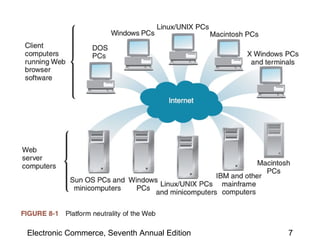
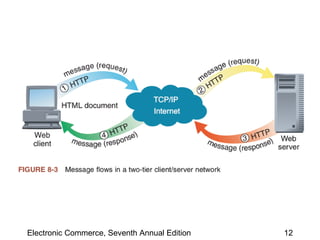
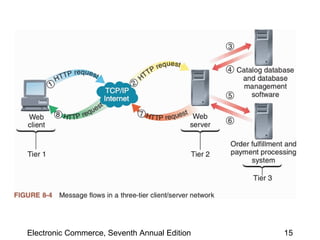
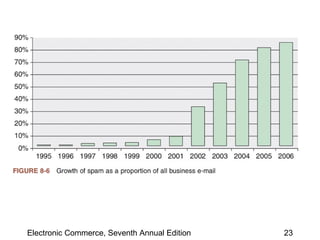
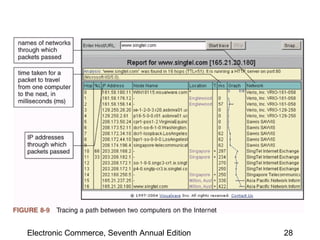
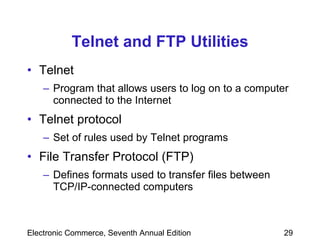
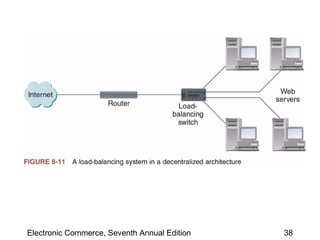
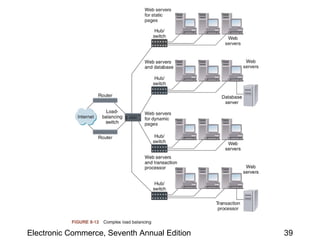
This chapter discusses web server basics, including hardware, software, and architectures. The main job of a web server is to respond to client requests. Common operating systems for web servers are Microsoft and UNIX-based systems. Utility programs like Finger, Ping, and Tracert are used to test connectivity. Unwanted commercial email (spam) has increased and content filters are being developed to address this problem. Web server hardware requires sufficient memory and disk space, while factors like the operating system, connection speed, and user capacity affect performance.