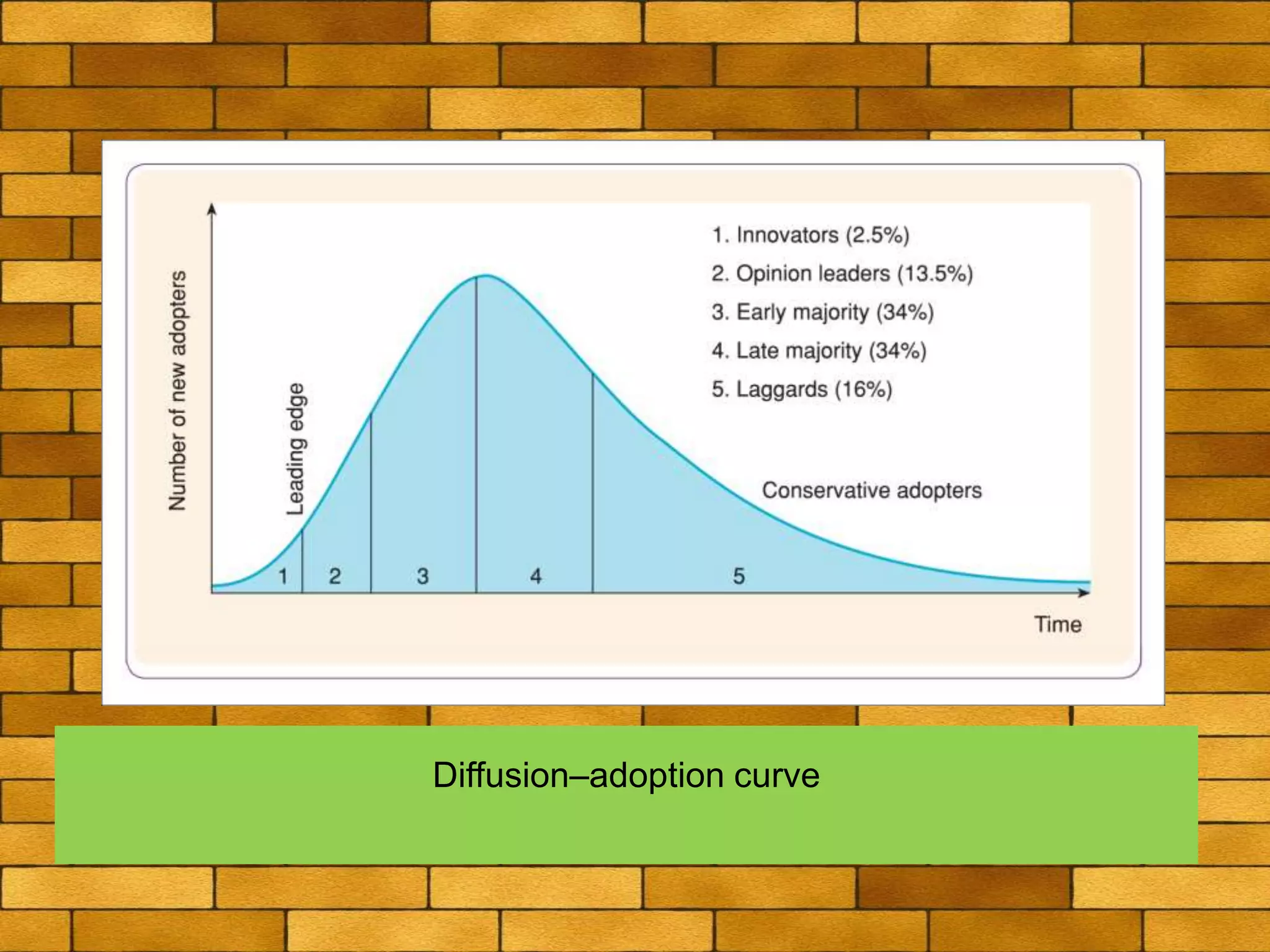
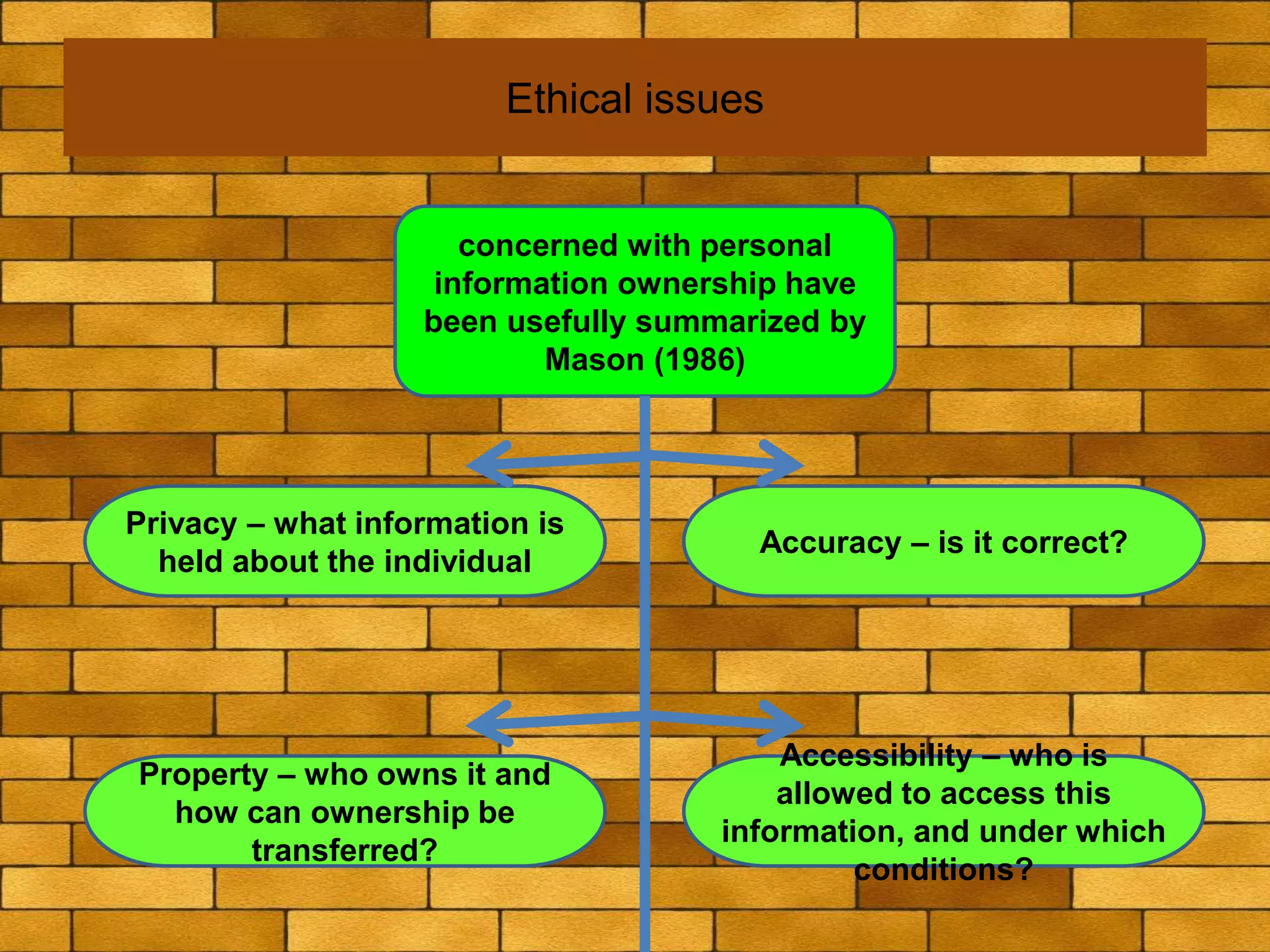
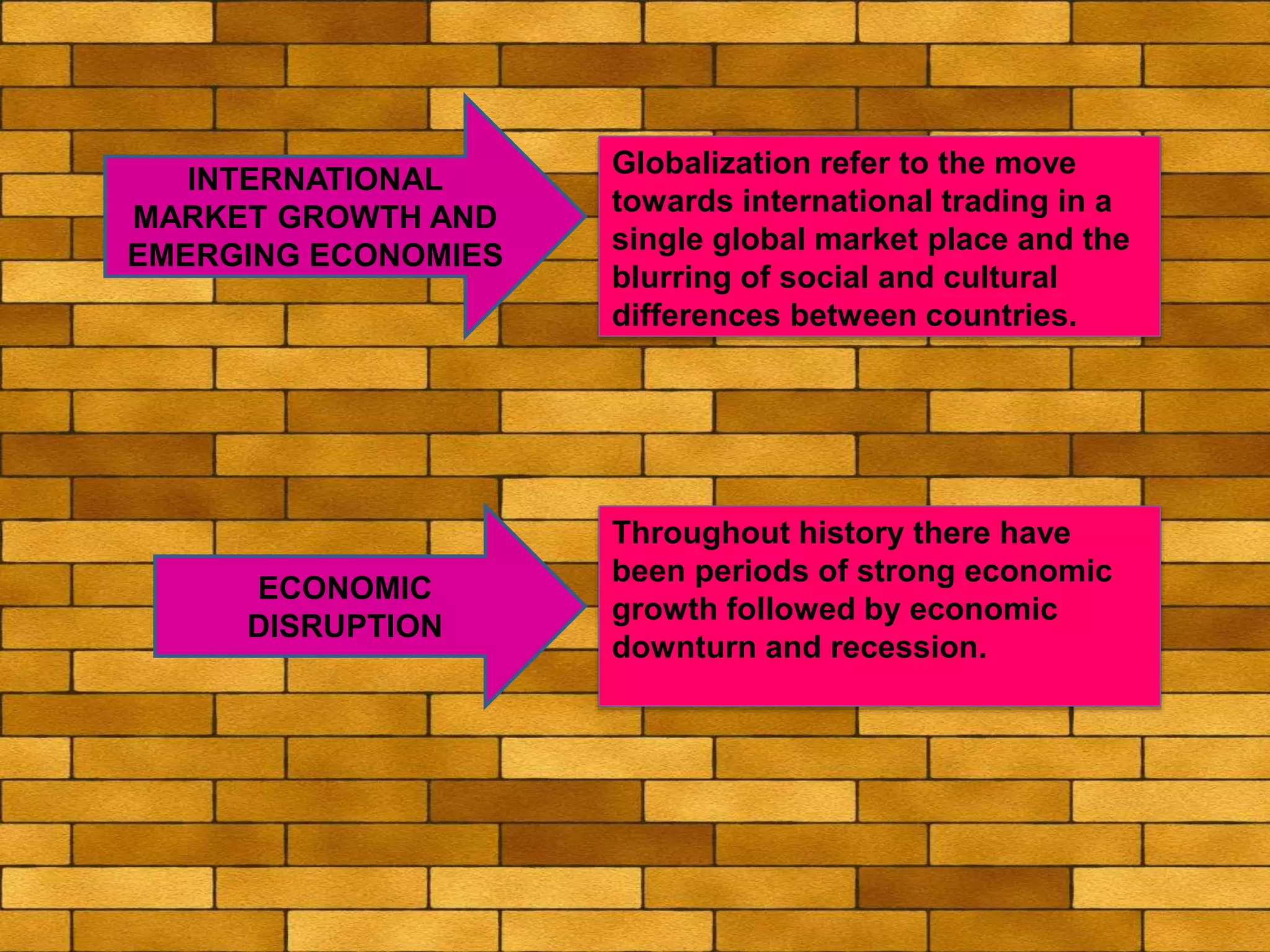
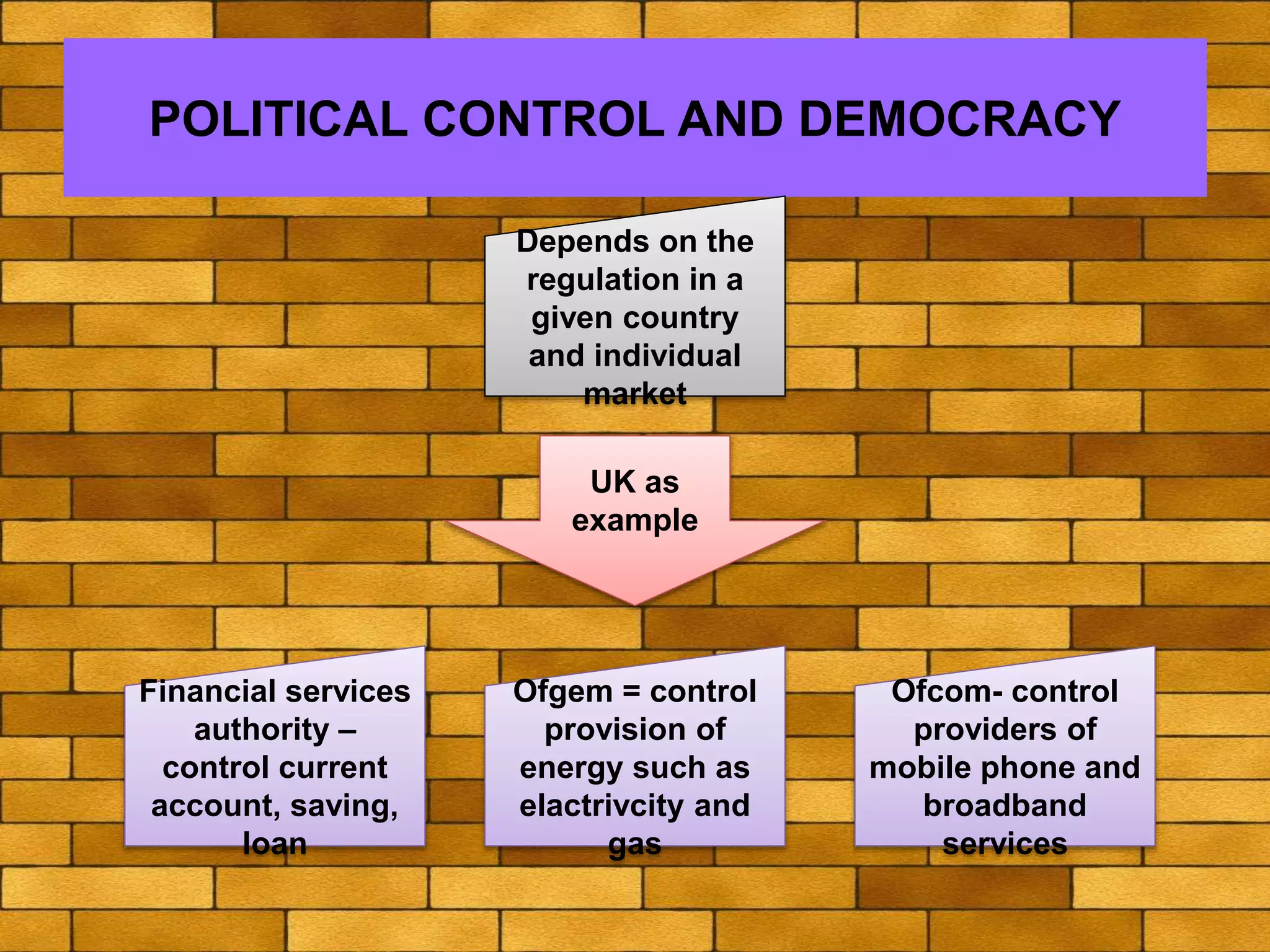
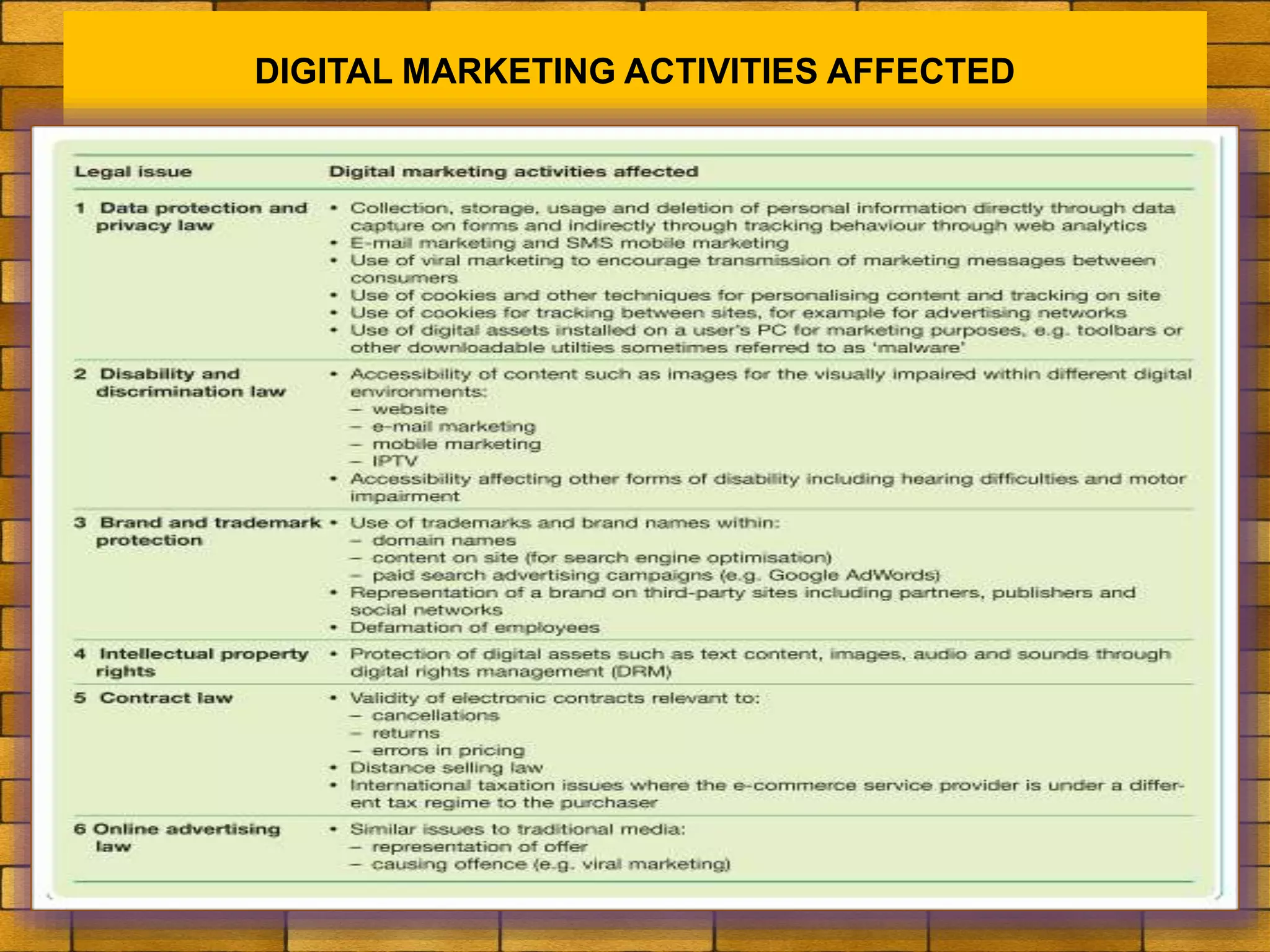
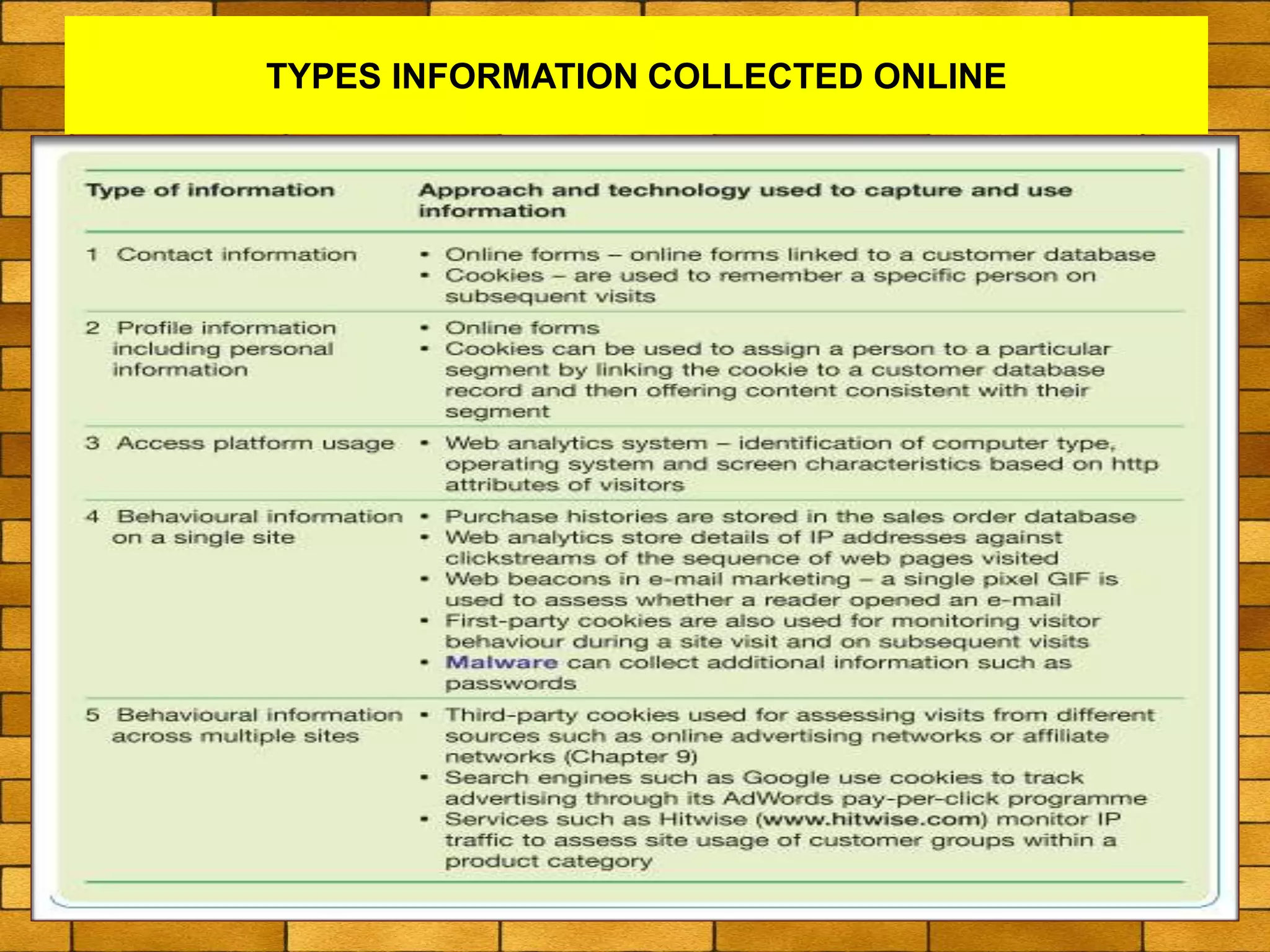
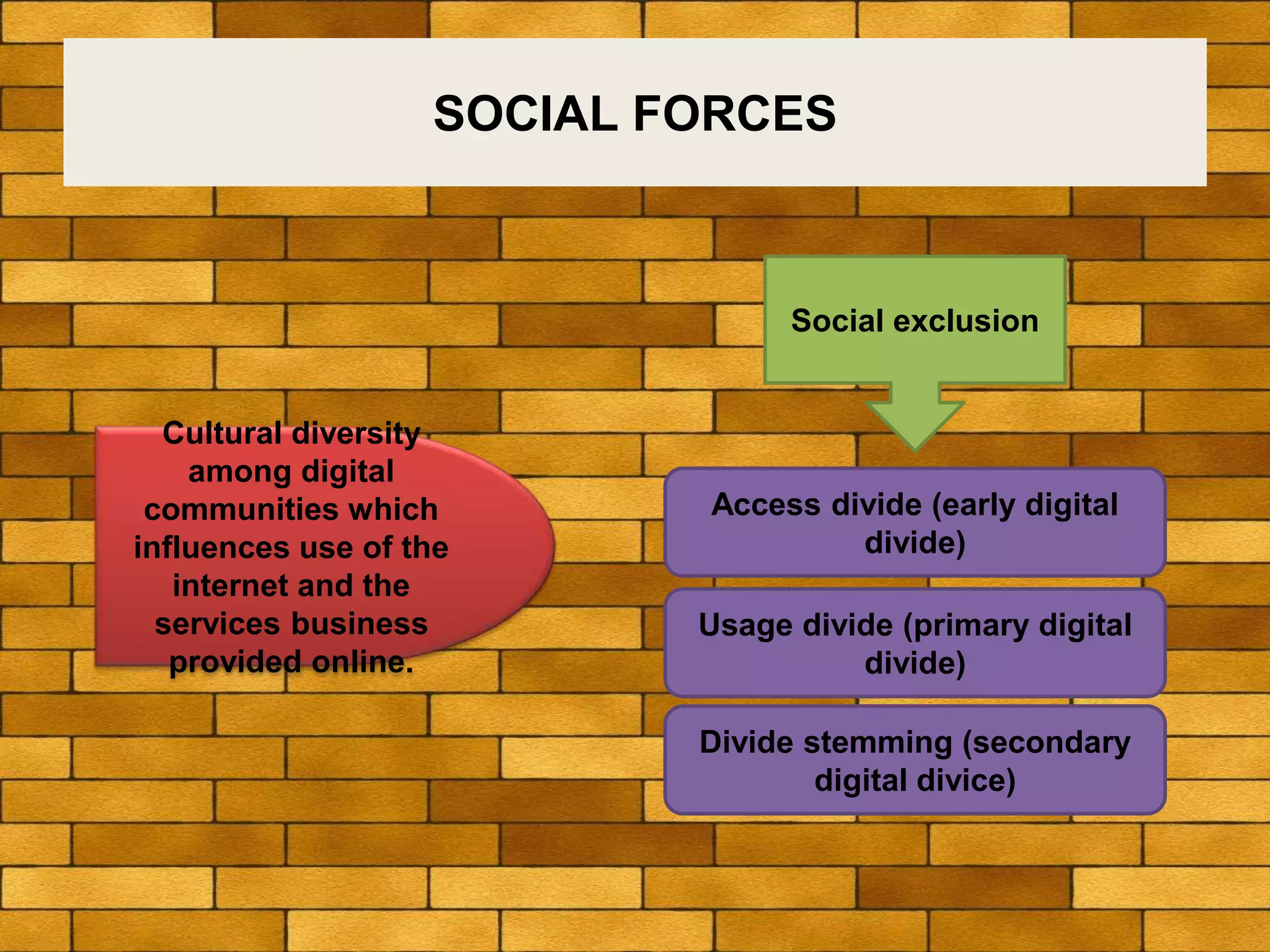
The document discusses various macro-environmental forces that can impact digital marketing strategies, including technological forces, economic forces, political forces, legal forces, and social forces. Technological forces refer to changing technologies that create new opportunities. Economic forces include factors like employment, income, and economic growth and disruption. Political forces involve government promotion and regulation of e-commerce. Legal forces relate to privacy, data protection and regulations on digital marketing activities. Social forces comprise cultural diversity and variations in internet usage among digital communities.