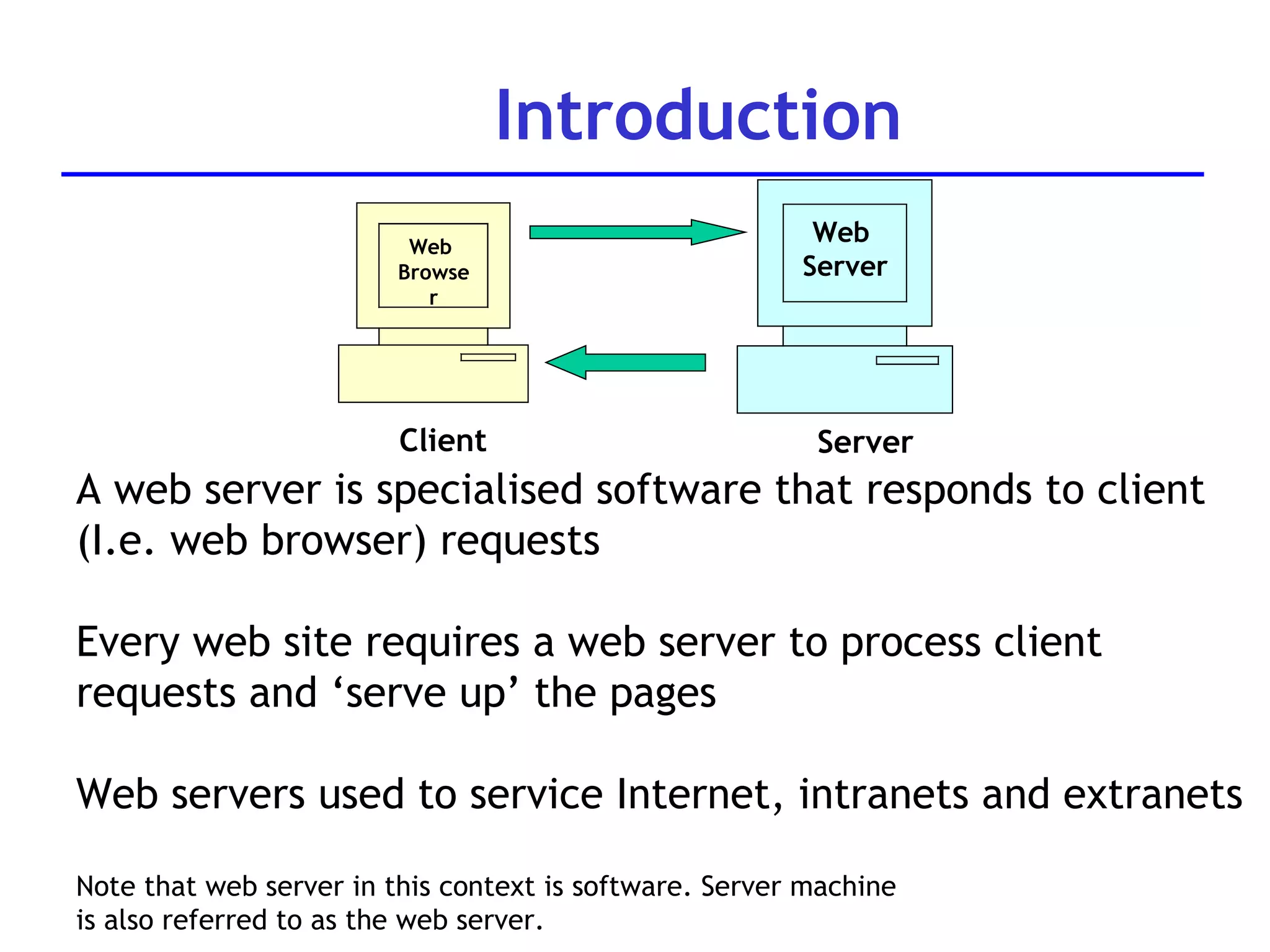
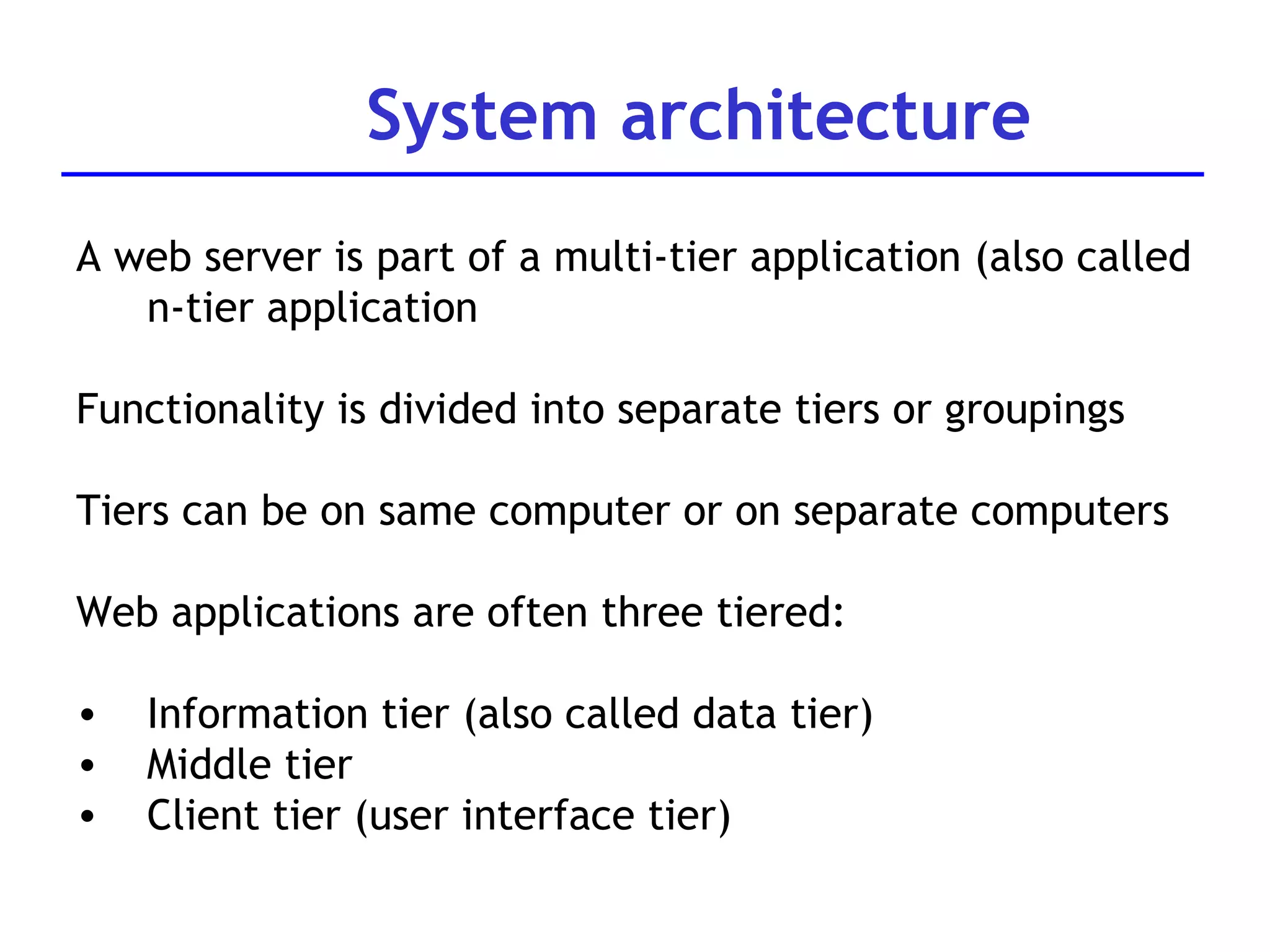
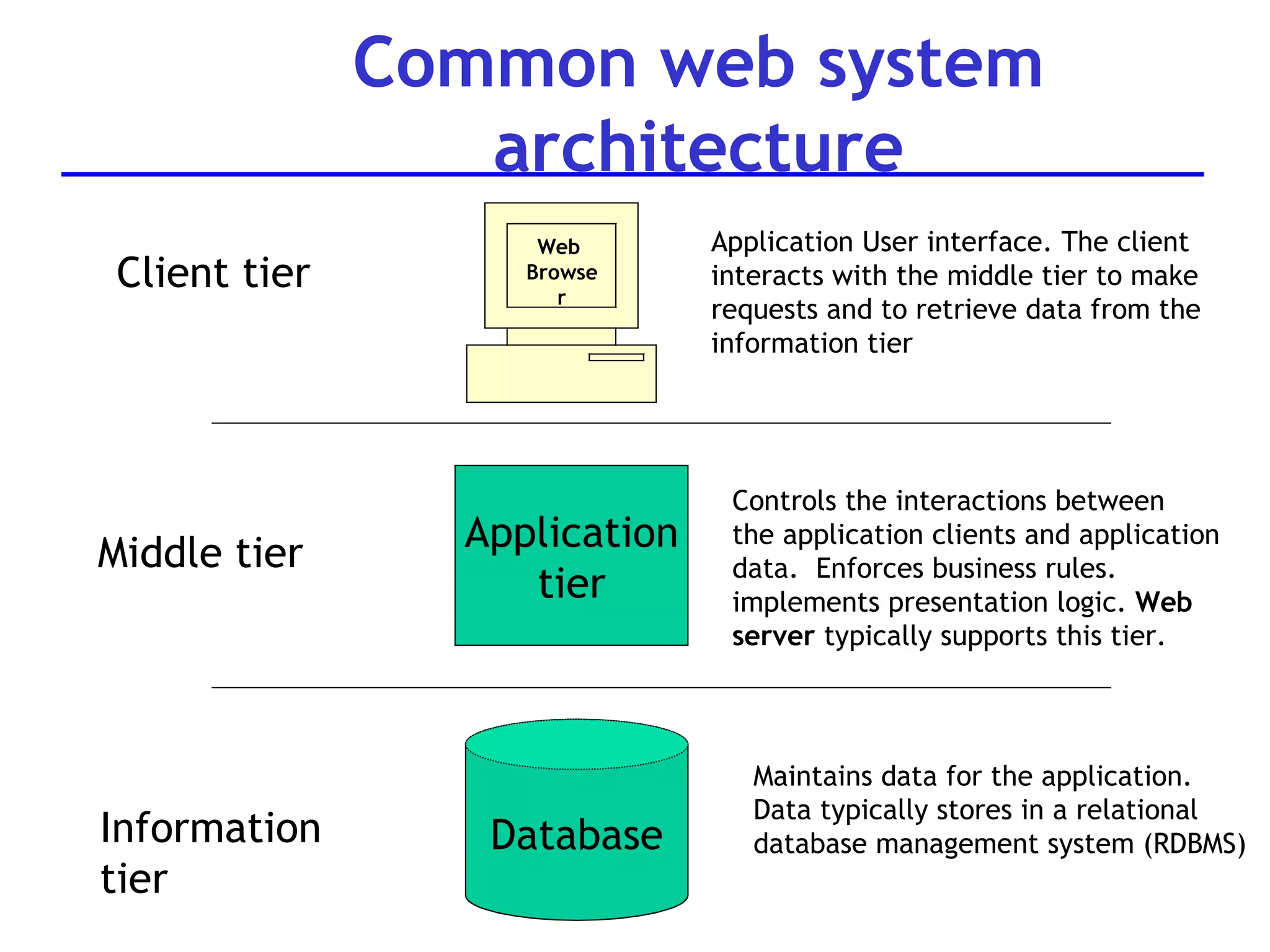
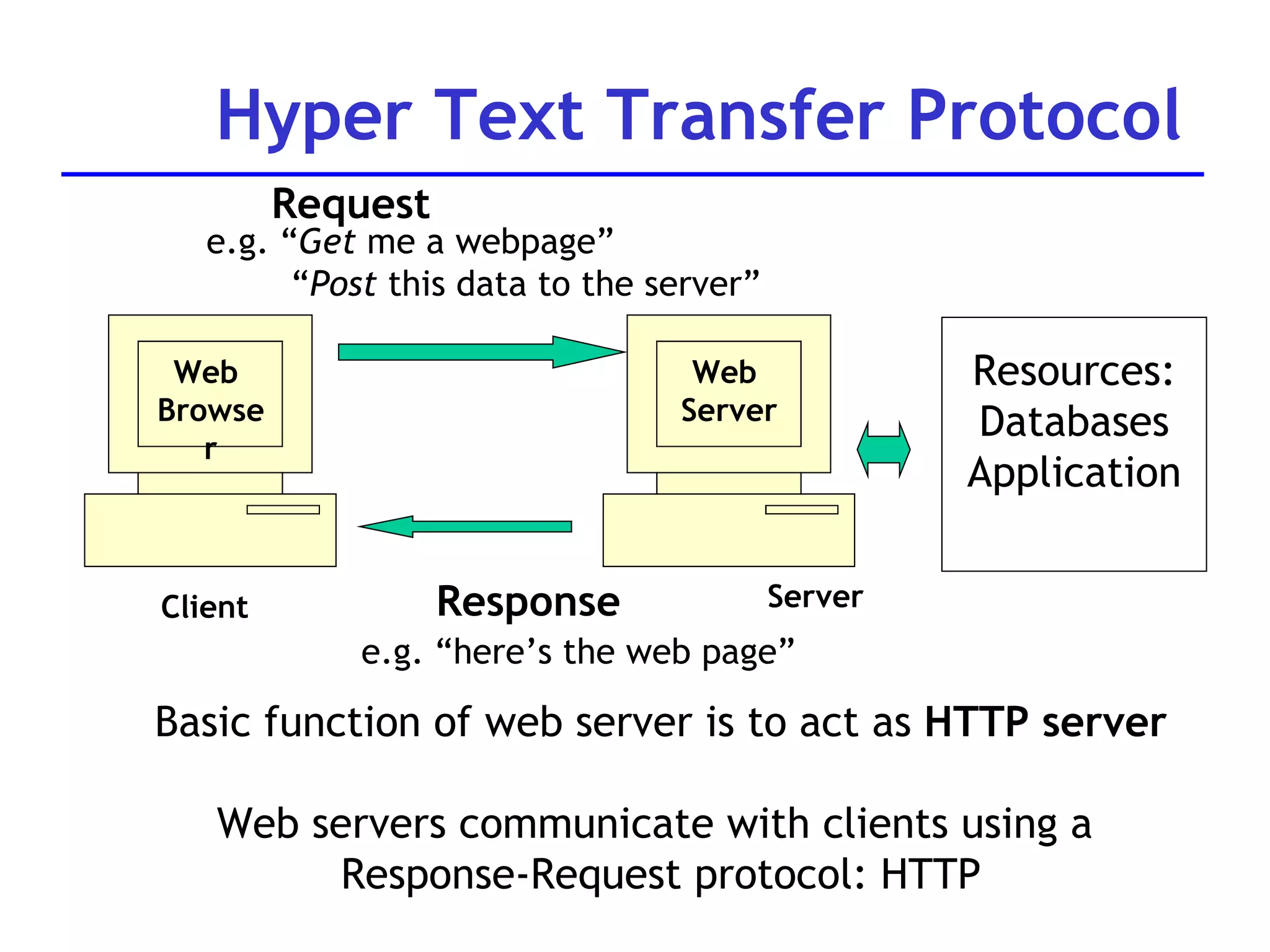
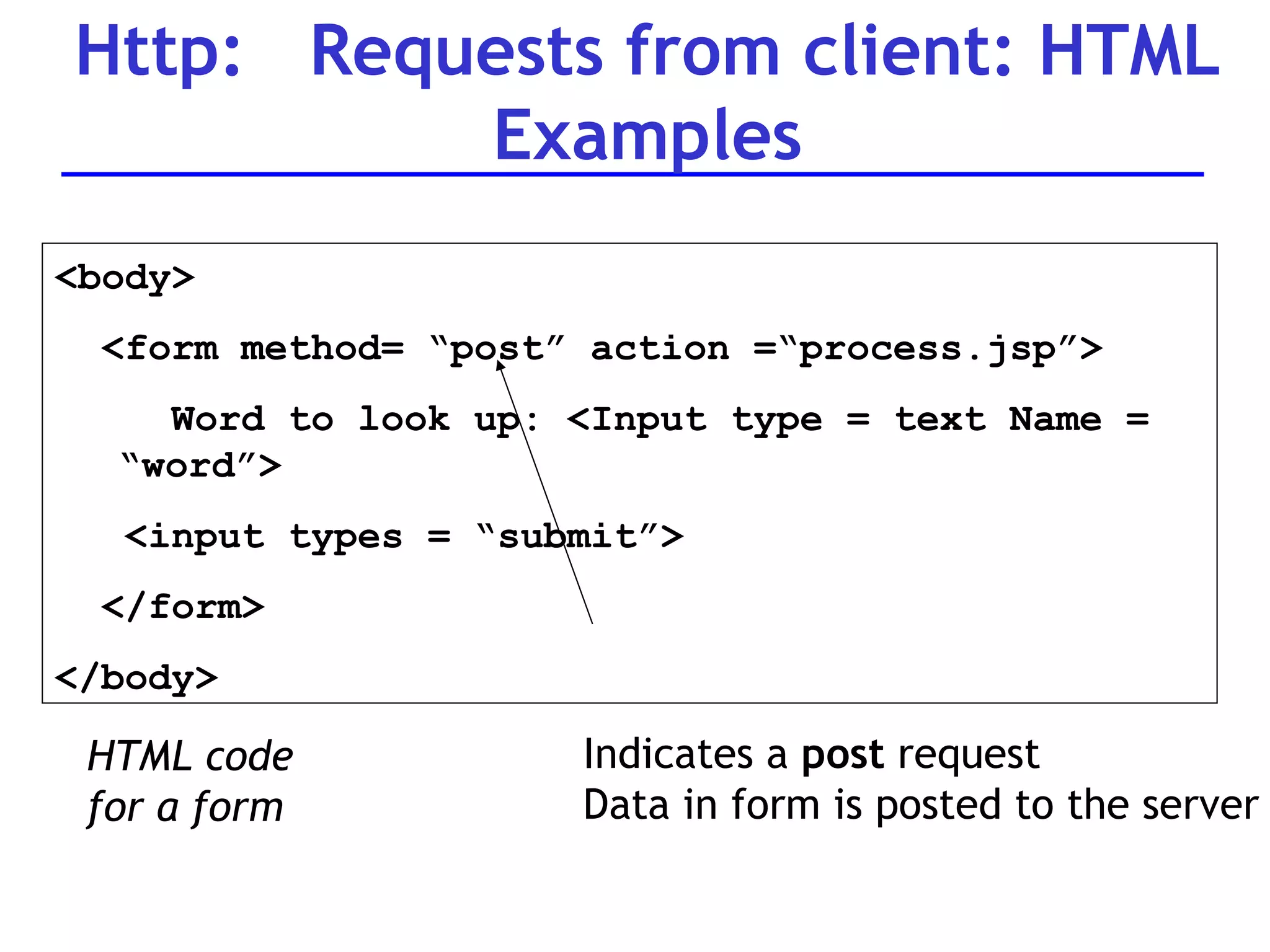
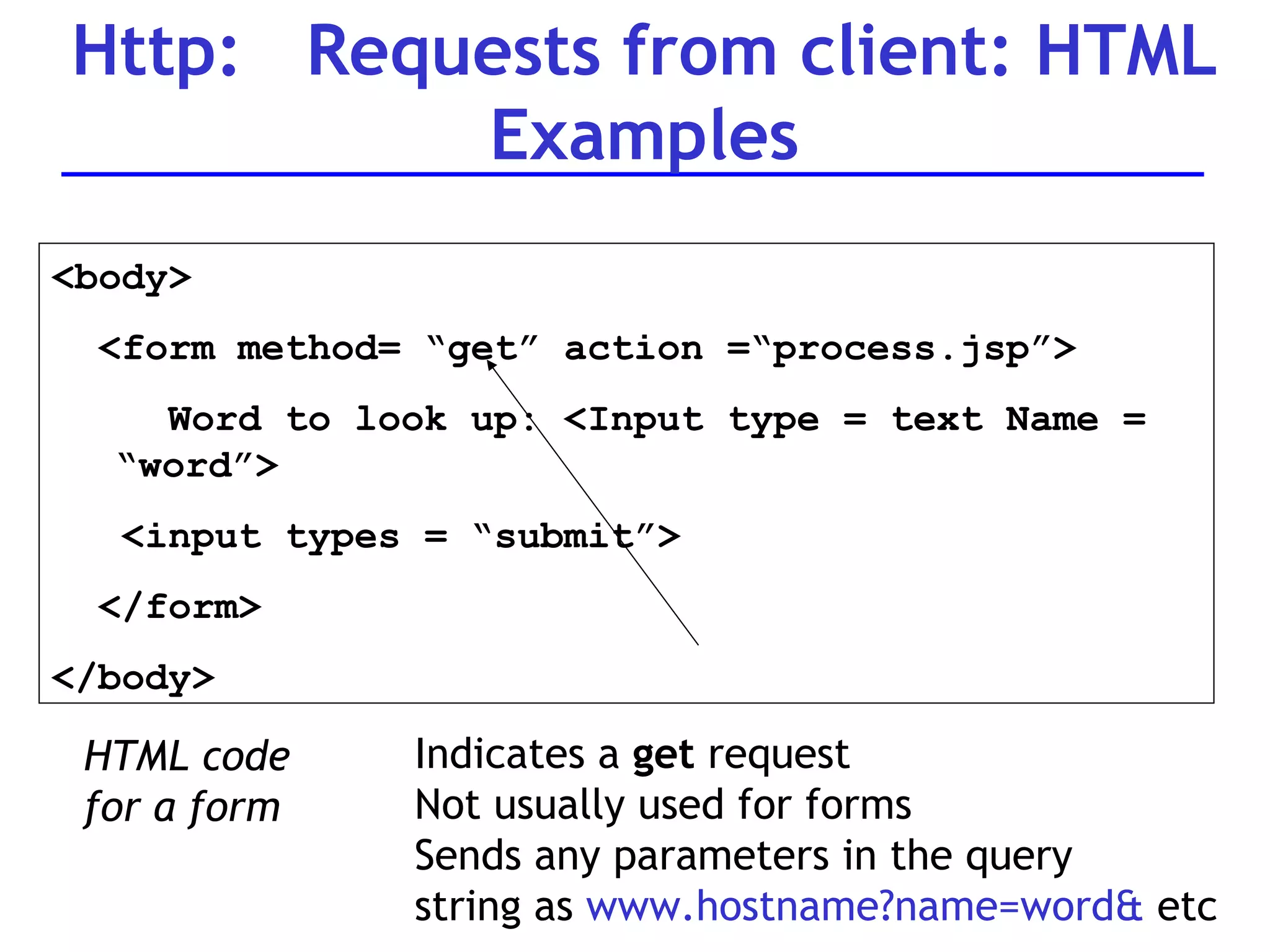
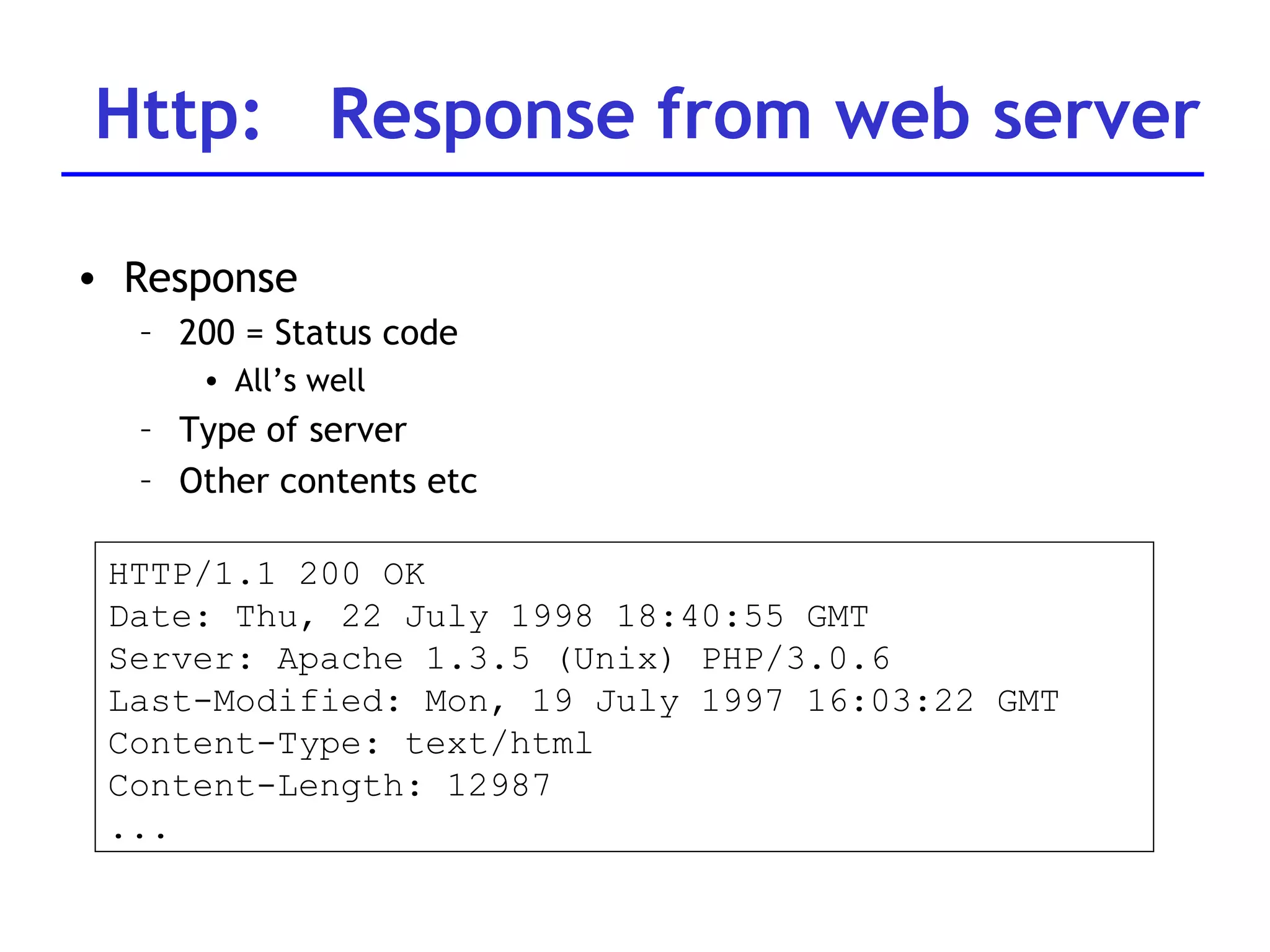
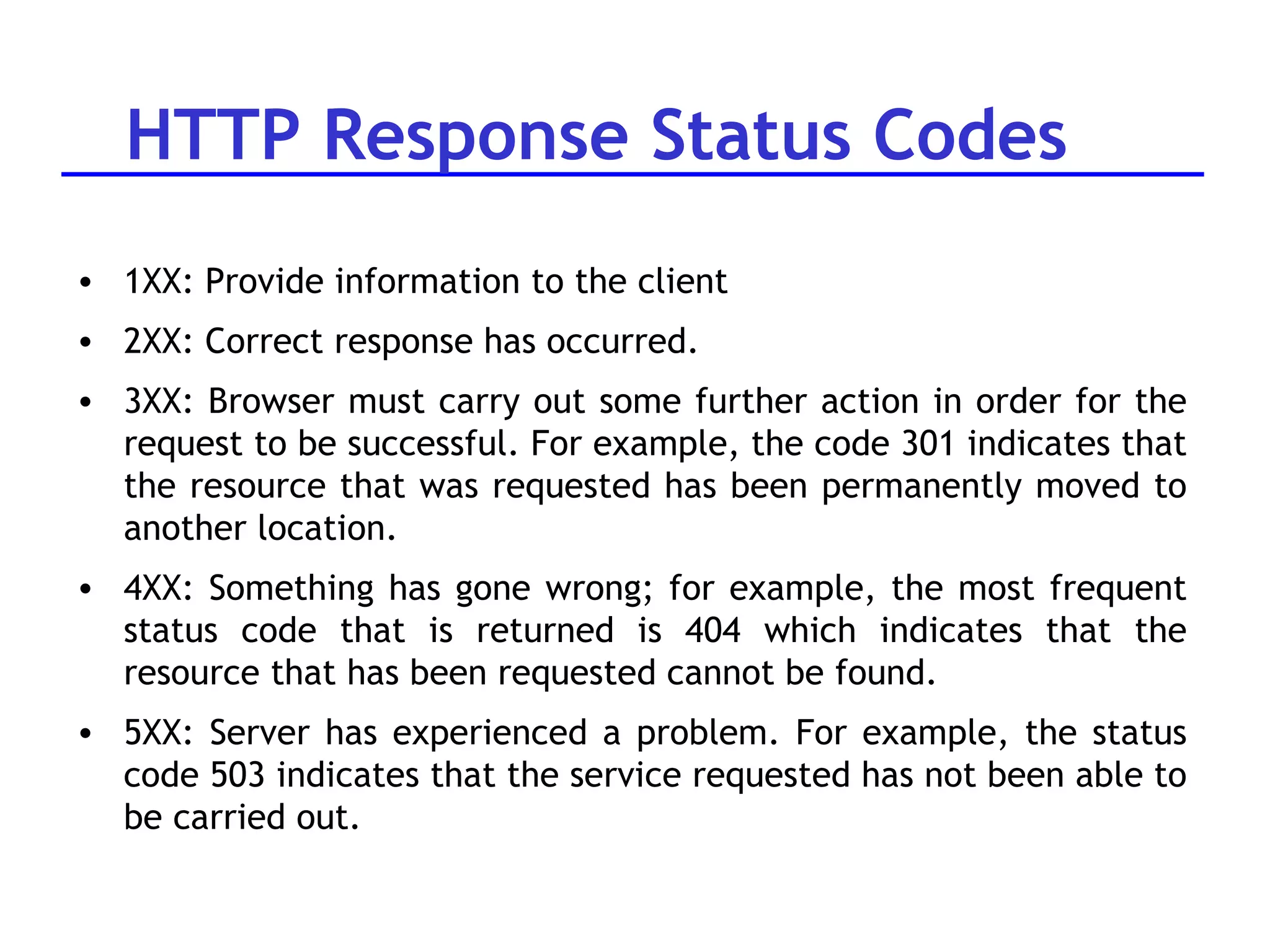
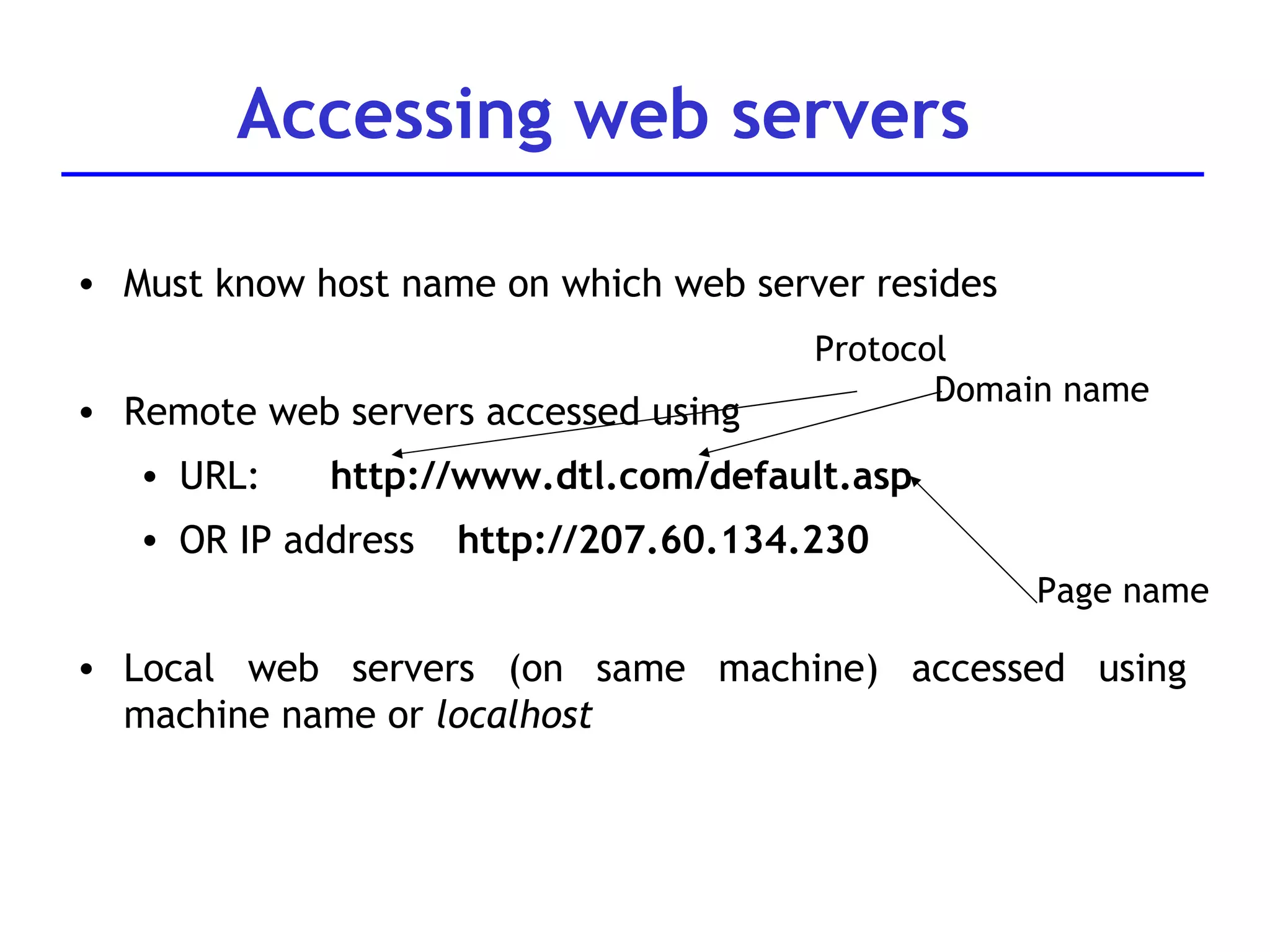
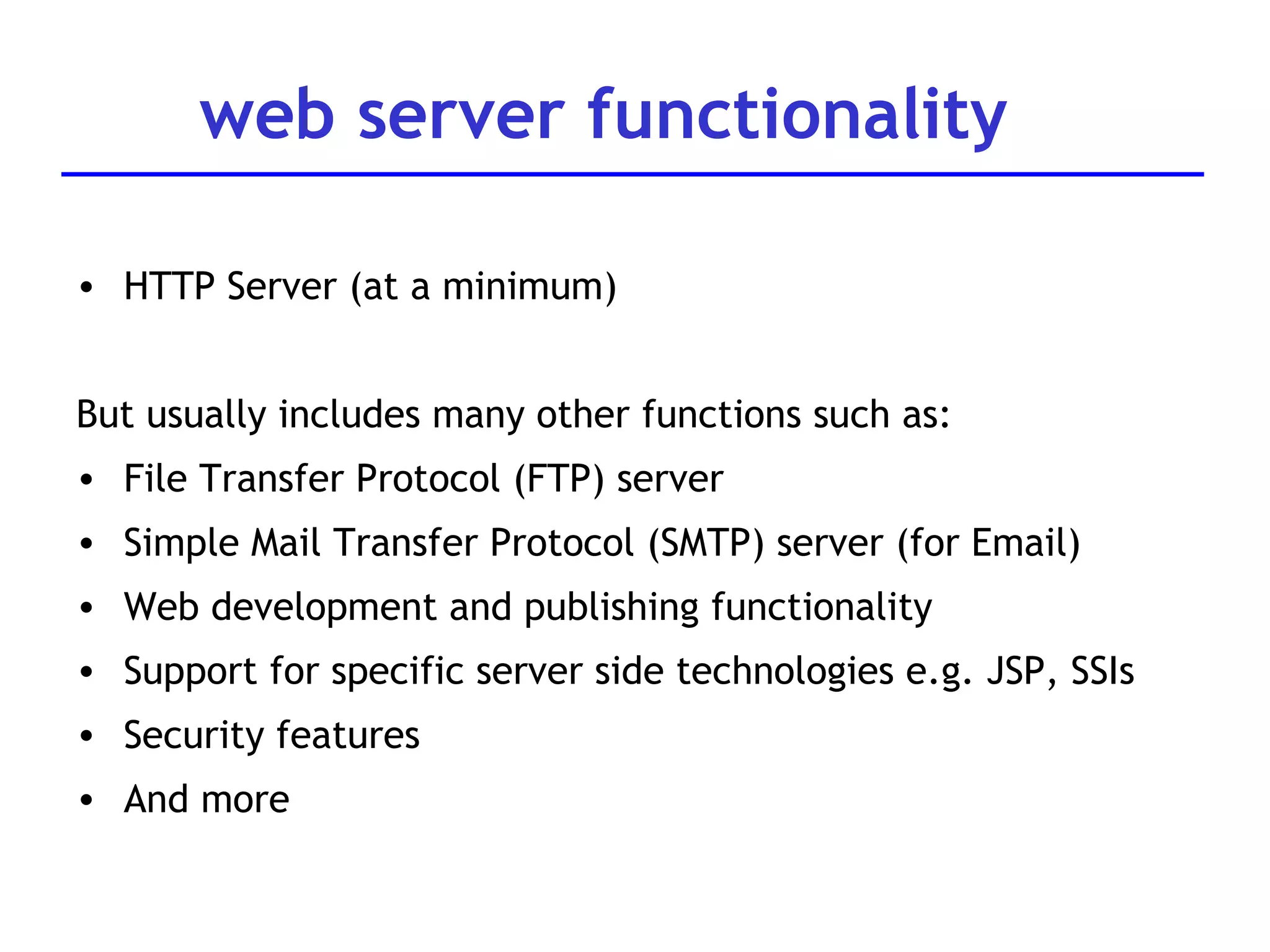
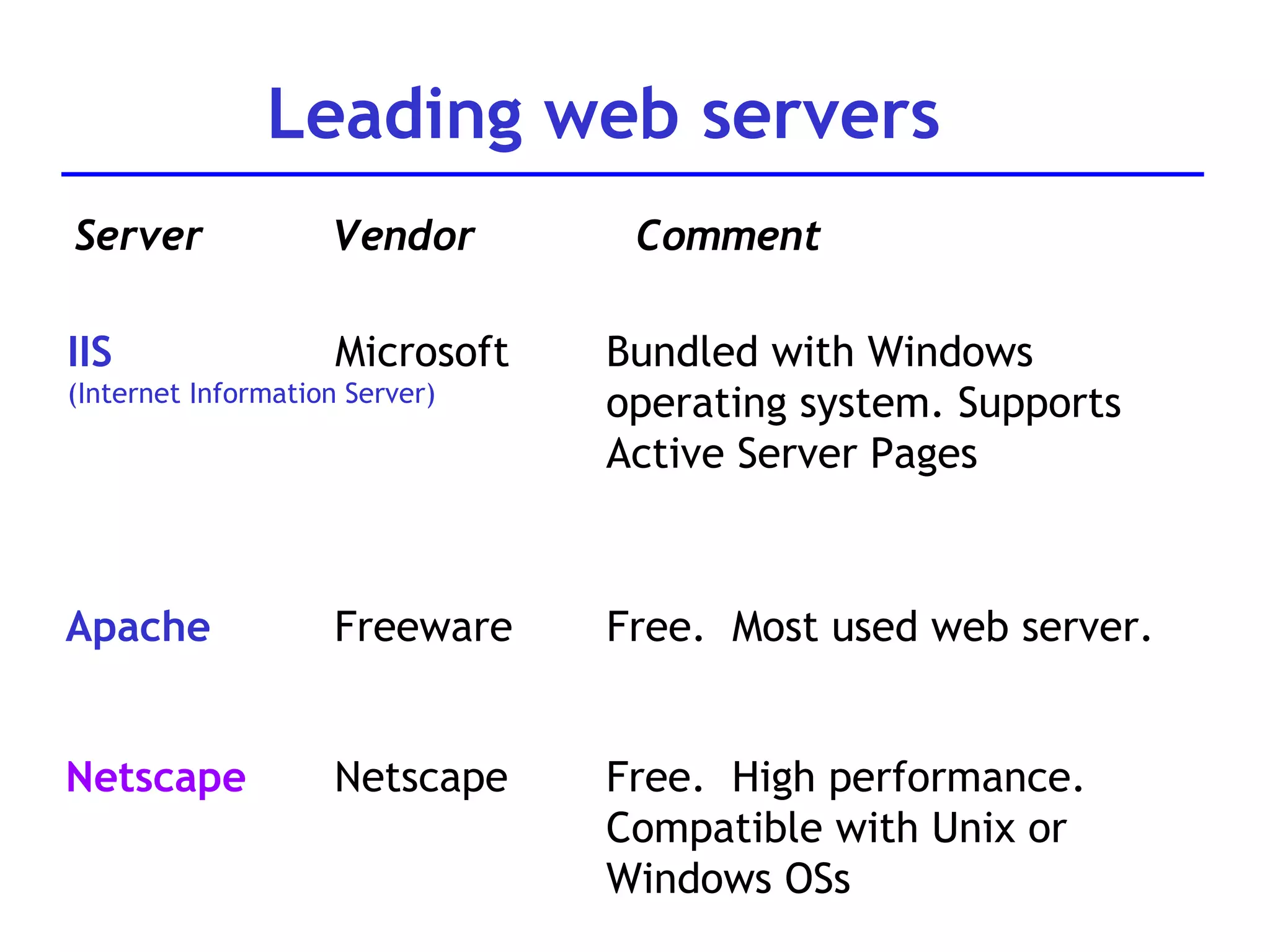
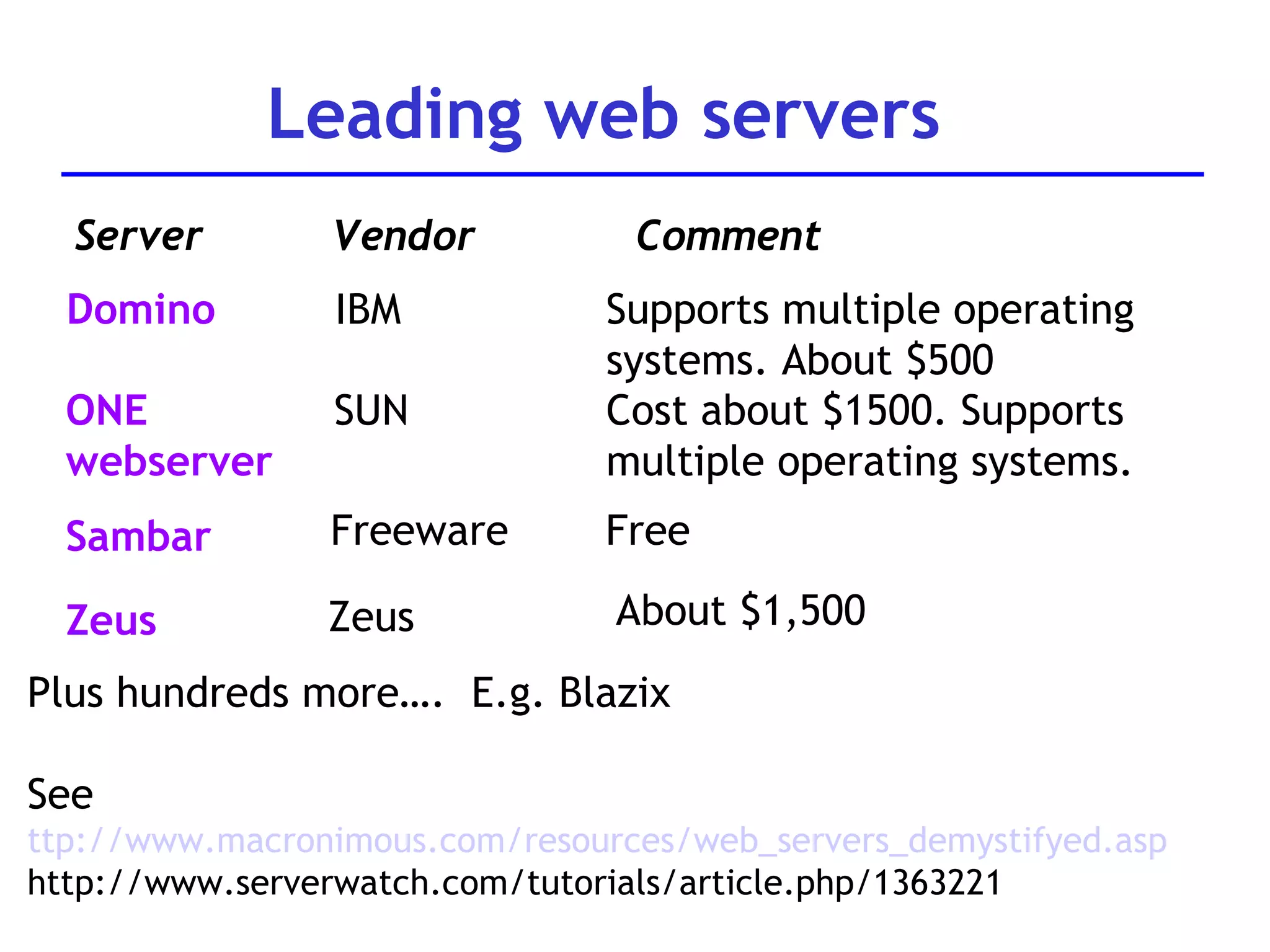
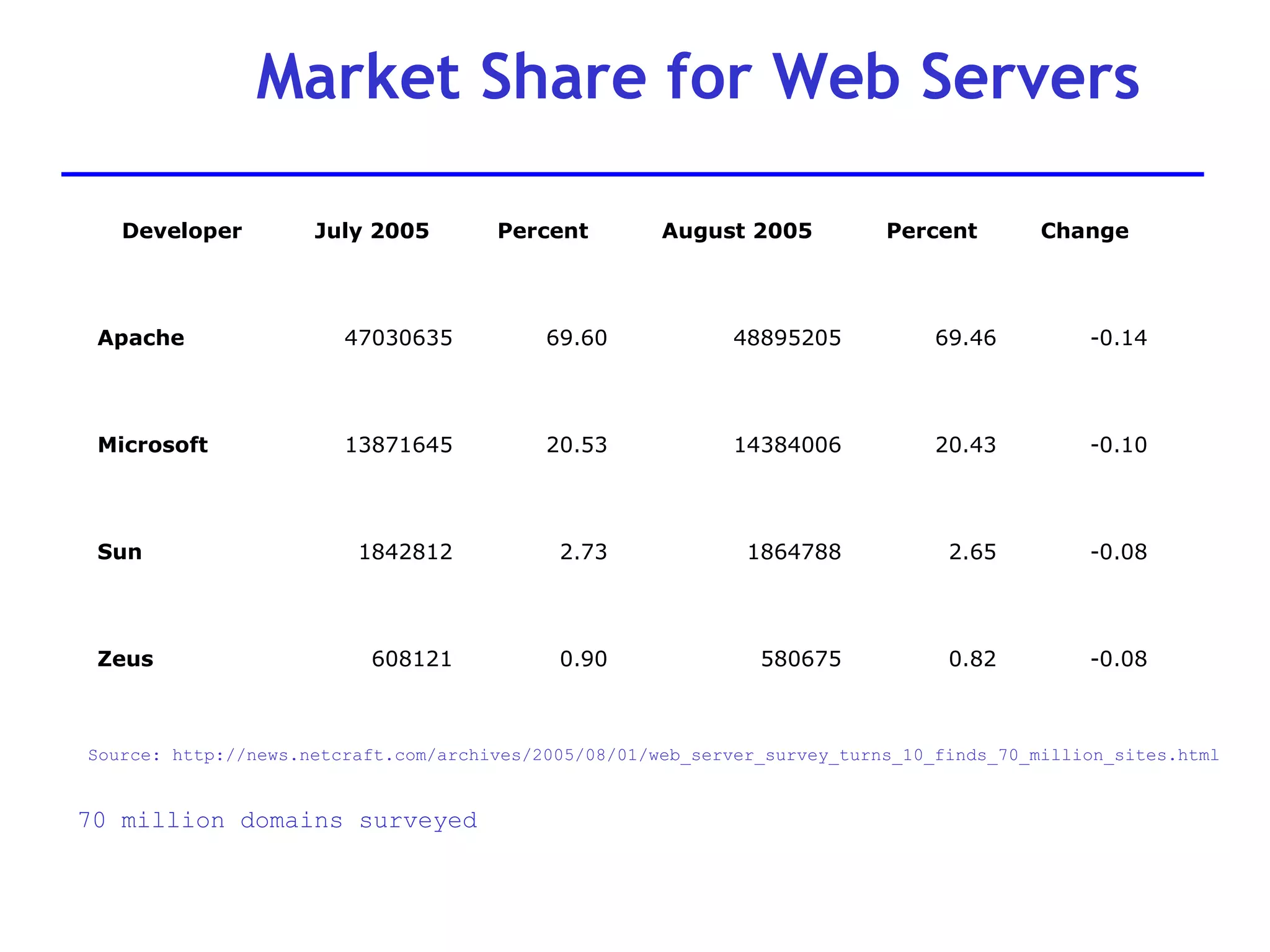
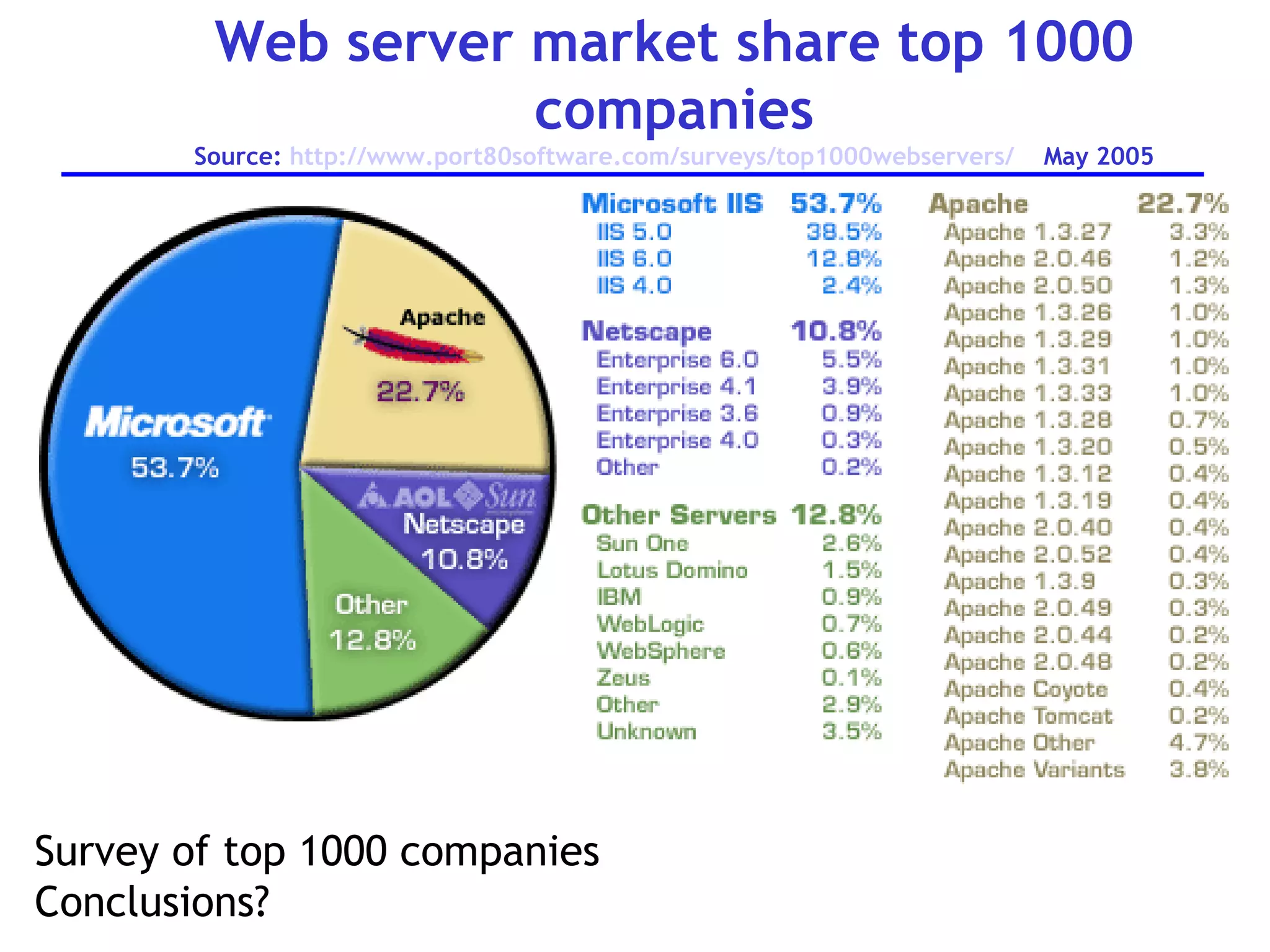
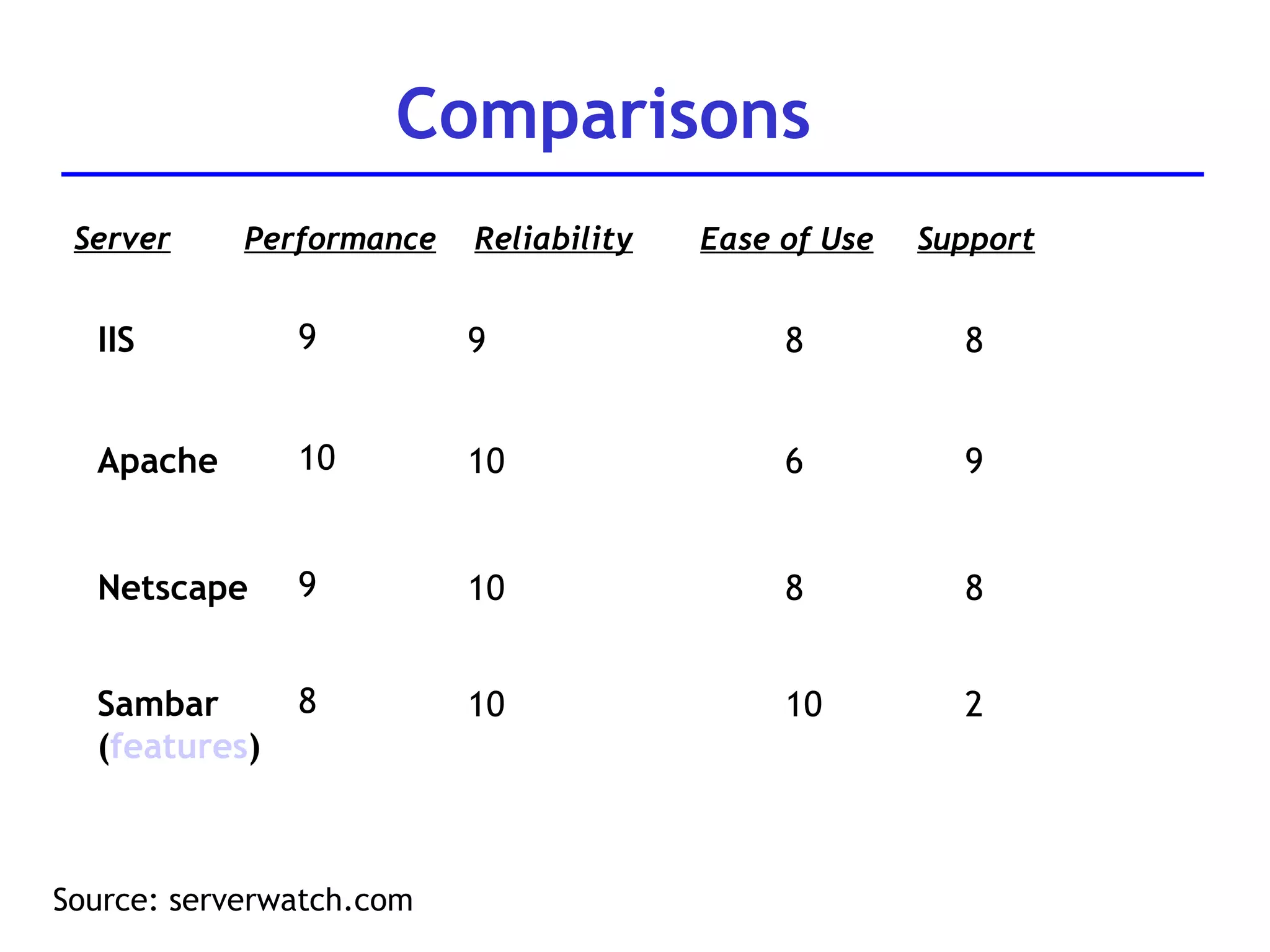
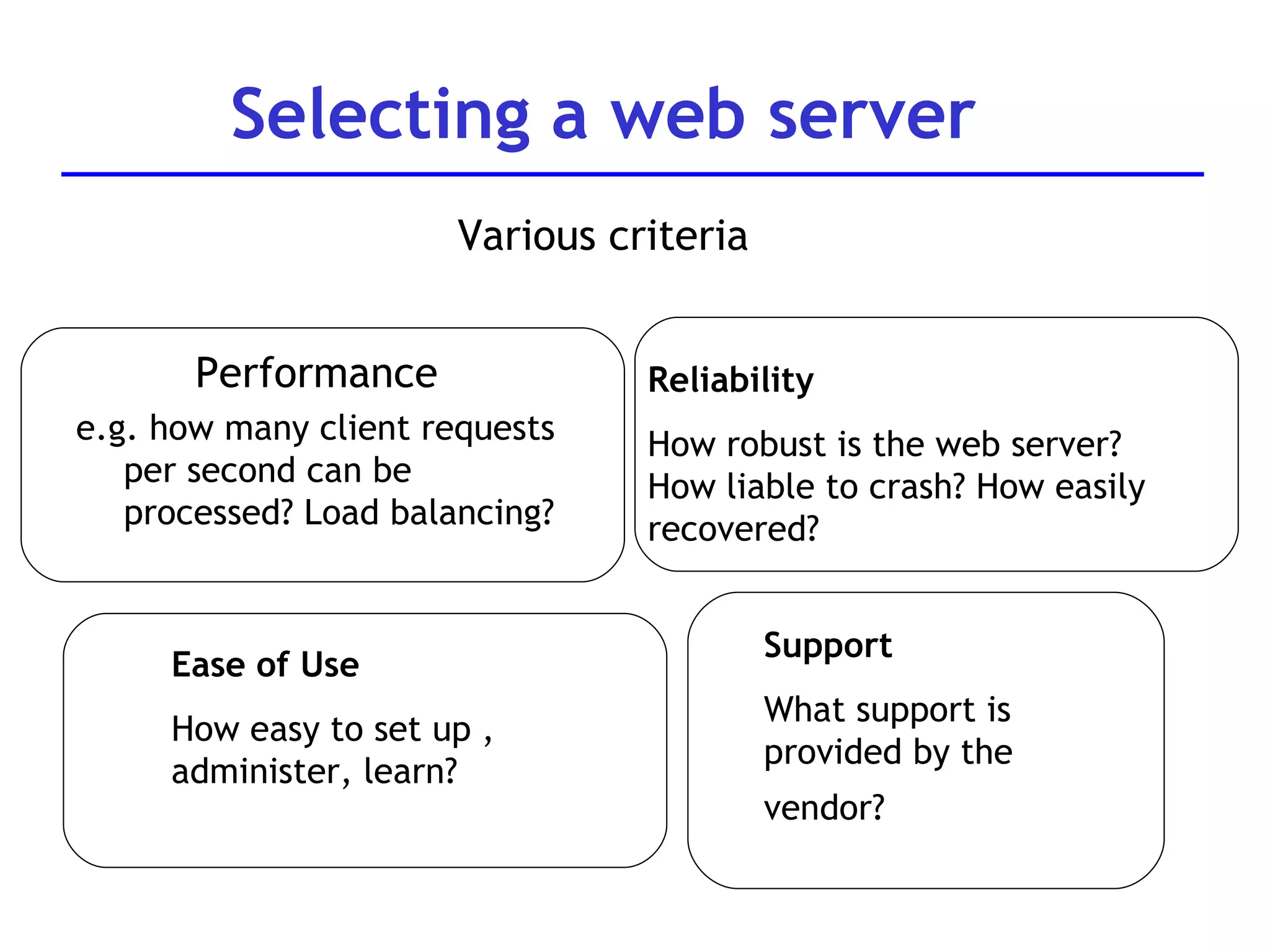
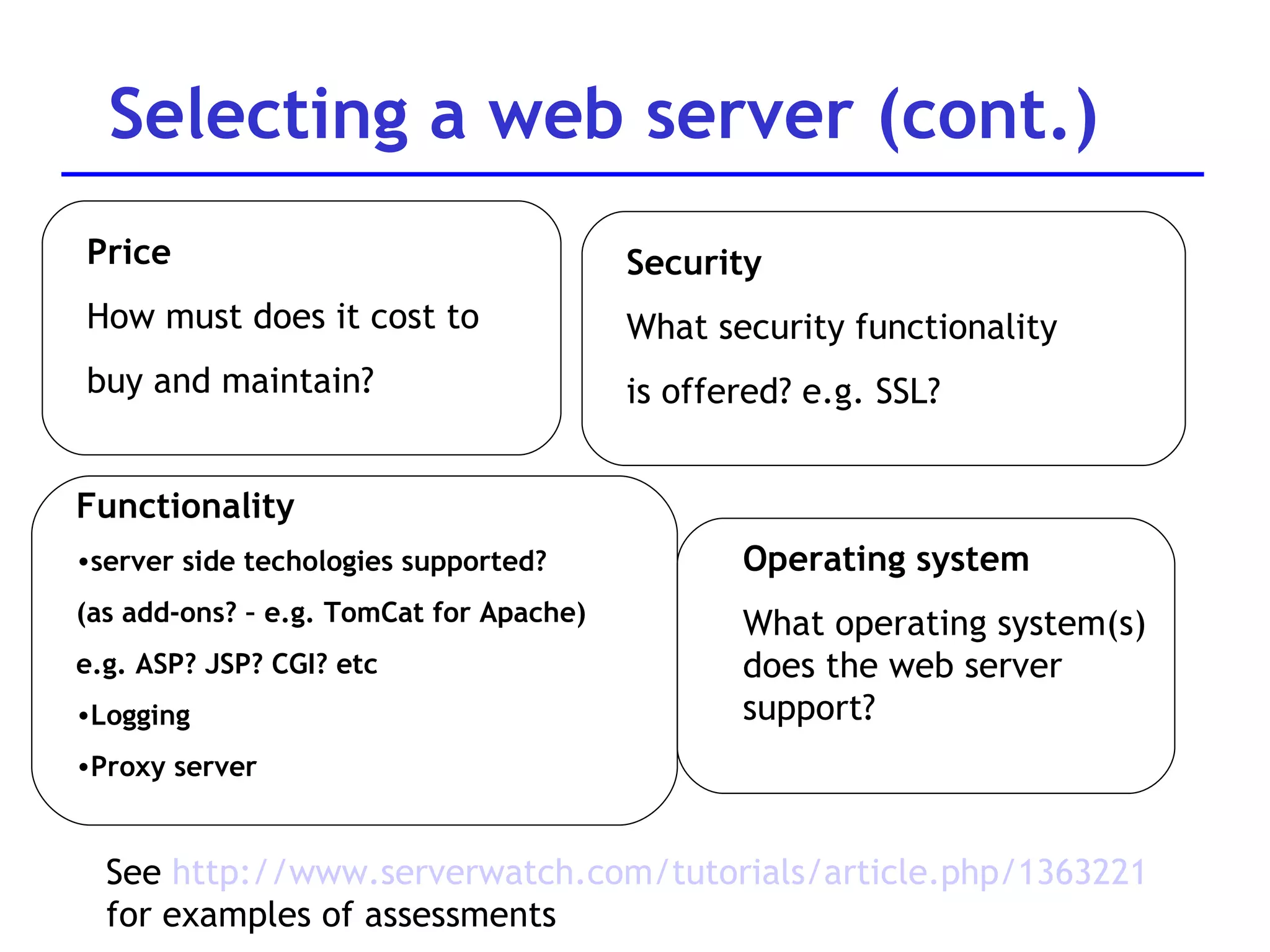
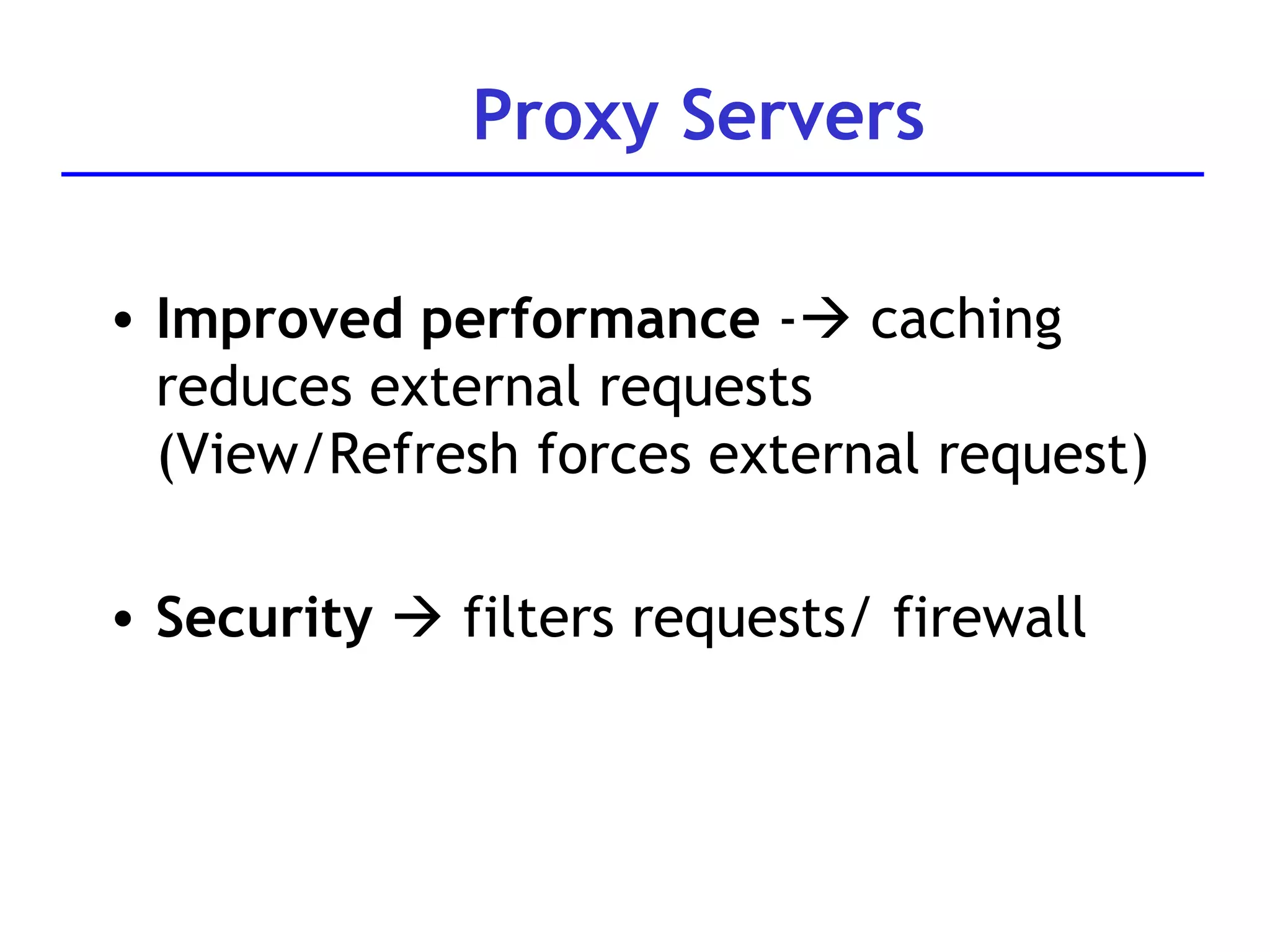
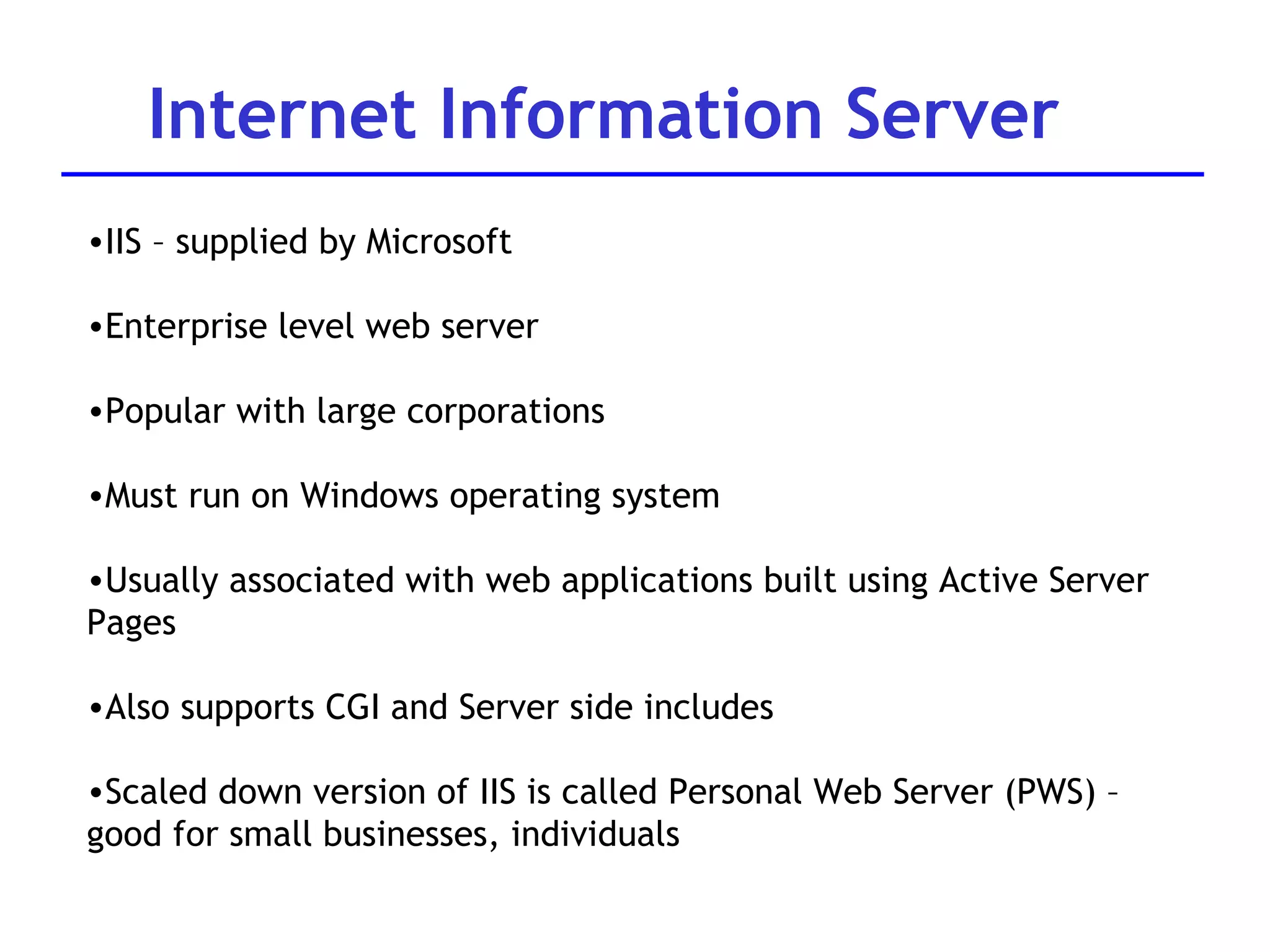
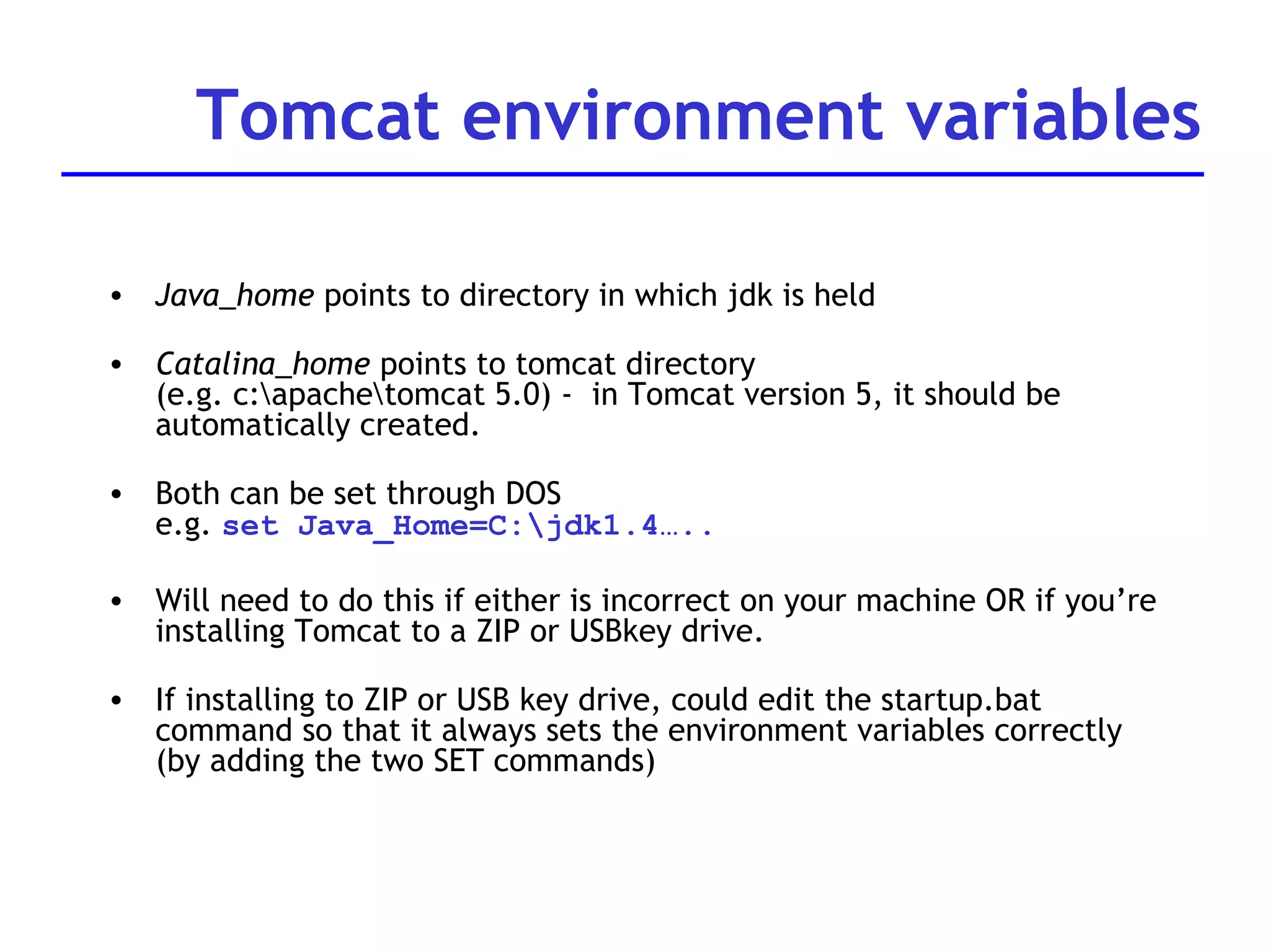
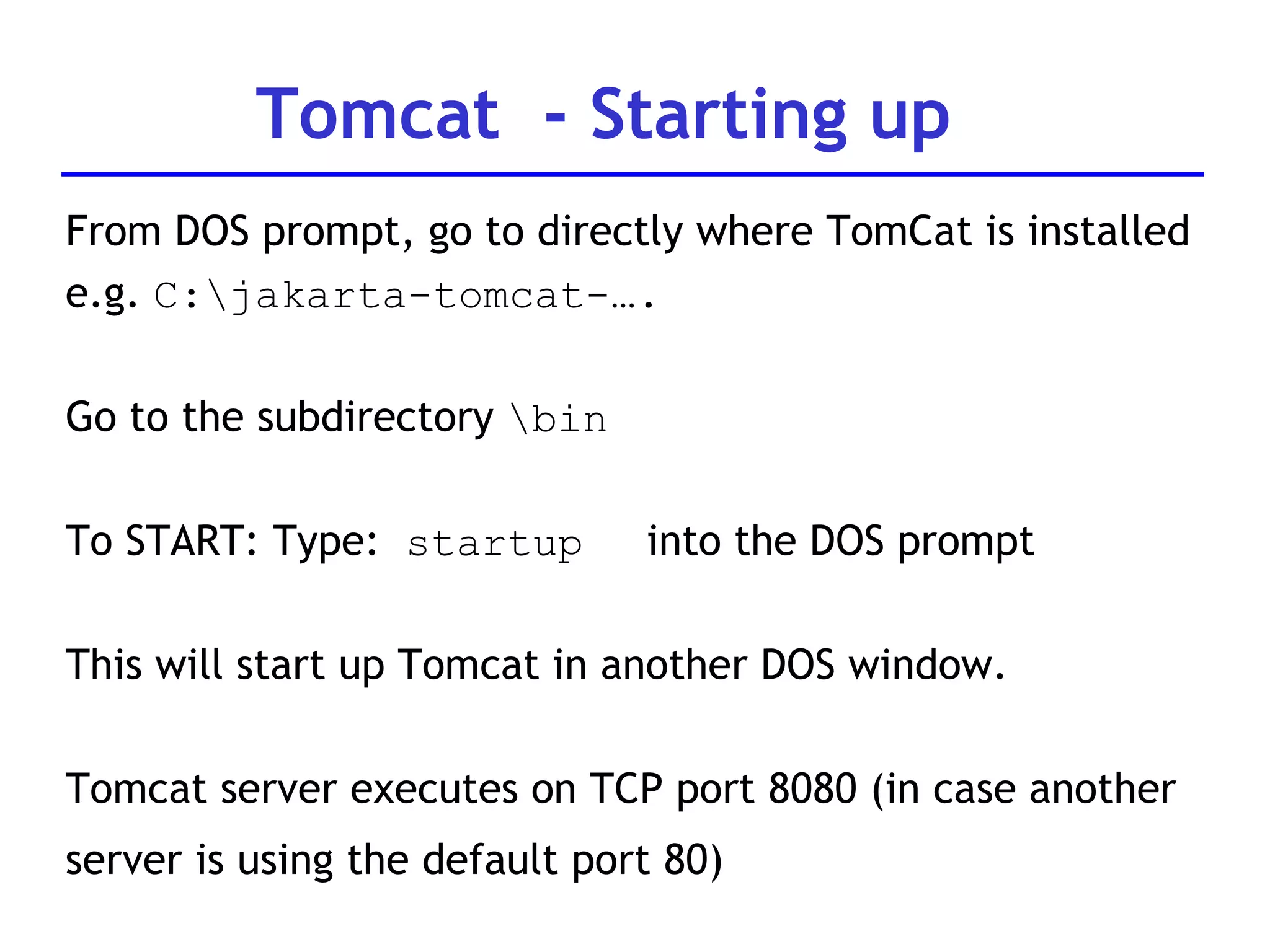
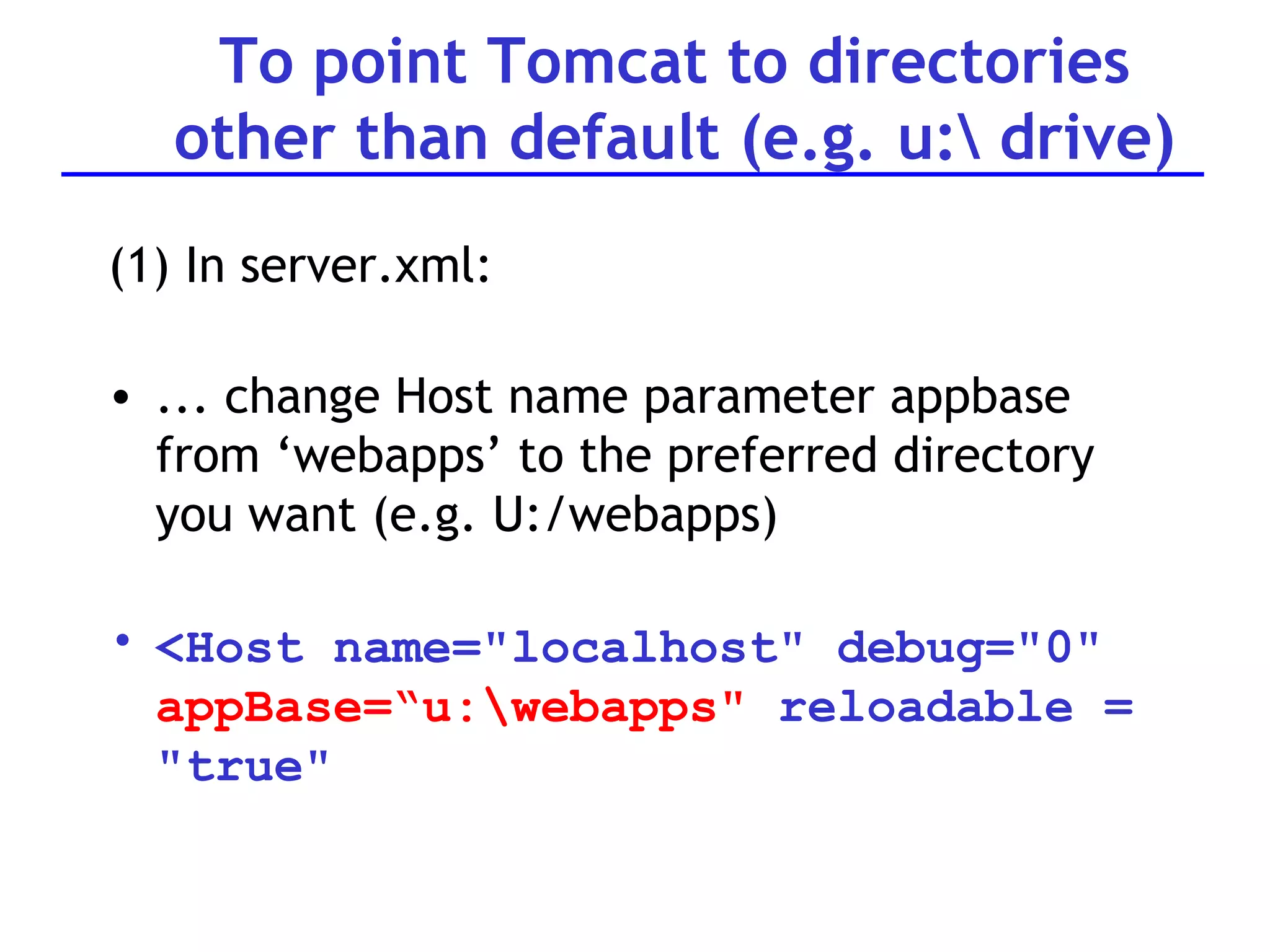
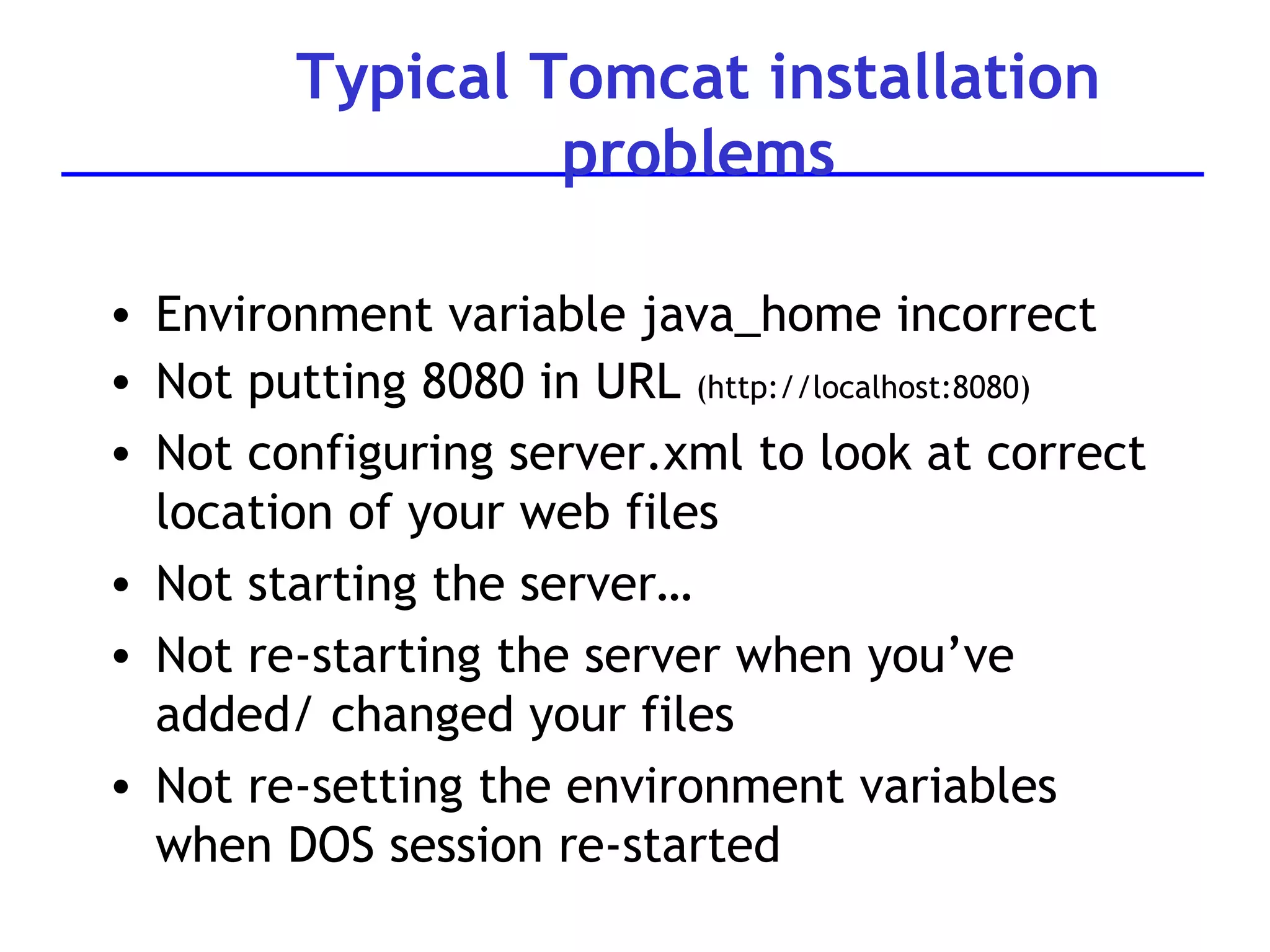
A web server is software that responds to requests from web browsers to serve web pages. It is part of a multi-tier architecture with an information tier (database), middle tier (application logic), and client tier (user interface). The most common protocol for communication between clients and servers is HTTP, with the server responding to GET and POST requests with web pages or other responses. Popular web server software includes Apache, IIS, and Tomcat.