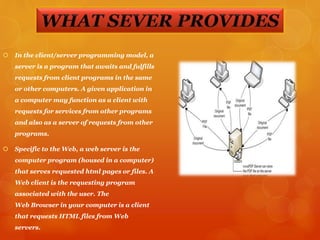
A server is a system that responds to requests across a network to provide services. Servers can run on dedicated computers or networked computers. Any computerized process that shares resources to clients is considered a server. While a laptop is not typically thought of as a server, it can fulfill the server role by running server software like a web server. Servers prioritize fast network connections and input/output throughput over absolute CPU speed. Servers often run without monitors or input devices and exclude unnecessary processes to allocate resources to their functions.