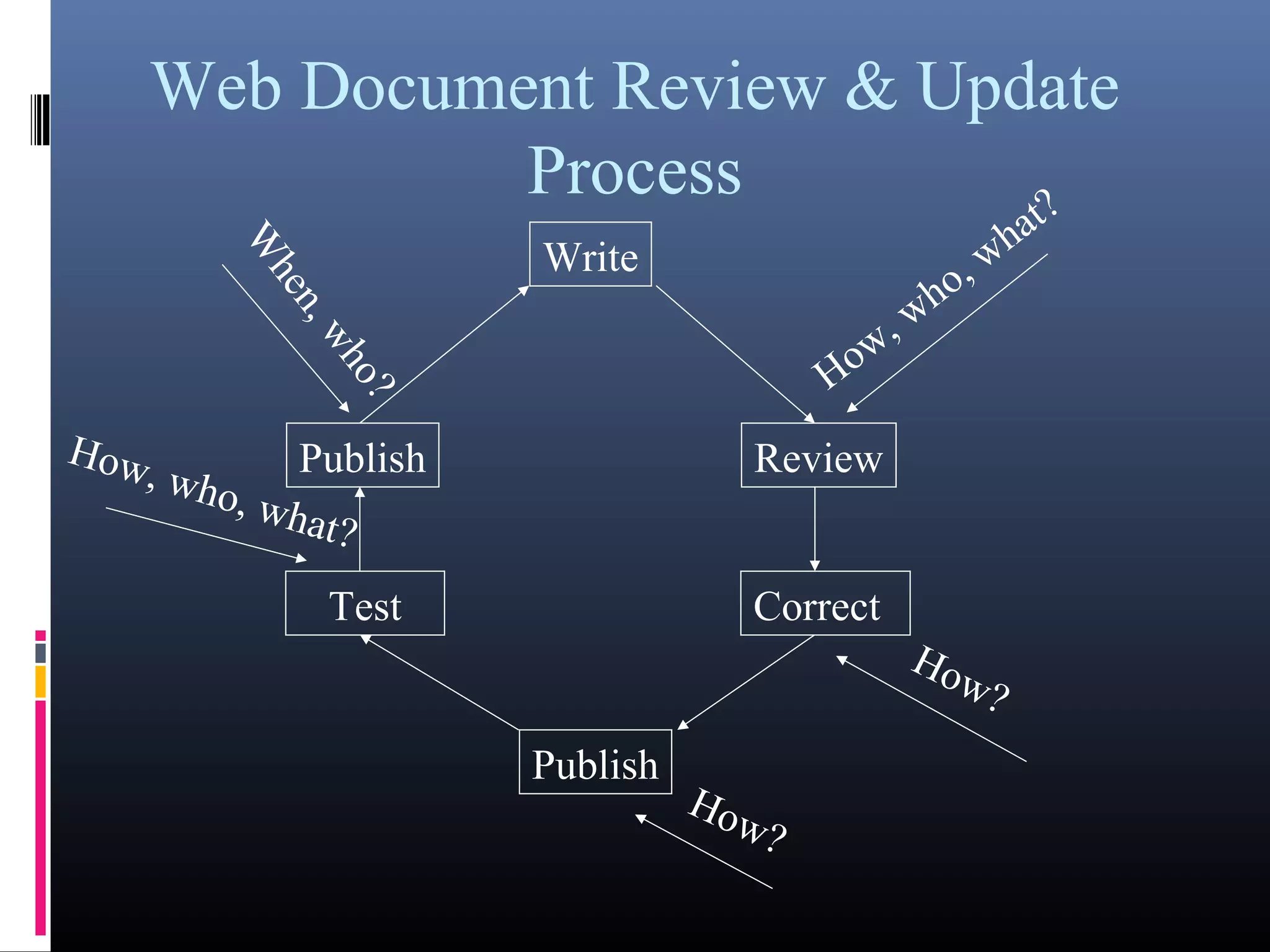
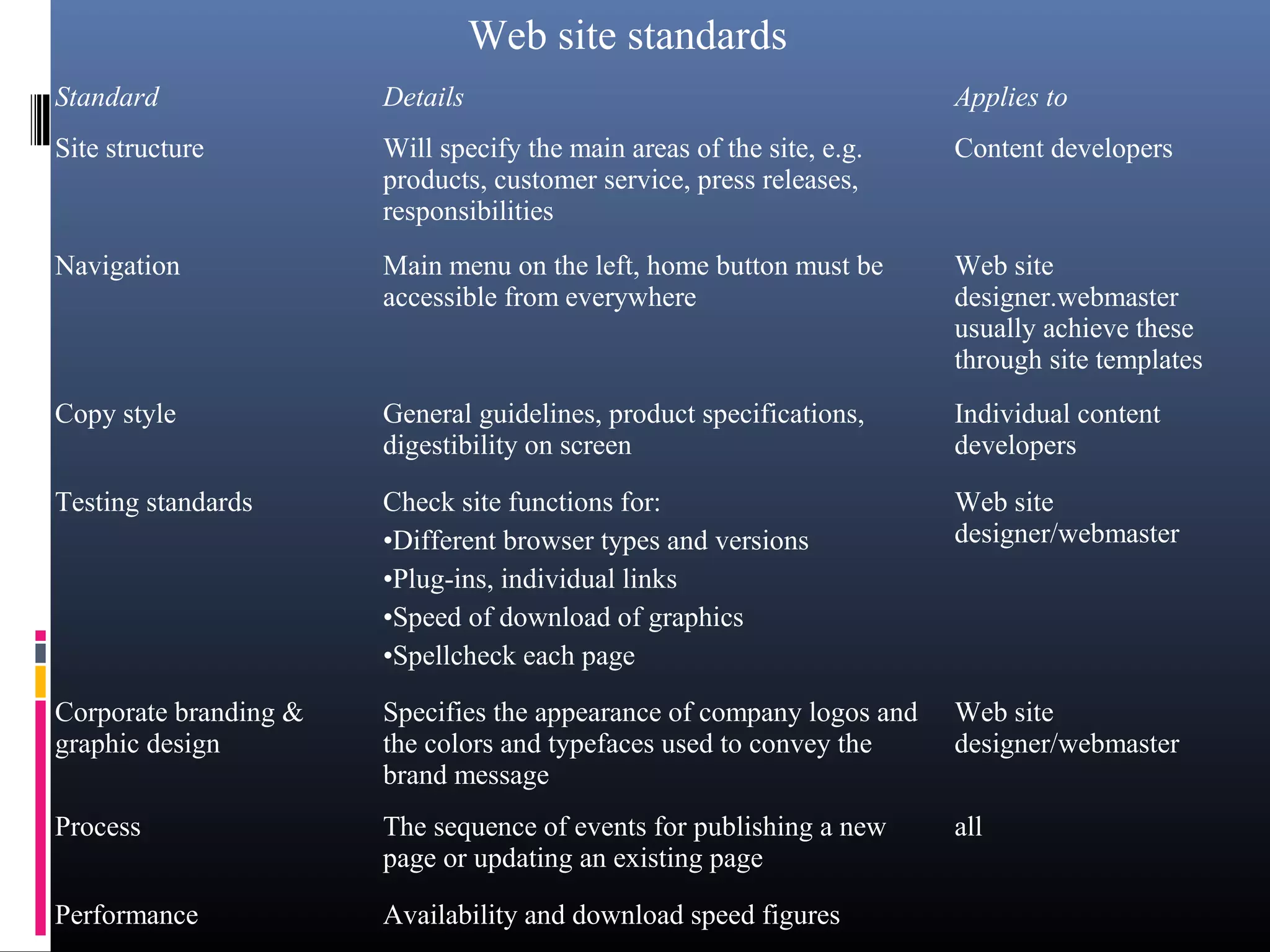
The document discusses web site maintenance and measuring internet marketing effectiveness. It outlines the maintenance process which includes writing content, reviewing for errors, correcting issues, publishing updated content, and testing. It also discusses responsibilities in maintenance like who owns each part of the process. Measuring effectiveness is done at three levels - business, marketing, and internet marketing. Various metrics are proposed for each level like revenue, leads generated, customer satisfaction. Both online and offline methods are suggested for collecting metric data.